Description
Function for imaging the results of 3D ZO-MF search.
This procedure gives possibility to create zero offset (ZO) MultiFocusing stack, perform velocity constrain picking and export MF parameters.
Input data – 3D ZO-MF database data handle
Output data – MF parameters
Visual – Location map, Projections of the semblance cube, Output gathers separate for IL/XL
Input data
Storage file 3D
GMFPickingItem
Link to velocity constrain picking that can be taken from another procedure
Parameters
Image creation parameters
Image creation is a stacking procedure of time-corrected events corresponds to the optimal MF parameters.The number of events to be preserved during the MF Search determined in Parametrization – MF engine → Wave values → Maximum number of directions. Each event stored in database has following properties:
•Semblance value
•Time
•And indexes corresponding to the MF parameter
During the stacking can be applied different criteria for selection: by angle range, by velocity range or by semblance distribution.
Directions
Maximum number of events to be stack.
•Default: 1
•Values: 1-Maximum Number of Directions preserved during the search
From angle
First value of angle range to stack.
•Default: -90
•Range: -90 - 0
To angle
Last value of angle range to stack.
•Default: 90
•Range: 0 - 90
SN Enhance
Turn ON/OFF normalization of data over semblance prior stacking.
Default: False
Correlation threshold
Threshold for event participation in the summation as a percentage ratio of the maximum value.
•Default: 10
•Range: 10 - 90
Min angle distance selection
Minimum distance in terms of semblance grid along angle axe, between events selected for summation. Parameter gives possibility to separate events with different correlation by angle (Figure 1).
•Default: 1
•Range: 1 - 100
Min radius distance selection
Minimum distance in terms of semblance grid along velocity axe, between events selected for summation. Parameter gives possibility to separate events with different correlation by velocity (Figure 1).
Default: 100
Range: 1 - 100
Visualization
Apply following filters on sections and velocity semblance, for visualization only
Shift to datum
Turn ON/OFF shift to final (flat) datum
Default: false
Datum
Value of final (flat) datum
Default: 0
VelocityAGC
PickingOnly
Map
Parameters for bin selection on location map
Option for magnet
Parameter for automatic choice during bin selection.
•Cross - will select nearest bins located on intersection of calculated inlines and crosslines
•Single – will select nearest calculated bin
Default: cross
Inline
Number of selected inline
Default:0
Value: inline range
Crossline
Number of selected crossline
Default:0
Value: crossline range
Band-pass
Apply Band-pass
Turn ON/OFF band pass filter
Default: false
Frequency 1
Default: 1
Frequency 2
Default: 5
Frequency 3
Default: 100
Frequency 4
Default: 105
Export Params
3D From Inline
First inline for export
Default:-1
Value: inline range
3D To Inline
Last inline for export
Default:-1
Value: inline range
3D From Crossline
First crossline for export
Default:-1
Value: crossline range
3D To Crossline
Last crossline for export
Default:-1
Value: crossline range
Write mode
Default: direct
Values: direct, append
Convert To Feet
Convert output measurement system to feet
No Zero Values For Velocity
Fill samples with zero velocities with V 0
Zero padded
Fill traces with zero fold (non calculated) with zeros and write them to the output
Otherwise this traces are not written to output SEG-Y
Shift to datum
Shift exported results to final (flat) datum
Default: false
Datum
Value of final (flat) datum
Default: 0
Types
Types of MF parameters to be created during imaging, created both vista item for visualization and gather
Stack
Create zero offset MultiFocusing stack section
Default:true
Correlation
Create MF correlation section
Default: false
Angle
Create MF emergency angle section
Default: false
Gamma
CRE
Create MF CRE section
Default: false
CRE2
CRE Azimuth
CEE
Create MF CEE section
Default: false
CEE2
CEE Azimuth
V Slow
Create MF V RMS-MF section
Default: false
V Fast
Dip
Azimuth Dip
VSlow / cos(Dip)
Create MF approximation of CMP stacking velocity
Default: false
VFast / cos(Dip)
Fold
Create MFfold section
Default: false
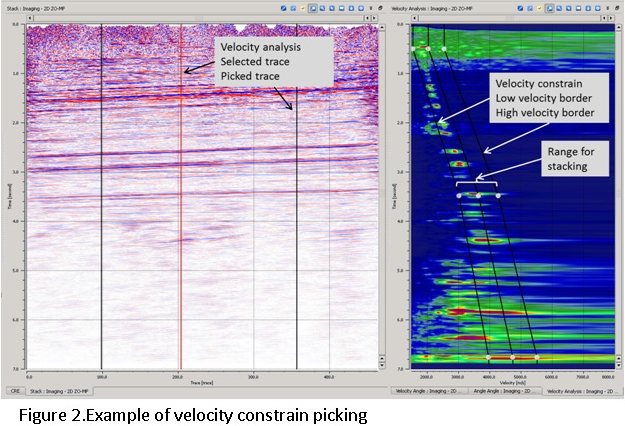
Velocity Analysis– Unlike the CMP processing MF has multidimensional semblance cube that makes picking too complex. For this picking of velocity function in MF replaced by picking of velocity corridor (constrain), the optimal parameters of MF selected automatically. For stacking will be used only events located inside the velocity constrain. Between two locations the velocity constrain interpolated, interpolation of velocity corridor reduce possibility of error in contrast to velocity interpolation during CMP velocity analysis (Figure 2).