 | RESIDUAL |
 | RESIDUAL |
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Navigation: Tutorials > Basics > Statics >
|
Residual static corrections are uniform time shifts that are applied to trace to compensate for time delays in the highly variable near-surface weathering zone. These delays occur near both sources and receivers (Wiggins et al., 1976). Residual static corrections are used for removing the short wavelength anomalies and may used in the processing land and shallow marine data. The application of residual corrections improves the final seismic section more than when only datum statics applied (Cox, 1999). Input seismic data must be a moveout-corrected CMP gathers. For this task we are going to use Surface-consistent residual static correction module.
At the initial stages of the pre-processing, the poor signal to noise ratio (SNR) of CMP stack quality is due to the near surface velocity anomalies and topographic changes of the surface. These changes give rise to travel time shifts and it can be corrected by using various methods like refraction statics by means of picking first breaks and calculate the statics and apply them. Second method is Surface Consistent Residual Statics.
Open the workflow and add all necessary modules as shown below:
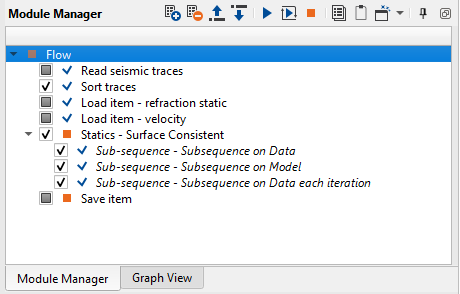
Sort traces: perform a CDP(CMP)-Offset sorting for residual static calculations.
Load item - refraction static: load refraction static library from DB. Define an input file name Refraction_statics_:
Load item - velocity: load stacking velocity library from DB. Define an input file name Velocity_iteration_01 and execute this module with previous three for loading seismic traces, sorting trace headers and loading static and velocity libraries:
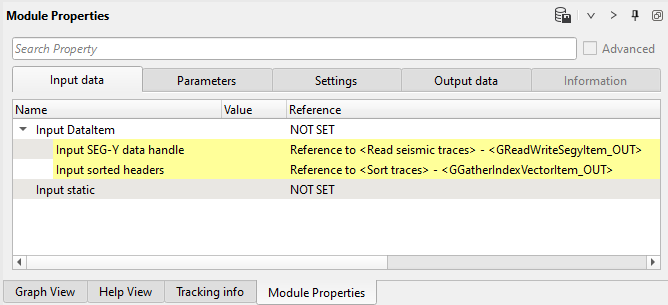
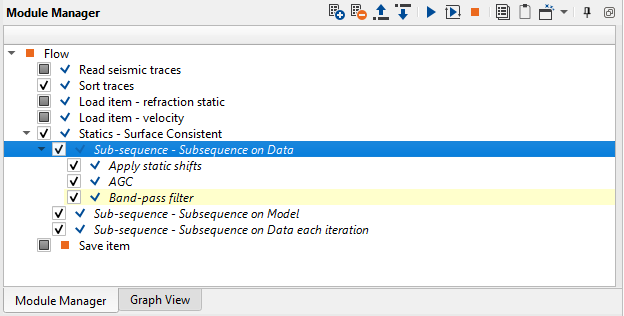
