Frequency Dependent Noise Attenuation
![]()
![]()
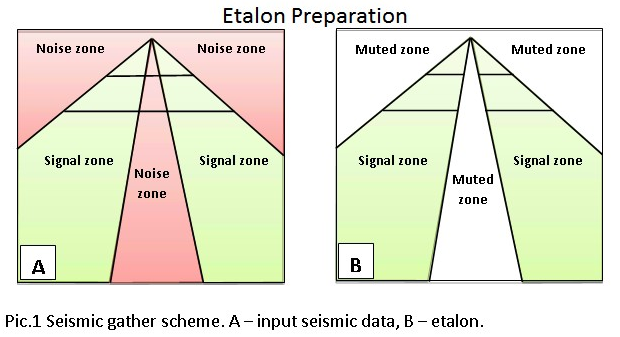
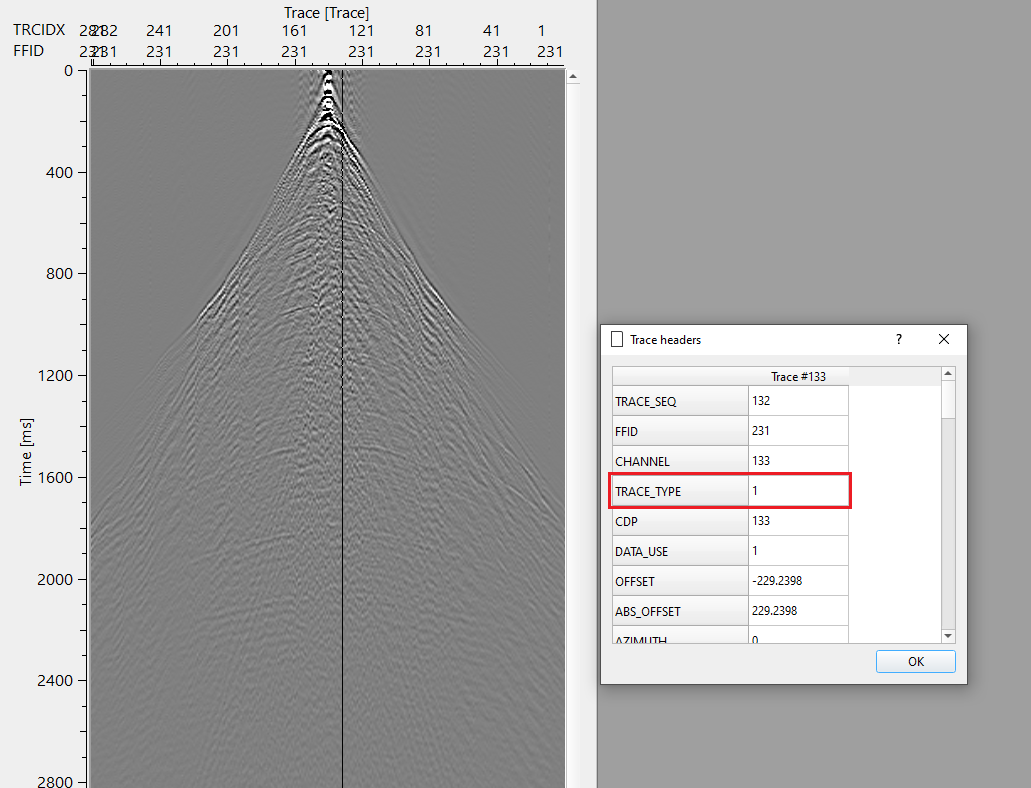
This module uses frequency-dependent and time-variant algorithm where an amplitude threshold values are defined in a trace neighbor area (T-X) for detecting and noise attenuation according to different frequencies and different time windows. The attenuation process consists of two steps – First prepare the etalon (model) and noise attenuation data sets. The etalon should contain only the signal zones, with the noise zone muted. The module estimates the median value of the amplitude spectrum in the sliding windows of the etalon data set, and for each window computes an operator using the threshold value. The procedure attenuates amplitudes whose values exceed the specified threshold.
Output data – 2D/3D seismic gathers in the same sort order as the input data with noise attenuated, and a before and after FDNA difference gather.
![]()
![]()
Input DataItem
Input gather - Two seismic data sets are input to the FDNA module.
The Input gather are 2D/3D seismic gathers in source or receiver sort order. It is better if they are NMO corrected and static corrections have been applied, but for this step we can apply denoise sequence in a soft mode without NMO correction.
Model gather - is the etalon of 2D/3D seismic gathers in source or receiver sort order. The same idea: it is better if they are NMO corrected and static corrections have been applied, but for this step we can apply denoise sequence in a soft mode without NMO correction.
Link to input etalon seismic gather with internal and external noise muted.
This module use the etalon for creating a correction filter for the input seismic data.
The user must prepare the etalon before running FDNA.
![]()
![]()
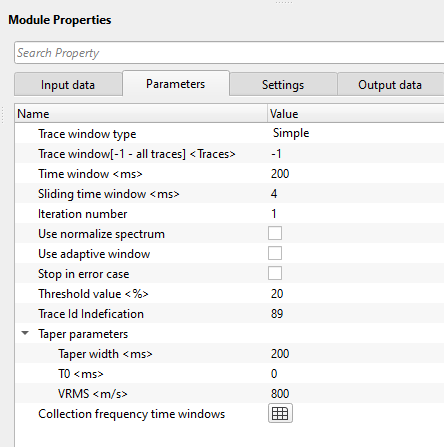
Trace window type { Simple, Time dependent } - trace window or horizontal window is used to attenuate the noise locally. There are two types of trace windows are available for the drop down menu.
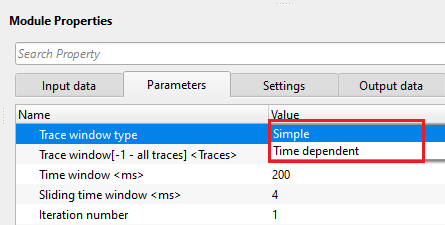
Simple - it works like normal trace window where the user should provide number of traces to be considered as a trace window.
Time dependent - as the name suggest, different number of traces will be considered at different times. As we know that FDNA is used for attenuating ground roll and it (ground roll noise) increases with the increase in time. So time dependent trace window will be a good option to attenuate the ground roll effectively.
Trace window[-1 - all traces] - number of adjacent traces used for comparing the spectrum of both input and model. These traces are used for the sliding window and also used for local attenuation.
•Default: -1 (all traces)
•Range: from 1 to max traces in the input gather
Time window - time in milliseconds for sliding window. This is used as vertical window and it analyzes the frequency content locally. This window used for local attenuation. The taper zone between sliding windows is ¼ of time window length default 200ms.
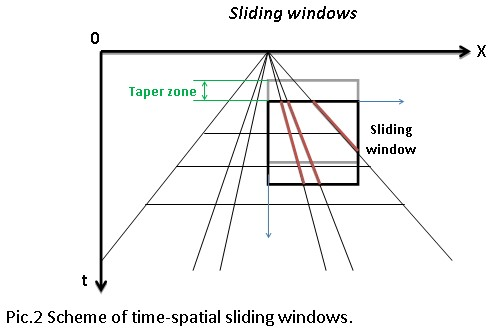
Sliding time window - amount to advance the sliding time window each shift
Iteration number - define the number of iterations to perform. The more number of iterations, more run time.
Use normalize spectrum - by default, FALSE (Unchecked). This option is used to normalize both input and model gathers to compare the spectrum. It is very useful when there is a huge amplitude difference.
Use adaptive window - by default, FALSE (Unchecked). If it's TRUE (Checked), it will adjust the time window size automatically depending on the local signal characteristics. If the signal is of low frequency then higher time window size and for higher frequencies it will be lower time window size.
Stop in error case - it stops the programs if the module throws any errors during the execution. By default, FALSE (Unchecked).
Threshold value - defines how much difference between and input and output is acceptable. If the threshold value is exceeded by the user defined value, it considered it as noise and attenuates it.
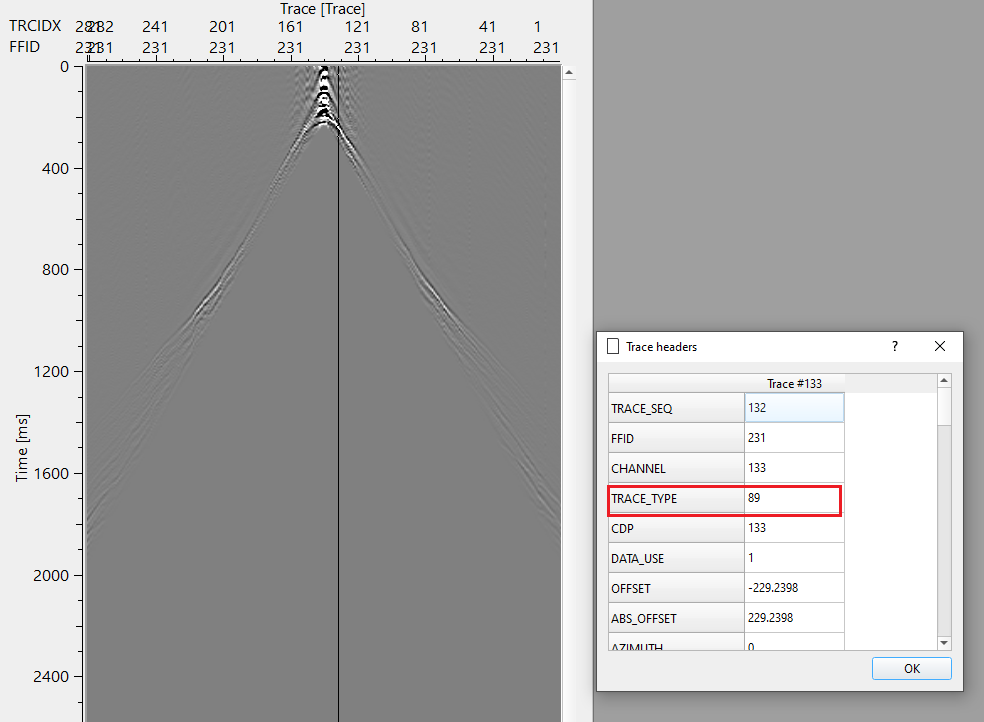
Trace Id Indefication - this is directly related to Threshold value. It checks with total number of non-zero values in both input and Etalon (model gather). If the Etalon is having less than the user specified threshold value then it changes the TRACE_TYPE or Trace ID from 1 to 89.
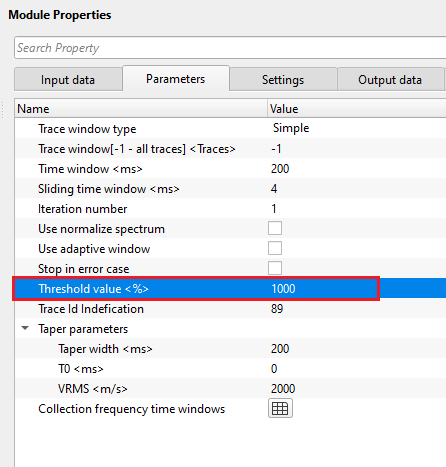
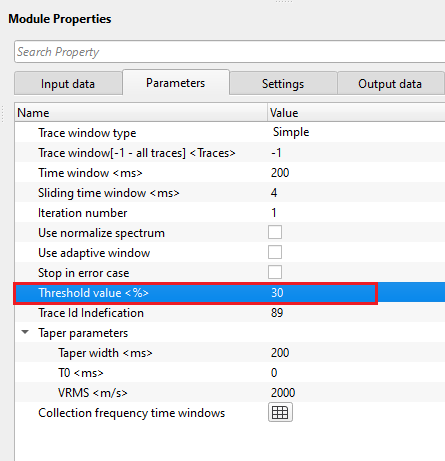
Taper parameters - taper is helpful in smooth transitioning of the processed data by not creating any sharp boundary, edge effects or artifacts.
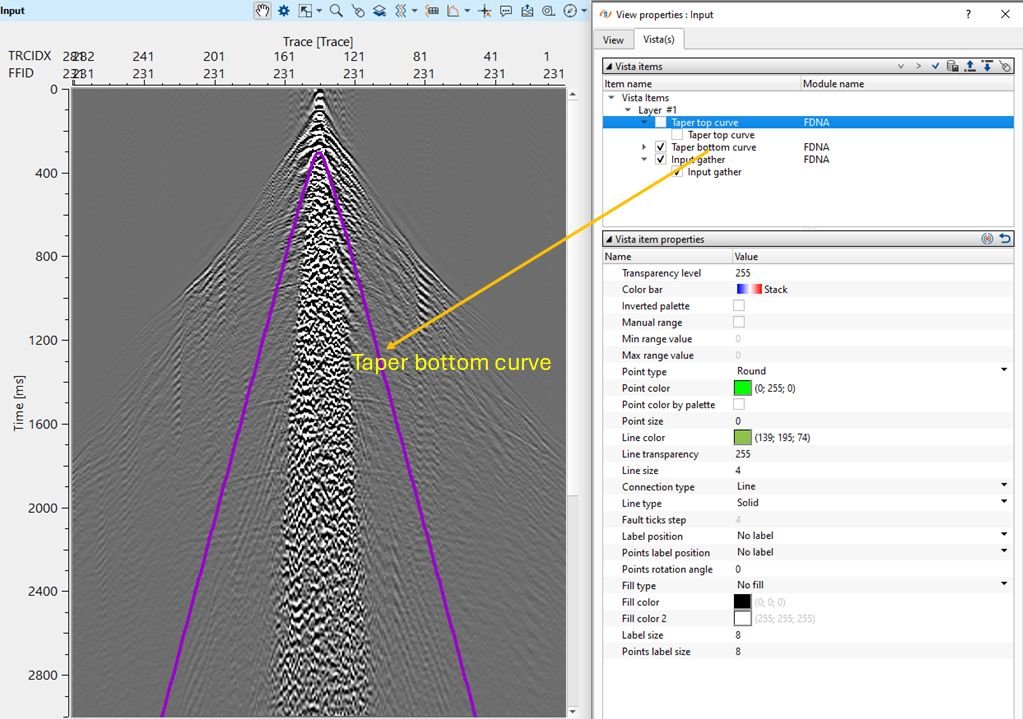
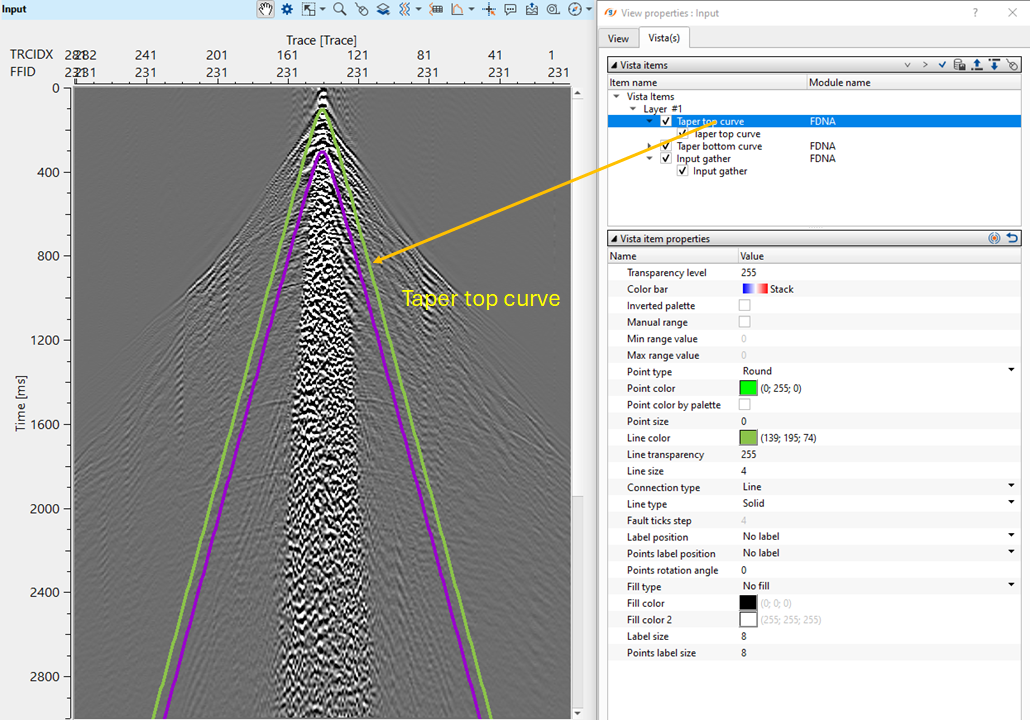
Taper width - there are two taper curves drawn based on the Vrms value. One taper curve will be the top and the other one will be the bottom curve. In between these two taper curves, the user should provide a taper width for smooth transitioning of the data to avoid any sharp boundaries or edge effects.
T0 - specify the central time for the taper curves to start with. By default, 0 ms. Based on this value, both the taper curves starts symmetrically on the both sides of the shot gather (for Split spread).
VRMS - specify the velocity value for the taper curves. By default, 1500 m/s.
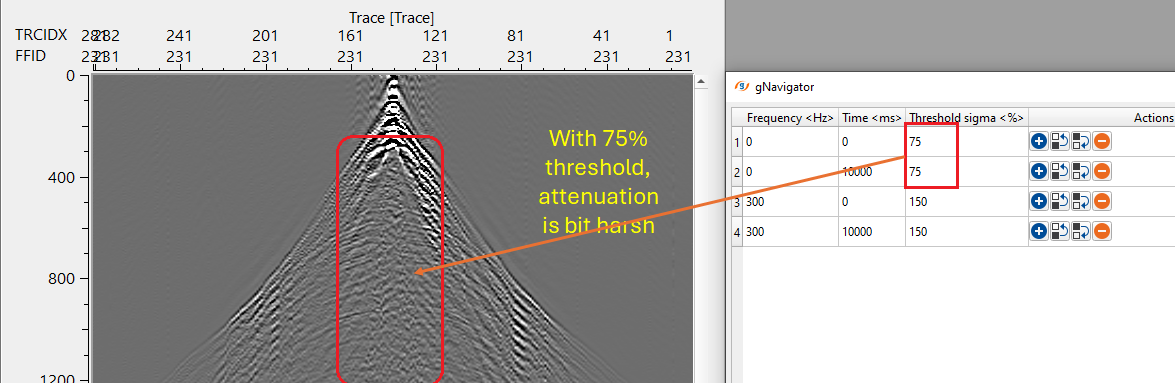
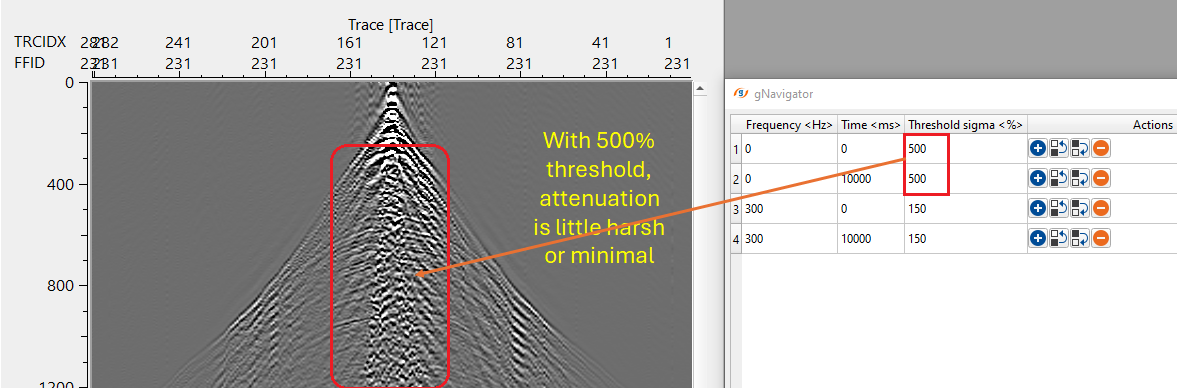
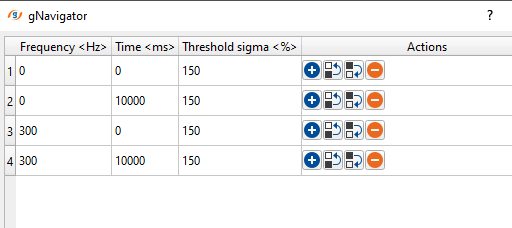
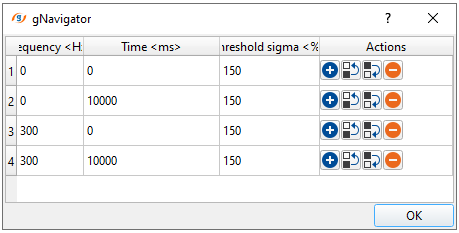
Collection frequency time windows - this section deals with the time frequency pairs to design noise attenuation parameters for different time and frequency bands. This is essential for different parts of the data. In case the user wants to apply less harsh parameters then the Threshold sigma (%) should be a higher value so that the shallower or near offsets are not impacted. These three parameters control basic noise attenuation.
• Frequency – frequency for attenuation
Default: 0 (Hz)
Range: from 0 to max sampling frequency (Hz)
•Time – time value for threshold
Default: 0 (Hz)
Range: from 0 to max trace length(ms)
•Threshold sigma (%) – the limiting parameter for calculating threshold values to attenuate excessive amplitudes
Default: 150 (%);
Range: from 0 to 99999 (%);
![]()
![]()
Auto-connection - By default, TRUE(Checked).It will automatically connects to the next module. To avoid auto-connect, the user should uncheck this option.
Bad data values option { Fix, Notify, Continue } - This is applicable whenever there is a bad value or NaN (Not a Number) in the data. By default, Notify. While testing, it is good to opt as Notify option. Once we understand the root cause of it, the user can either choose the option Fix or Continue. In this way, the job won't stop/fail during the production.
Notify - It will notify the issue if there are any bad values or NaN. This will halt the workflow execution.
Fix - It will fix the bad values and continue executing the workflow.
Continue - This option will continue the execution of the workflow however if there are any bad values or NaN, it won't fix it.
Calculate difference - This option creates the difference display gather between input and output gathers. By default Unchecked. To create a difference, check the option.
Number of threads - One less than total no of nodes/threads to execute a job in multi-thread mode. Limit number of threads on main machine.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output DataItem
Output gather - generates noise attenuated output gather
Gather of difference - generates the difference gather before and after noise attenuation.
There is no information available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
Carefully prepare the etalon (model) data, try to mute the high amplitude zones and include the signal zones. Control the noise attenuation by using the threshold parameters and the ability to specify the thresholds in a time variant manner and by frequency.
This procedure is more effective in the first steps of the seismic data processing flow when noise zones still have high amplitudes. The input seismic data should not be amplitude normalized.Create the Etalon (model) in a Seismic loop.
Seismic loop makes automatic connections between all modules in a sequence under that seismic loop and the user cannot disconnect them. In this case, we need to use an additional “Flow” module inside of the Seismic loop for etalon preparation. Put the mute modules into a “Flow” inserted into the Seismic loop and then connect the output muted data to the Model gather field of the Input data tab of the FDNA module. The Input gather on the Input data tab will be automatically connected to the previous module in the Seismic loop processing flow.
Let's have a look at the example workflow.
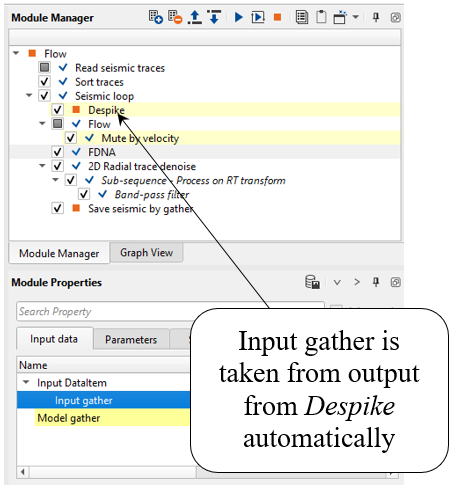
Seismic loop makes automatic connections between all modules in a sequence under that seismic loop and the user cannot disconnect them. In this case, we need to use an additional Flow module inside of the Seismic loop for etalon preparation. Put the mute modules into a Flow inserted into the Seismic loop and then connect the output muted data to the Model gather field of the Input data tab of the FDNA module. The Input gather on the Input data tab will be automatically connected to the previous module in the Seismic loop processing flow.
Create an etalon for FDNA by using Mute by velocity module:
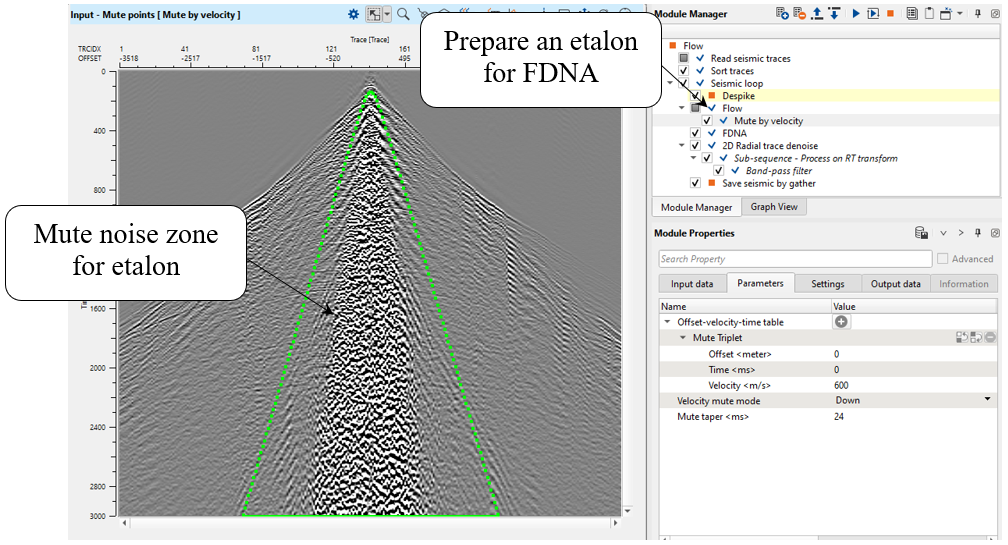
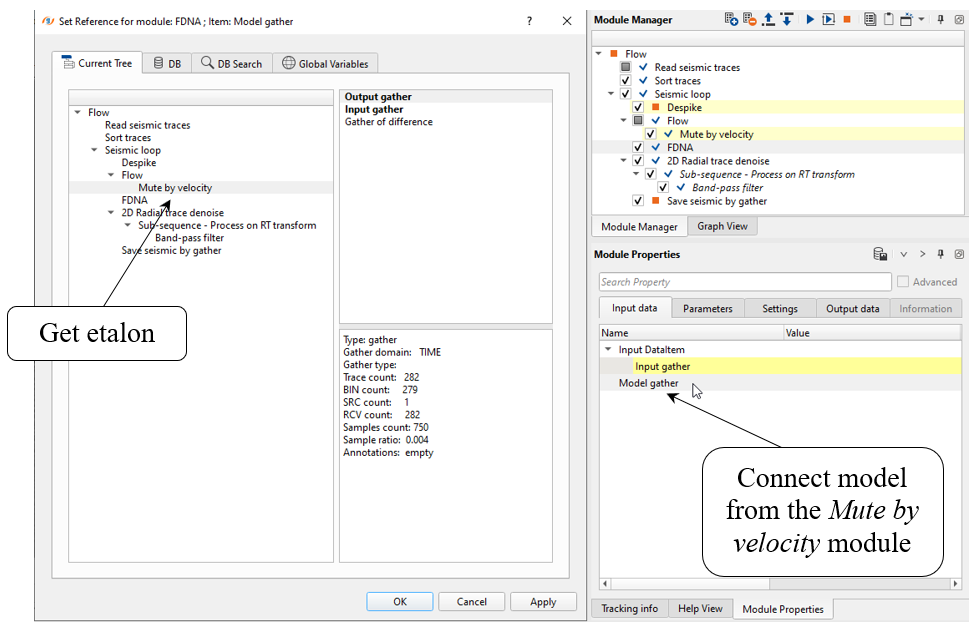
Next, we need to connect input Model gather (etalon) with output from the Mute by velocity module:
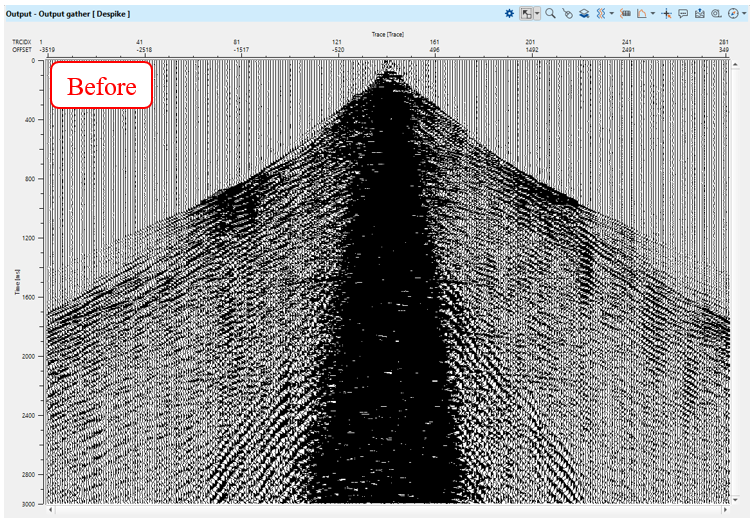
Input data is taken from Despike:

FDNA parameters:
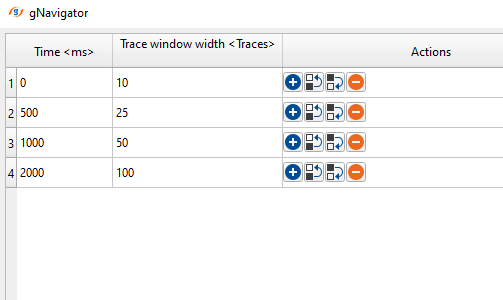
Collection frequency time windows:
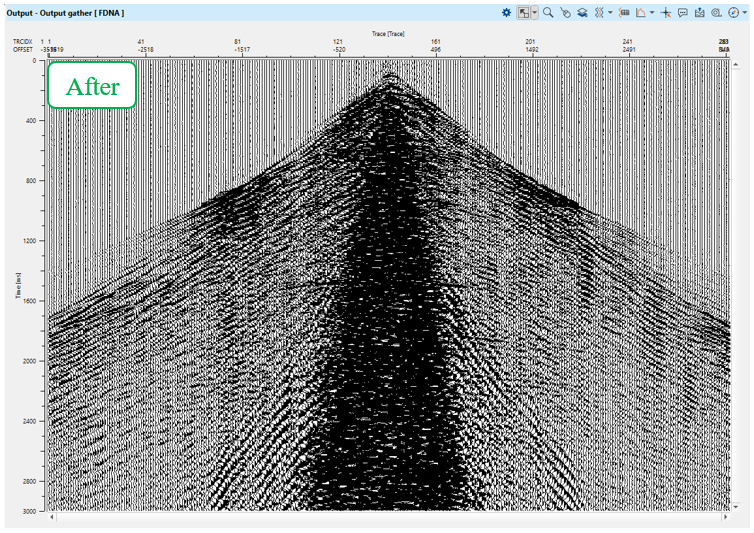
Execute FDNA and check the results, source gathers before - after - difference:
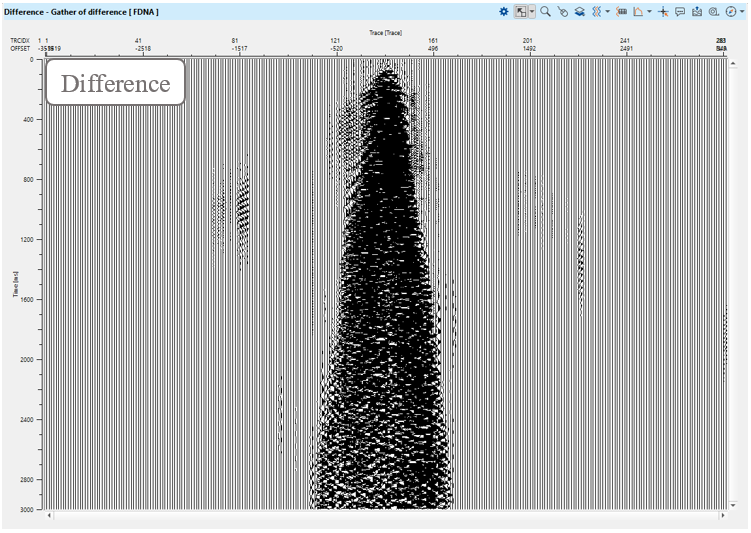
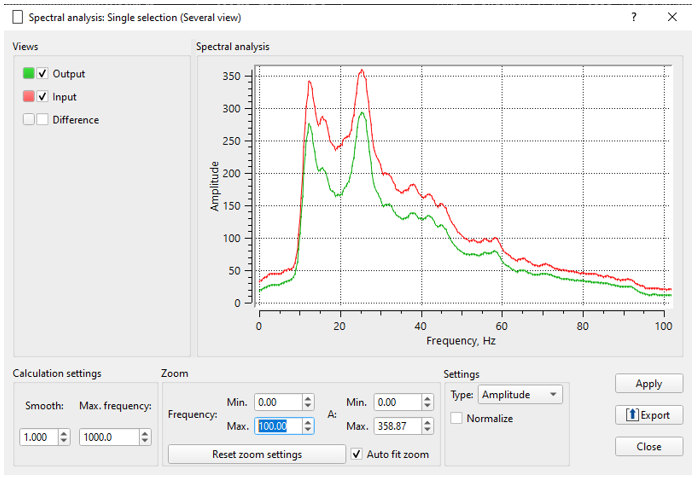
