Sharpening of the seismic data
![]()
![]()
What is a Diff Filter?
A Diff filter (short for differentiation filter) is a filter that computes the second derivative of a seismic signal. In other words, A diff filter measures how quickly the trace is bending or changing. It highlights sharp events (reflections) and suppresses slow trends.
It is also called:
•Second derivative filter
•Laplacian filter
•Edge enhancer
How Does It Work?
First derivative = rate of change
Tells us how fast the signal is going up or down.
Second derivative = change of the change
Tells us where the signal bends sharply (like corners).
A reflection is a sudden change in amplitude - this creates large second derivatives, so reflections become sharper and more visible.
Slow background trends (low frequencies) - small second derivatives - get suppressed.
What Does the Diff (Second Derivative) Filter Do to Seismic Data?
Highlights edge-like features - Reflections, faults, thin beds become clearer.
Reduces long-wavelength trends
Removes:
•low-frequency noise
•gradual amplitude changes
•baseline drift
•ground roll (partially)
Acts like a “sharpening filter” - It makes seismic events appear sharper and more detailed.
How Is the Diff Filter Applied?
Time-domain form:
A common second-derivative operator is: y(t) = x(t+1) – 2x(t) + x(t-1)
This is the discrete second derivative.
•If the trace is flat then output = 0
•If it changes slowly then small output
•If it changes sharply then big output (highlighted)
Frequency-domain form:
The second derivative multiplies the spectrum by: -(2πf)2
This means:
•Low frequencies suppressed
•High frequencies enhanced. This is why diff filters behave like high-pass filters.
Where Is Diff Filtering Used in Seismic Processing?
•As a pre-conditioning step - Before deconvolution or inversion.
•To sharpen events in migrated stacks - Imaging looks crisper.
•To highlight thin beds - Second derivative produces two strong opposite-polarity peaks for thin reflectors.
•To remove low-frequency noise or sag - Especially useful in VSP and some land data.
•In attribute analysis - Second derivative - curvature-like structural attributes.
Advantages
•Very simple & fast
•Enhances reflectivity
•Emphasizes thin layers
•Removes low-frequency noise
•Improves resolution
Disadvantages
•Can amplify high-frequency noise
•Edges are exaggerated → may need smoothing
•May distort amplitude if overused
![]()
![]()
Input DataItem
Input gather - connect/reference to pre or post-stack gather.
![]()
![]()
Diff type { First derivative, Second derivative } - select the differentiators from the drop down menu. By default, Second derivative.
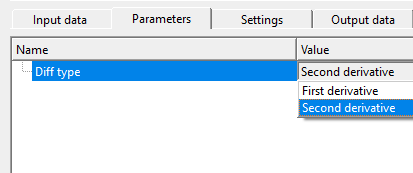
First derivative - tells us how fast the signal is going up or down.
Second derivative - tells us where the signal bends sharply (like corners).
![]()
![]()
Auto-connection - By default, TRUE(Checked).It will automatically connects to the next module. To avoid auto-connect, the user should uncheck this option.
Bad data values option { Fix, Notify, Continue } - This is applicable whenever there is a bad value or NaN (Not a Number) in the data. By default, Notify. While testing, it is good to opt as Notify option. Once we understand the root cause of it,
the user can either choose the option Fix or Continue. In this way, the job won't stop/fail during the production.
Notify - It will notify the issue if there are any bad values or NaN. This will halt the workflow execution.
Fix - It will fix the bad values and continue executing the workflow.
Continue - This option will continue the execution of the workflow however if there are any bad values or NaN, it won't fix it.
Calculate difference - This option creates the difference display gather between input and output gathers. By default Unchecked. To create a difference, check the option.
Number of threads - One less than total no of nodes/threads to execute a job in multi-thread mode. Limit number of threads on main machine.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output DataItem
Output gather - generates output gather
Gather of difference - generates difference gather if opted.
There is no information available for this module.
![]()
![]()
In this example workflow, we are reading a post stack gather by using Read seismic traces module. Make sure to change Load data to RAM from NO to YES.
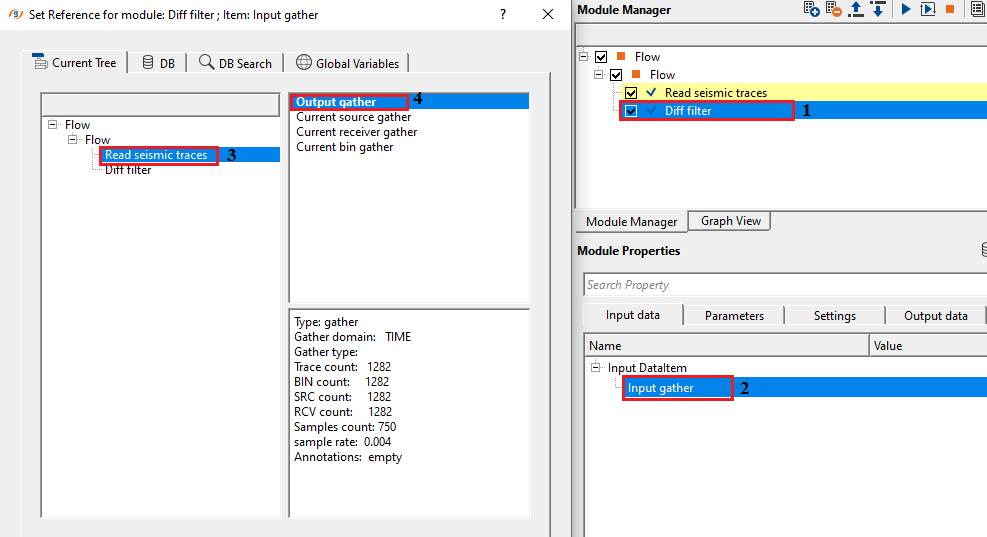
Select the appropriate differentiators from the drop down menu. We've selected second derivative for this exercise.
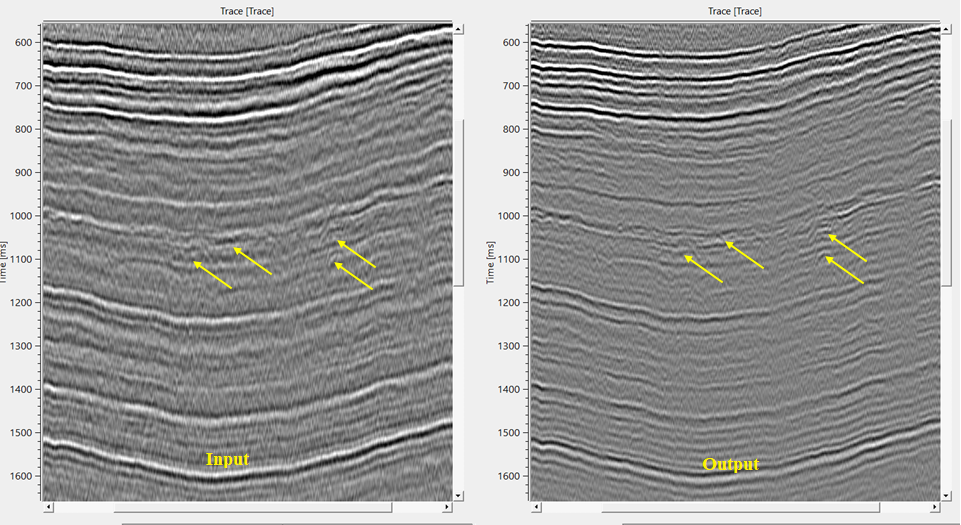
If we observe the output gather, it is more sharp and revealing the finer details which are masked by the low frequency content in the input gather.
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *