Converting SEG-2 files to SEG-Y format
![]()
![]()
What is SEG-2 Data Format?
SEG-2 is a lightweight, PC-friendly seismic recording format using ASCII-based headers and trace-level metadata, widely used in engineering, refraction, and shallow seismic acquisition systems. SEG-2 is a digital seismic data file format introduced in the late 1980s for field recording, mainly for:
•Land seismic surveys
•Refraction seismic
•MASW / surface-wave surveys
•Engineering geophysics
•Shallow seismic applications
It was designed to be simple, flexible, and PC-compatible, unlike older tape formats such as SEG-B and SEG-C.
Key Features of SEG-2
1. Header + Trace Data Structure
A SEG-2 file generally contains:
•A file-level header
•Followed by a series of trace records
•Each trace record has:
oA trace header (ASCII + binary key-value pairs)
oSample data (usually 16-bit or 32-bit integers or floats)
Headers store:
•Trace number
•Shot number
•Receiver/channel number
•Sample interval
•Number of samples
•Coordinate info (if available)
2. Human-Readable Text Headers
SEG-2 uses embedded ASCII text inside headers, making it easier to inspect or diagnose compared to SEG-B.
Example:
CHANNEL_NUMBER = 5
SAMPLE_INTERVAL = 0.5
NUM_SAMPLES = 2048
3. Designed for Disk Files (Not Tape)
•Stores data in little-endian byte order (Intel PC format).
•Works well on Windows/DOS systems.
•Popular with geotechnical and refraction instruments.
4. Flexible and Lightweight
•No rigid fixed-size headers like SEG-Y.
•Instrument vendors can add custom fields easily (e.g., GPS time, sensor ID).
Where SEG-2 is Commonly Used
•Shallow seismic (< 500 m)
•MASW and refraction surveys
•Electrical resistivity instruments with seismic add-ons
•VSP in small-scale engineering studies
•Academic experiments
•Scintrex, Geometrics, OYO/ABEM instruments
Advantages
•Easy to read and parse
•Human-readable header components
•Compact file size
•Flexible structure for many acquisitions systems
Limitations
•Not ideal for large exploration surveys
•No universal standard for geometry fields
•Many vendor-specific variations
•Not suitable for major processing environments compared to SEG-Y
![]()
![]()
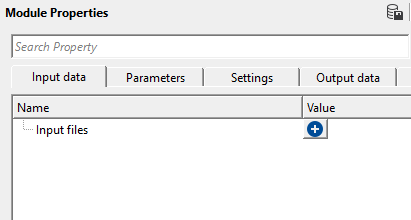
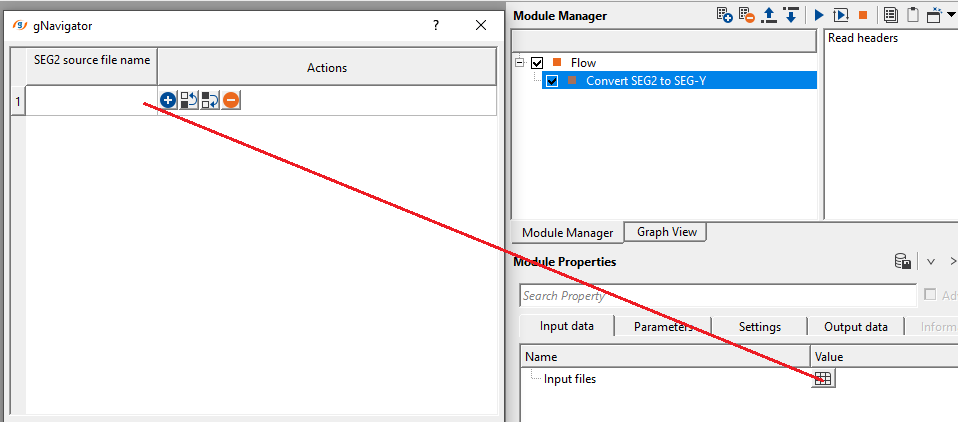
Input files - click on  icon. It will open a new window. Click on
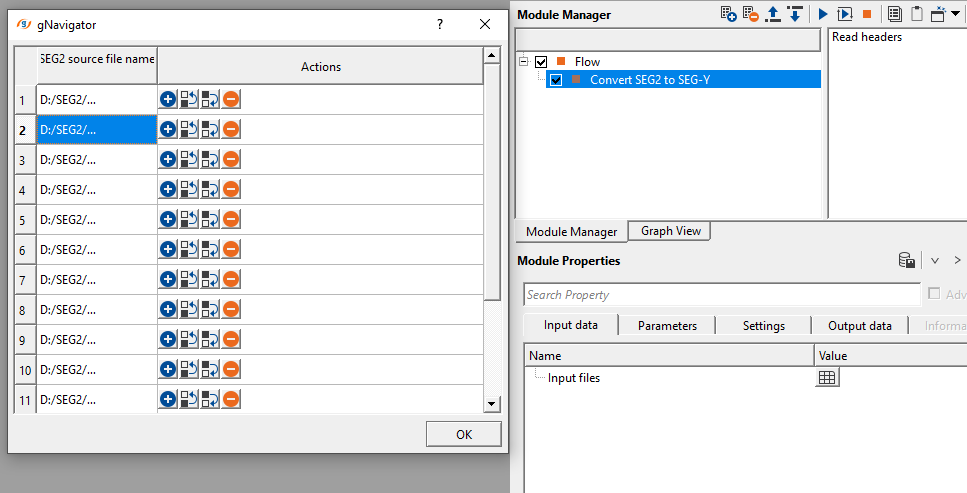
icon. It will open a new window. Click on  icon again. Click inside SEG-2 source file name field and provide the input files. For multiple input files, hold SHIFT key and select all the input files.
icon again. Click inside SEG-2 source file name field and provide the input files. For multiple input files, hold SHIFT key and select all the input files.
