Enhancing signal output quality and reducing noise by Tau-P Deconvolution
![]()
![]()
Deconvolution in Tau-P Domain. Deconvolution is nothing but filtering, which removes the wavelet recorded by seismic trace by means of reversing the process of convolution. Deconvolution can be performed by designing a Weinger Levinson Filter and transform from one wavelet into another wavelet.
Tau is a time shift parameter and P is slowness (inverse of the velocity). The main goal of Tau-P Deconvolution is to improve the signal quality and reduce the noise. Tau-P transforms the seismic data into different components which are later separated based on their time shift and slowness parameters. Primaries have different Tau & P parameters, noise has different and multiples have different Tau & P parameters.
Deconvolution can be performed in T-X domain and Tau-P domain. Results obtained in Tau-P domain are bit superior in comparison to T-X domain because multiples are better separated in Tau-P domain based on their periodicity. Tau-P Deconvolution is very useful if there are steeper dip events or non-stationary events which are difficult to separate in T-X domain.
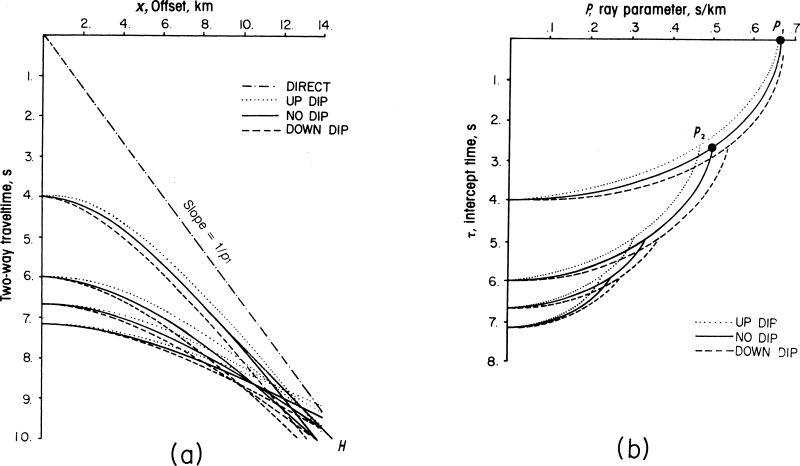
(a) An end-on seismic record is f(x,t) where x=source-geophone distance (offset) and t=arrival time.
(b) Its tau-p transform is F(τ,p) where p=dt/dx=1/Va and τ=intercept time at x=0.
The reciprocal of the apparent velocity, p, is called slowness. Hyperbolic reflections transform into ellipses, straight events into points (the direct wave into P1, the head wave into P2).
![]()
![]()
Input DataItem
Input gather - Connect/reference to Output gather. If the module is inside the Seismic loop, it will automatically connect to the previous module's output gather.
![]()
![]()
Trace Aperture - total number of trace (horizontal distance) to be included in the calculation. Higher aperture introduces noise and artifacts and lower aperture may not include all the information required for the calculation. Choose the trace aperture wisely.
Frequency1 - Starting of the first frequency taper. From here, it will go gradually to F2 and avoid any abrupt cutting off the frequencies or to avoid any edge effects.
Frequency2 - This is the starting frequency to be considered for deconvolution.
Frequency3 - End frequency range to be part of the deconvolution.
Frequency4 - End of the high frequency taper. This starts from F3 and slowly taper
V0 - Replacement velocity or near surface velocity.
Delta Tau - This is the sampling interval in Tau domain. Like the sampling interval in Time domain. This parameter plays a key role in Tau-P. The higher the Delta Tau value, lesser resolution results and the output may not good enough to separate the events in the Tau-P domain however the execution will be faster. On the other side, lower Delta Tau values increases the resolution which eventually gives a better result. The disadvantage of this is higher execution times. Choose the optimum Delta Tau value.
Radon prewhitening - Prewhitening is used to filter out the noise and enhance the signal. In Radon transform, this is very much essential to improves the separate the reflections events from the multiples energy.
Decon Params - This section deals with the deconvolution parameters. Deconvolution helps in increasing the resolution of the seismic signal.
