Attenuates periodic/ringing events
![]()
![]()
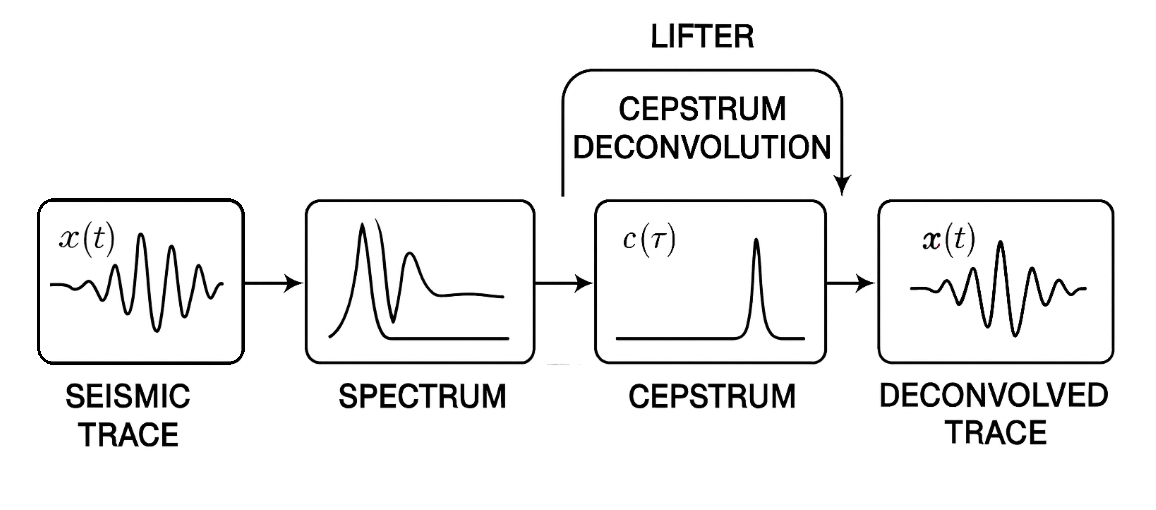
Cepstrum(reverse order of Spec) Deconvolution is a wavelet-removal technique that works by transforming seismic data into the cepstrum where source periodicities (multiples, bubble pulses, reverberations) appear as isolated peaks. By applying a lifter (reverse order of fil) filter in the quefrency domain, these periodic components are removed, producing a cleaner, more reflectivity-like trace.
What is Cepstrum Deconvolution?
Cepstrum deconvolution is a method for removing the source wavelet from seismic data by converting the signal into the cepstrum domain — a special domain where reverberations, multiples, and periodic wavelet signatures appear as distinct peaks and can be isolated and removed.
It is especially good at:
•Removing short-period multiples
•Removing source bubble effects in marine data
•Removing ghosts
•Flattening reverberations
•Extracting the minimum-phase wavelet
Why Use Cepstrum Deconvolution?
Traditional deconvolution (spiking/predictive) struggles when:
•Wavelet is mixed-phase
•Reverberations are embedded inside the wavelet
•Multiples have regular periodicity
•Data have strong source bubble oscillations
Cepstrum deconvolution excels because:
•Convolution becomes addition in the cepstrum
•Periodic wavelet features show up as distinct spikes
•These can be suppressed using windows or filters
How Cepstrum Deconvolution Works?
A seismic trace is: x(t) = w(t) * r(t)
Step 1 — Fourier Transform: X(f) = W(f) . R(f)
Step 2 — Take Log Spectrum: ln X(f) = ln W(f) + ln R(f)
This is the key: Convolution becomes addition.
| Step 3 — Inverse FFT of log spectrum → Cepstrum |
C(Ƭ) = F-1 {ln X(f)}
•Ƭ is called "quefrency"
•Peaks at particular t correspond to periodicities (multiples, bubble oscillations)
Step 4 — Apply a “lifter” (cepstral filter)
•Suppress long-period or short-period components
•Remove wavelet periodicity
•Keep reflectivity terms
Step 5 - Transform back
Ẍ(f) = exp {FFT(Cfiltered)}
Inverse FFT gives the cepstrum-deconvolved trace.
What Cepstrum Deconvolution Removes?
Short-path multiples - Bubble pulse or peg-leg multiples appear as repeating periodic events that are strong in cepstrum.
Ghost effects - Source/receiver ghost period appears as a cepstrum peak.
Source wavelet periodicity - Any oscillatory wavelet component (Vibroseis sweep edges, bubble oscillation).
Reverberations / ringing - Room acoustics / poor weathering layers.
![]()
![]()
Input DataItem
Input gather - connect/reference to the Output gather. This gather can be a pre or post stack gather.
![]()
![]()
Time start - time of Primary - specify the start time of the primary energy/signal. This is the minimum quefrency (smallest cepstral time) to include in the primary cepstral window. This defines where the primary cepstrum begins. Too small value includes the lower frequencies and distort the wavelet. Too high value may attenuate the primaries.
Time end - time of primaty + Multiples - specify the end of the primary energy/signal along with multiple energy. This is the maximum quefrency included in the primary region. Beyond this value contains bubbles, short period multiples, reverberations, ringing, source and receiver ghosts etc. This is the key parameter in the cepstrum deconvolution. It sets where the primary/multiple ringing begins in the cepstrum. Anything beyond this value will be attenuated.
If value is too small - we may be attenuating the primaries, if the value is too big , we may not attenuating the multiples. Optimum values are recommended. For marine bubbles, anything between 20-40ms is a good starting point.
Noise - specify the percentage of white noise is added to the deconvolution to stabilize the output.
![]()
![]()
Auto-connection - By default, TRUE(Checked).It will automatically connects to the next module. To avoid auto-connect, the user should uncheck this option.
Bad data values option { Fix, Notify, Continue } - This is applicable whenever there is a bad value or NaN (Not a Number) in the data. By default, Notify. While testing, it is good to opt as Notify option. Once we understand the root cause of it,
the user can either choose the option Fix or Continue. In this way, the job won't stop/fail during the production.
Notify - It will notify the issue if there are any bad values or NaN. This will halt the workflow execution.
Fix - It will fix the bad values and continue executing the workflow.
Continue - This option will continue the execution of the workflow however if there are any bad values or NaN, it won't fix it.
Calculate difference - This option creates the difference display gather between input and output gathers. By default Unchecked. To create a difference, check the option.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output DataItem
Output gather - generates the deconvolved output gather.
Gather of difference - if opted, generates the difference gather after cepstrum deconvolution.
There is no information available for this module.
![]()
![]()
Cepstrum deconvolution separates convolution into addition by taking log of the spectrum and inverse transforming it (the “cepstrum”). This allows us to detect and remove periodic wavelet components.
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
![]()