![]()
![]()
Output file - this section deals with output file name, file type, trace header format etc.
File type { SEG-Y } - specify the output file type. By default, SEG-Y
Output file name - provide output file name after
Trace header format { Geomage format, SegFormat, Seg-Y, rev.1, 2002, Geomage Office Post, Coordinates Only, Constant Elevation, VSP format, teapot_dome_3d, segy_v2, Kingdom format, attaphol, d-001, Test_gom } - choose the SEG-Y trace header format from the drop down menu. By default, Geomage format which is SEG standard rev.1, 2002 format.
Geomage format - this is Geomage internal format which is equivalent to SEG-Y standard rev.1, 2002 format.
Load full data - it will load all the data in the file. By default, FALSE (Unchecked).
Get FFID from file name - extracts the FFID information from the input file name. By default, FALSE (Unchecked).
![]()
![]()
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Current SEG2 file - this is an output vista item of current SEG-2 file among the Vista items generated by the module.
Current SEG2 trace - one of the vista items and displays the selected/current SEG-2 trace
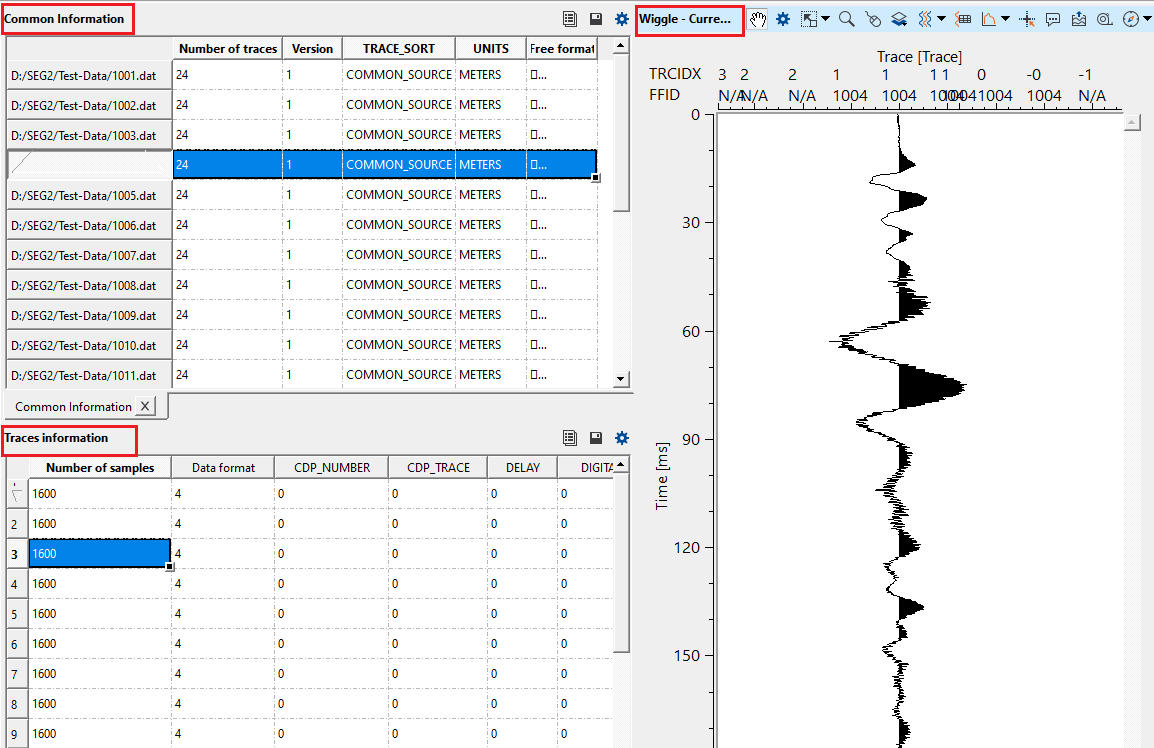
Common Information - displays the information of the file, FFID, no of samples, sample size etc
Traces information - displays the trace information like the FFID and the corresponding trace.
There is no information available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
In this example, we are reading multiple SEG-2 files and reading the headers.
After reading all the input files, click on "Read headers" from the action items menu. Launch Vista groups -> All Groups-> In new window by right clicking on the module. It will provide Vista items like Common information, Traces information, Current SEG-2 file & Wiggle - Current SEG-2 displays.
To view the data, click on any input data file in the Common information window. It will display all the information in the Traces information window. Select any trace and the corresponding display will appear in the Wiggle - Current SEG-2 window.
![]()
![]()
Read headers - this action items allows the user to read the input trace headers. This will generate all the trace headers information that can be displayed as Vista items.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
![]()