Statics - Surface Consistent. This module was added in the begging of current chapter, so we need to define input data and parameters. In the input data connect seismic from Read seismic traces and headers form Sort traces. There is also an Input static parameter, but we will use other way for applying refraction static corrections: add Apply statics shifts module into Sub-sequence - Subsequence on Data process, as we as AGC and Band-Pass filter. It provides opportunity to apply any processing procedures before calculation of residual static, i.e. we need to prepare input seismic data for residual statics: apply refraction statics, automatic gain control and band-pass filtering:
Input data:
Sub-sequence:
Sub-sequence -> Apply statics shifts:
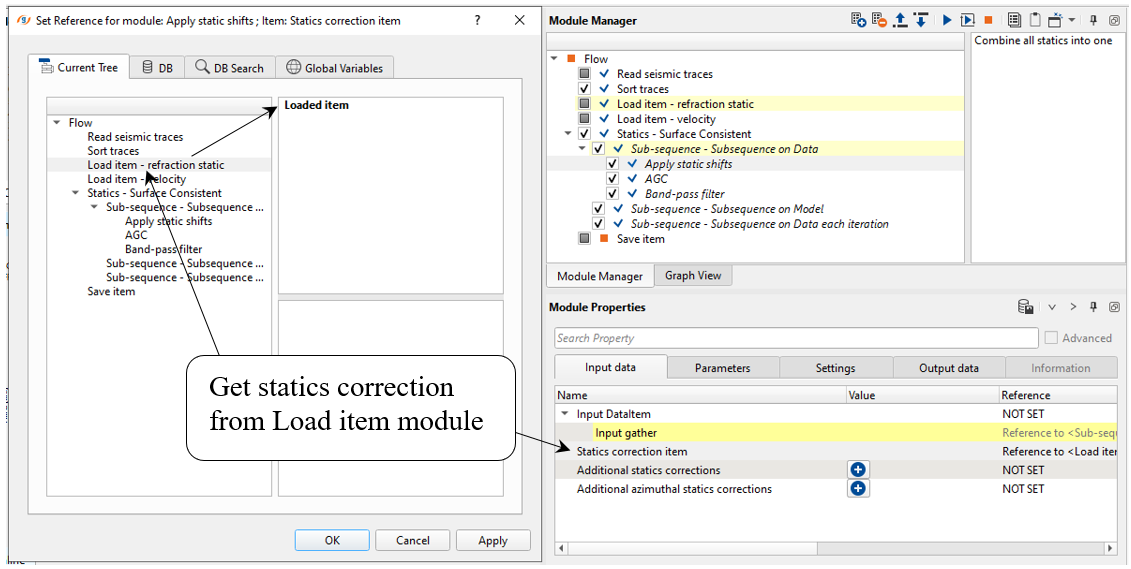
In the surface consistent statics, it computes single static solution for all the traces that is coming from the same shot gather. In the case of receiver, separate statics corrections are applied for all the traces from the same receiver. For the combined statics correction, each trace coming from single shot and single receiver will have separate shot static and separate receiver statics. Combining these source and receiver statics give rise to single time shift or static correction.
In g-Platform, module Statics – Surface Consistent builds the pilot trace from the CMP stack based on the Model aperture (CMP) defined by the user at the Model & Stack Parametrization. For example if user input the Model aperture (CMP) as 1, it means there will be 3 traces for generating the model trace. There is one trace on the left of the center trace and one on the right side. As a first step, the center trace is cross correlated with the traces on both side of it and generates a model trace and stores in the memory and the process follows to the next trace and so on till to the last trace. In the final step, we are solving the equations using Gauss Seidel in an iterative way to get the shifts for each individual shot and receiver gathers. Within this module, we have Velocity Update parameter where in user can enable Velocity updates to automatically update the velocities with each iteration.
Parameters:
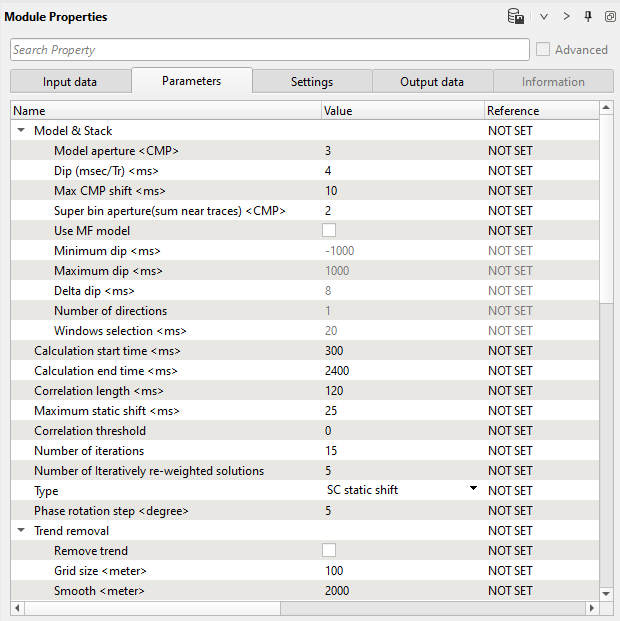
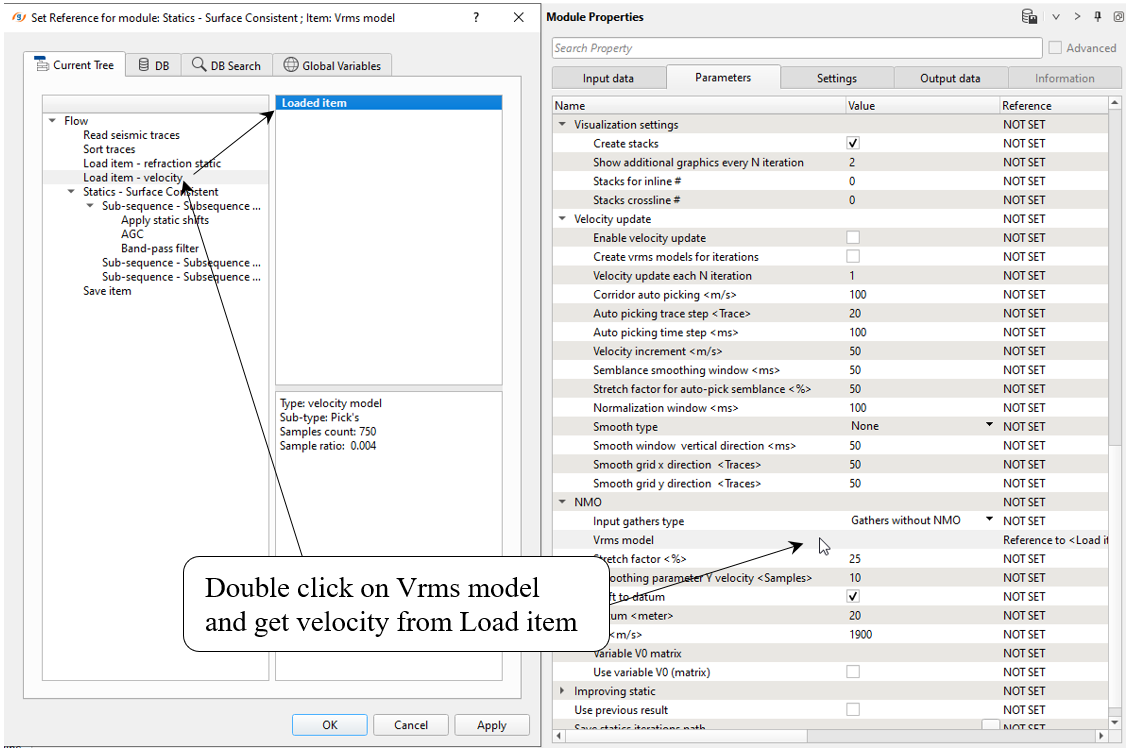
We are not going to update velocity during residual static calculations, but keep in mind that you have this option. Input seismic gathers are not NMO-corrected, so we need to apply stacking velocity inside the module. Therefore, we have to define Vrms model parameter:
Other parameters leave by defaults without changes. Execute residual statics and check results, open all visual vista views. Configure visual setting, for example as it shown below:
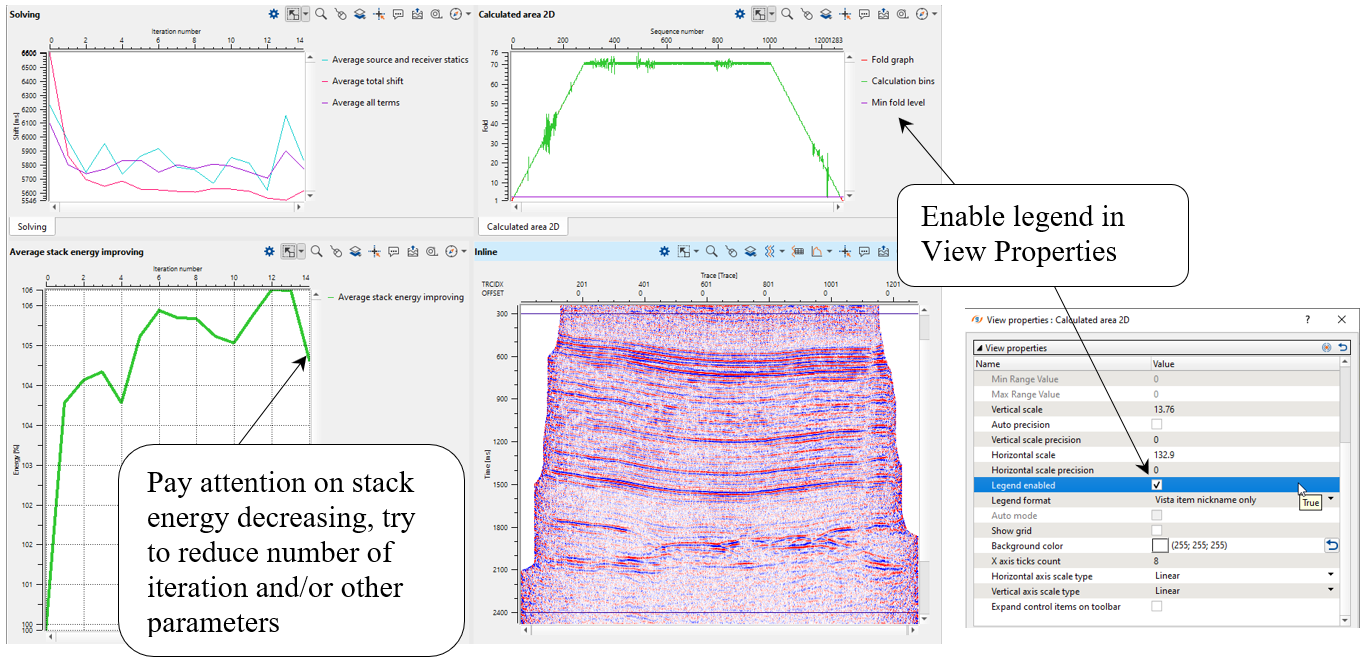
How to check stacks before and after residual statics: module calculates stacks automatically on each iteration. Open View Properties of the Inline vista window and compare different iterations:
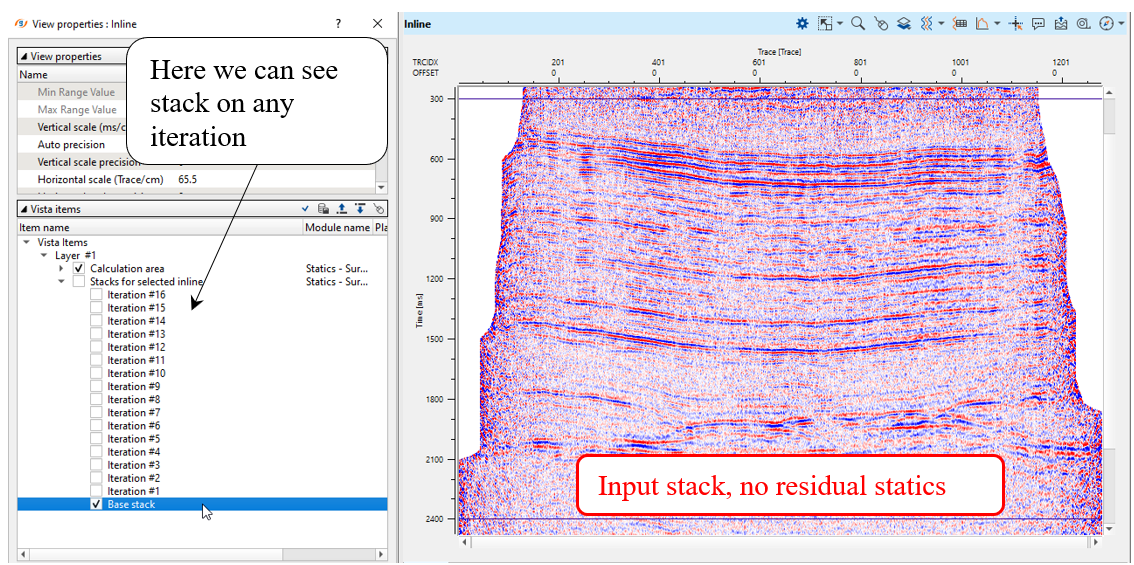
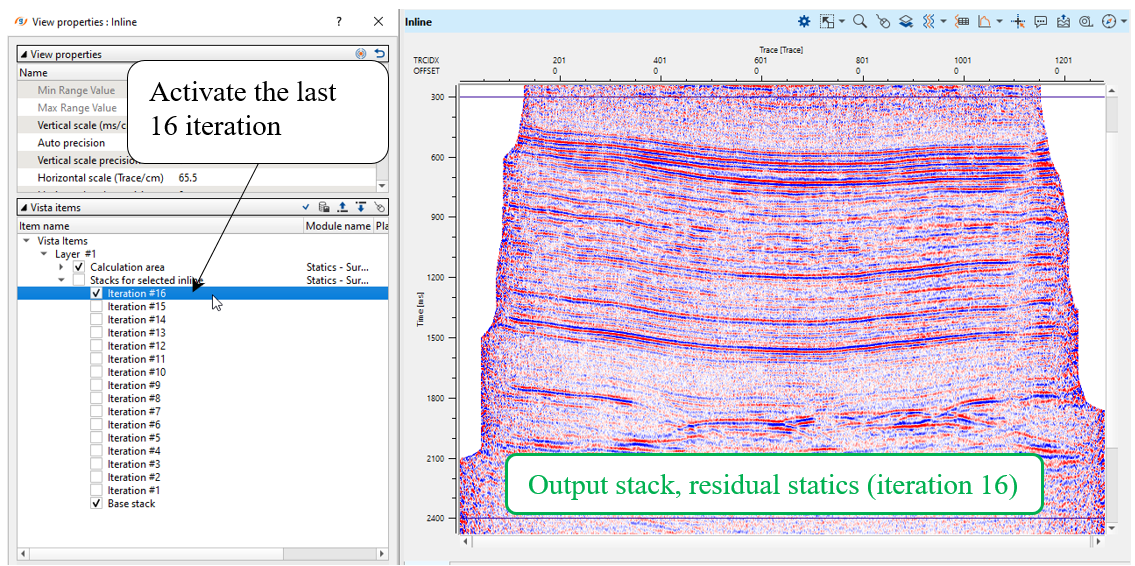
On the stack section of the final 16 iteration we can observe some problems with statics (how do you think it is a cycle or geology-fold?), look at the right side of the stack:
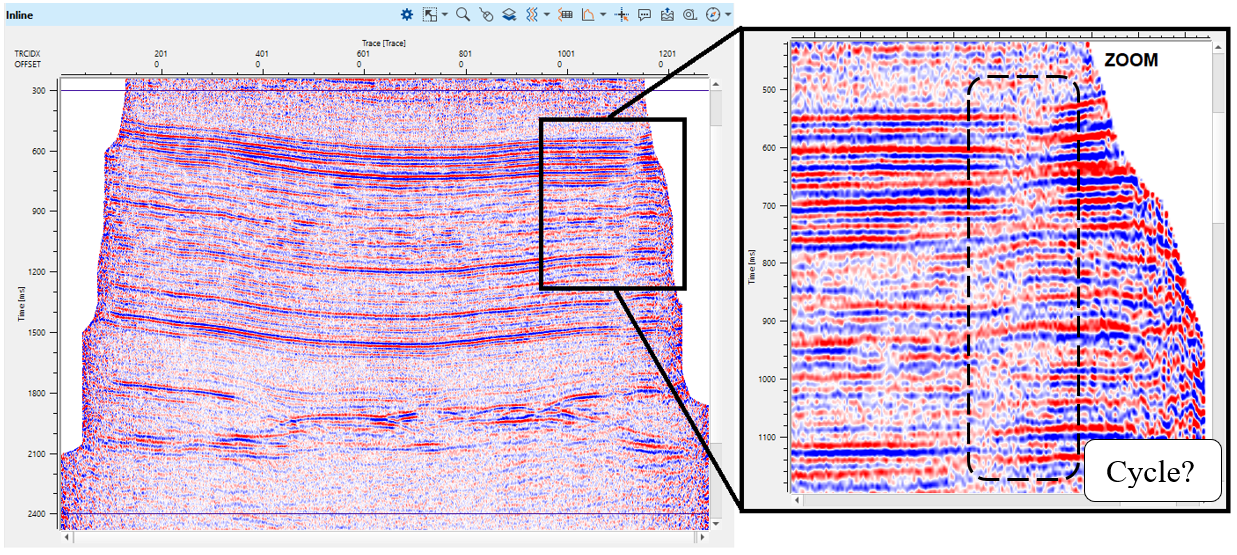
Try to solve this issue by changing parameters of residual static calculation (window, iteration, length of correlation, max.shift statics, etc.).
6) Save item: When you satisfied with the result save residual static corrections to DB via Save item module:
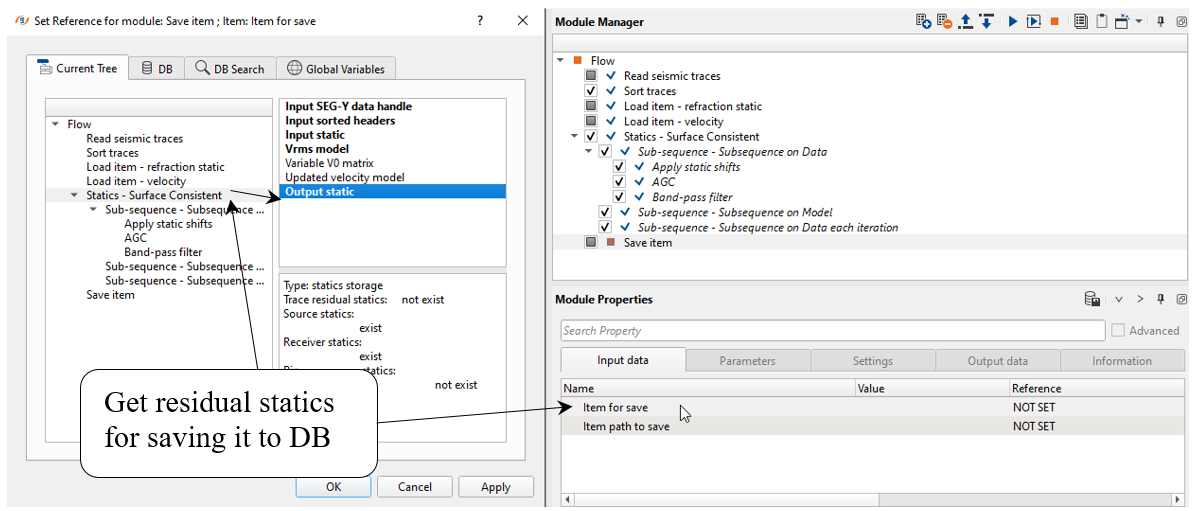
And define an output name for residual static library, write Residual_statics and execute the module:
Input data:
Now we can use residual static correction in other work flows.