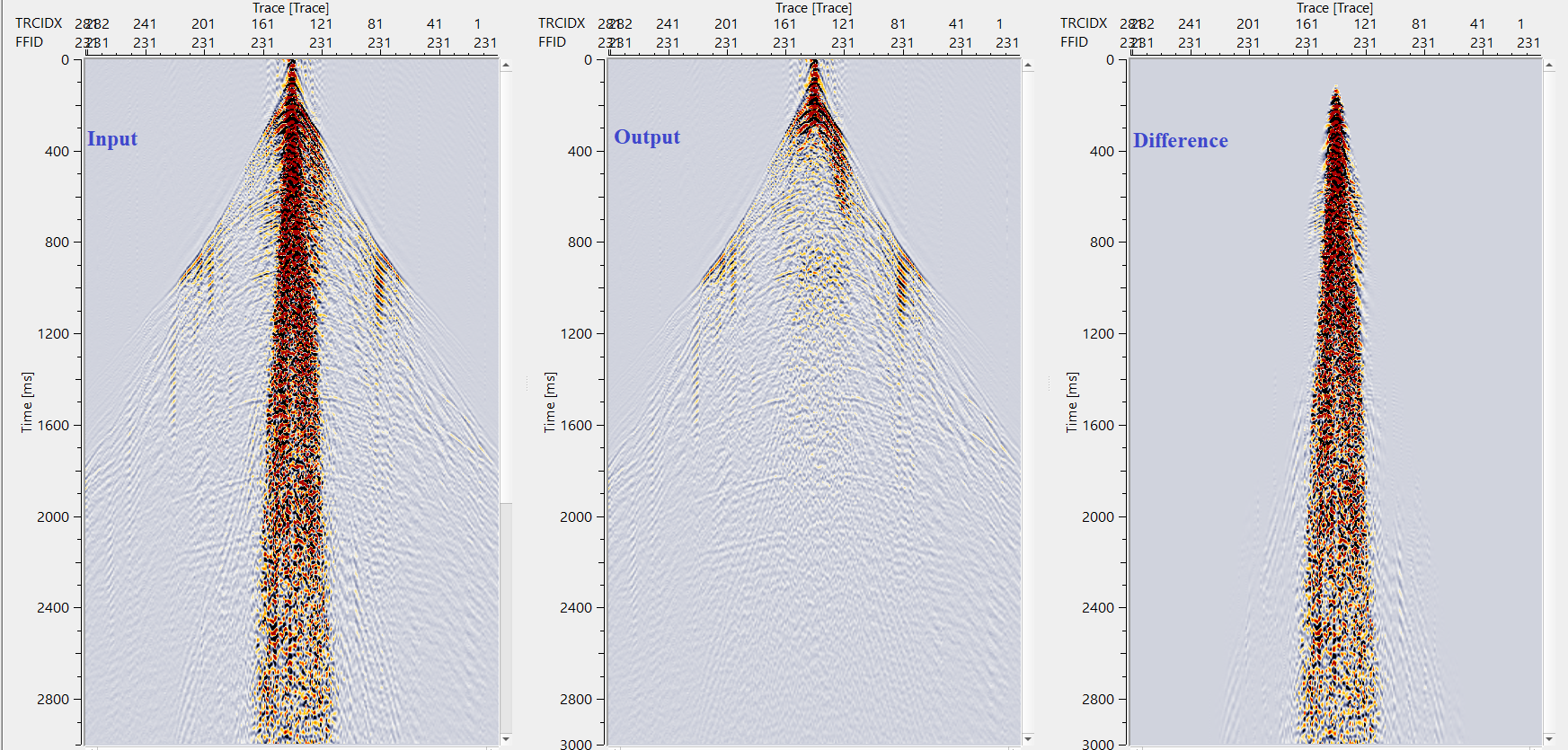
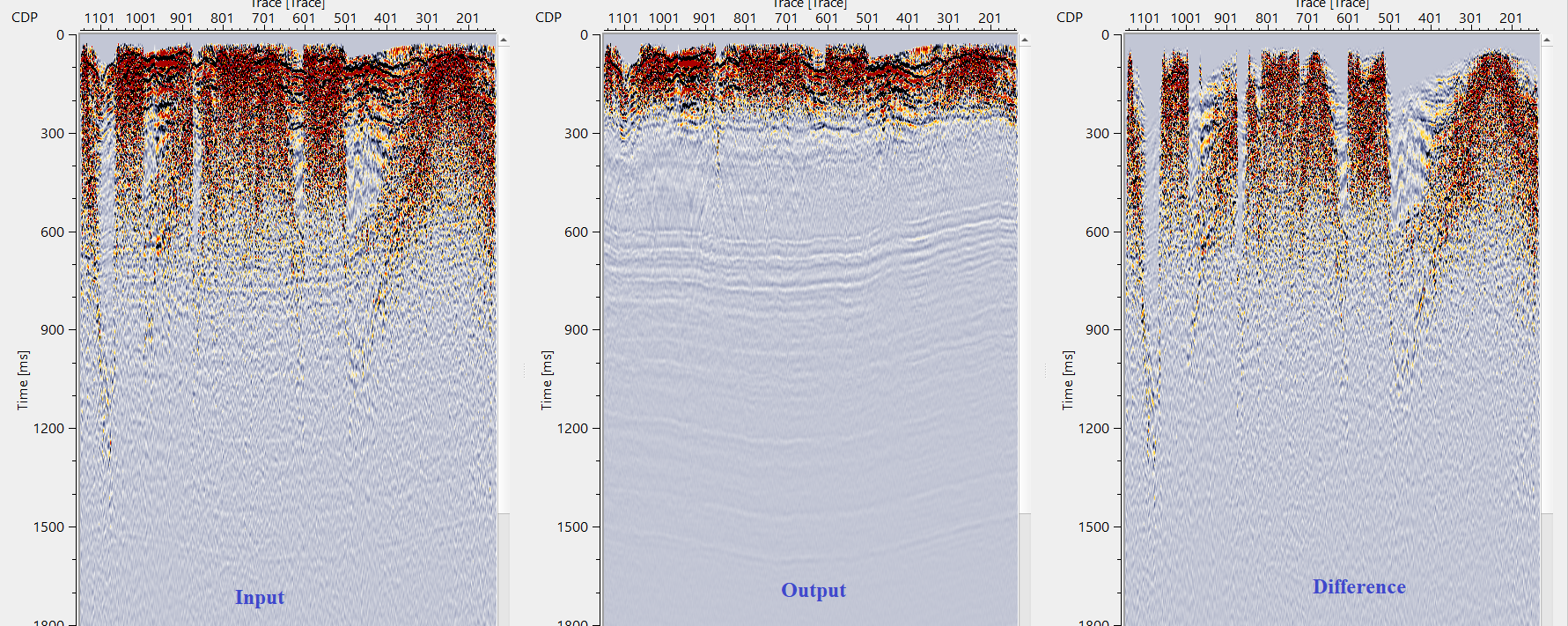
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicists
Shettar A., 2019, F-K Filtering for Seismic Data Processing
 If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com
If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com