Decon prewhitening - Prewhitening is applied prior to the deconvolution process to increase the signal strength by minimizing the noise component from the data and reducing the lower frequencies.
Operator legtth - Length of the deconvolution operator is applied in the tau-p domain. With higher operator lengths, it includes both primary and multiples however it may introduce unwanted noise. Whereas with lower operator lengths, there may not be enough samples to model the reflection energy.
Lag time - this parameter takes care of the time shift that should be applied prior deconvolution.
![]()
![]()
Auto-connection - By default, TRUE(Checked).It will automatically connects to the next module. To avoid auto-connect, the user should uncheck this option.
Bad data values option { Fix, Notify, Continue } - This is applicable whenever there is a bad value or NaN (Not a Number) in the data. By default, Notify. While testing, it is good to opt as Notify option. Once we understand the root cause of it, the user can either choose the option Fix or Continue. In this way, the job won't stop/fail during the production.
Notify - It will notify the issue if there are any bad values or NaN. This is halt the workflow execution.
Fix - It will fix the bad values and continue executing the workflow.
Continue - This option will continue the execution of the workflow however if there are any bad values or NaN, it won't fix it.
Calculate difference - This option creates the difference display gather between input and output gathers. By default Unchecked. To create a difference, check the option.
Number of threads - One less than total no of nodes/threads to execute a job in multi-thread mode.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output DataItem
Output gather - This module outputs the tau-p deconvolution applied gathers.
Gather of difference - Generates the difference between input and output gathers.
There is no information available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
In this example workflow, we are sorting the data in common shot domain (FFID/SOURCE_SP - ABS OFFSET).
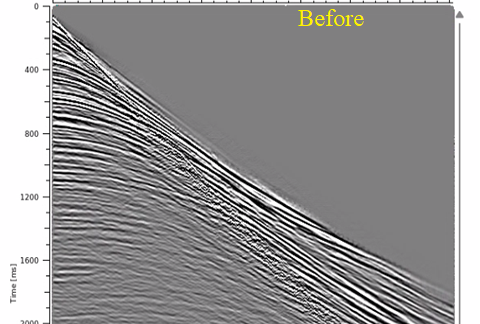
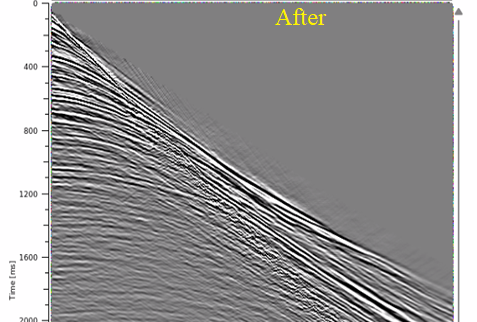
Test various parameters like Deconvolution operator length and lag time. Also, pay attention to the Radon prewhitening (%) value. Here are some of the shot and stack responses before and after Tau-P Deconvolution.
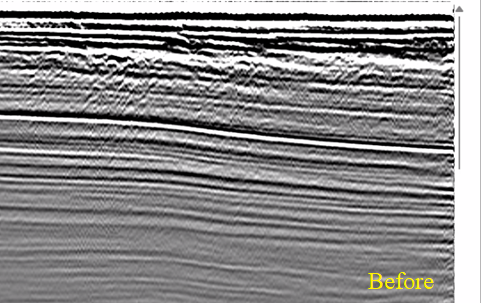
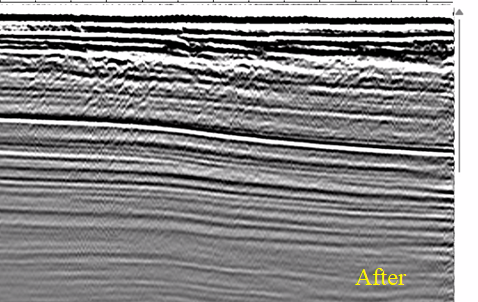
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
SEG Wiki (https://wiki.seg.org/wiki/Dictionary:Tau-p_mapping)
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *