Deghosting
Deghosting
 Deghosting
Deghosting
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Navigation: Tutorials > Seismic Processing 2D MARINE >
|
Ghost is an issue in marine data processing and it is important to remove or attenuate the ghost effect because Ghost makes the seismic data interpretation difficult.
Ghost is created or presented in the seismic data due to traveling of the up going wave towards the water surface and return back and recorded at the receivers so as at the source end.
So in marine data we have to deal with Source Ghost and Receiver Ghost. If we want to explain the ghost in simple way we can say like …
Recorded Data = Primary + Source Ghost + Receiver Ghost
In order to get the ghost free data (Primary), we have to remove the source side ghost and receiver side ghost.
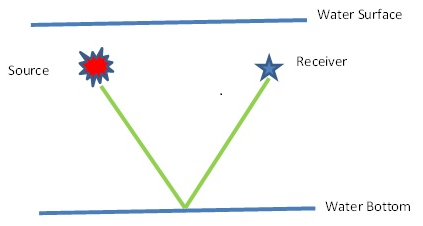
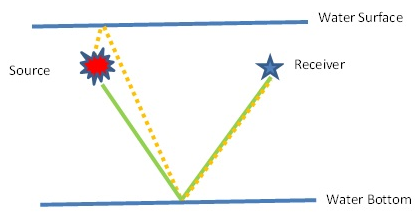
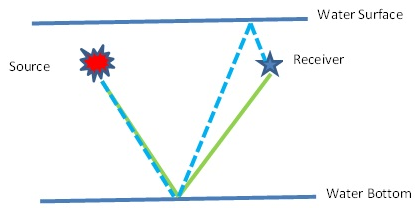
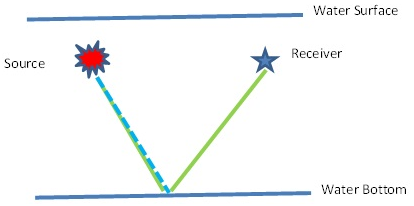
| Schematic Diagram of Ghost free data | Schematic Diagram of Source Ghost Schematic Diagram of Receiver Ghost Schematic Diagram of Source and Receiver Ghost |
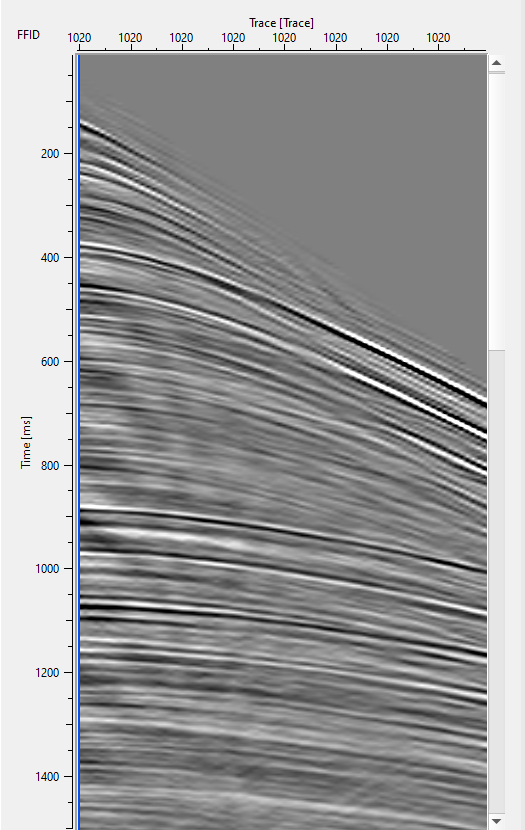
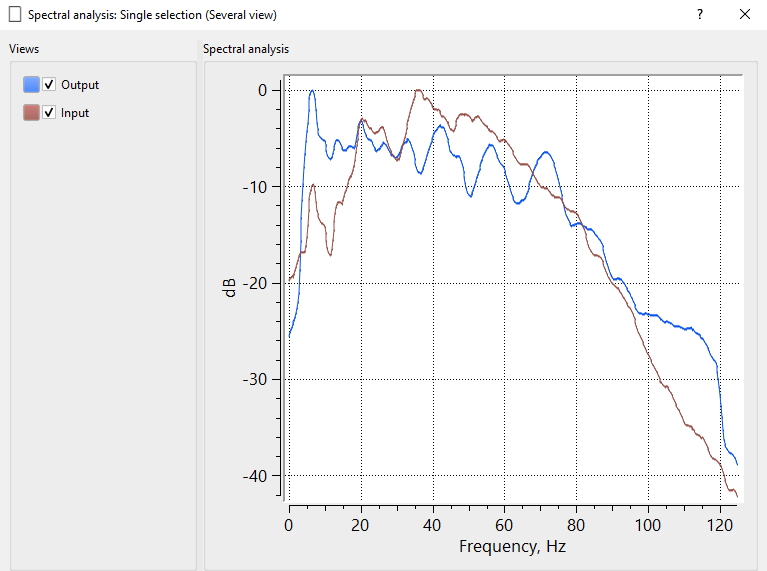
Deghosting enhances the signal to noise ratio. And also boost the low frequency In the case of shallow data, the data looks higher frequency due to the removal of the side lobes. For deeper events, data looks like low frequency. There are two factors which influences this. One is due to the attenuation of energy and second one is of elimination of side lobes. Due to this data looks higher frequency in the deeper part of the section. Once we apply the Deghost filter then the data look low frequency.
There are various methods to minimize the ghost. During the acquisition, we can lower the streamer to a bit deeper level to minimize the receiver ghost effect. Also we can use variable depth streamers to minimize receiver ghost effect. This works due to the notch diversity created by variation in the receiver depths.
In the case of data processing/imaging, we have different methods to attenuate ghosts. In g-Platform we perform the Deghosting in Tau-P domain. Make sure that we have source and receiver depths are stored in the trace headers
User recommendations:
To run the receiver deghosting, sort the data into FFID/Source_SP as Primary Key and Channel as Secondary key. The output will be Receiver ghost free data.
Create a workflow 0090-debubble
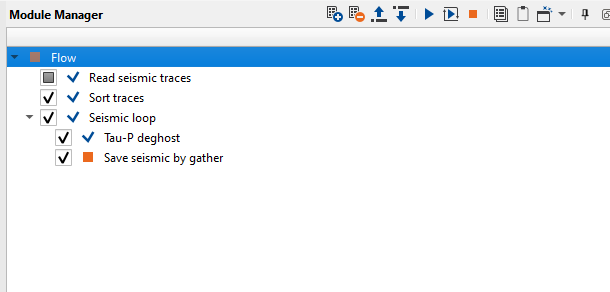
1. Read seismic traces
2. Sort traces
3. Seismic loop
4.Tau-P deghost
5. Save seismic by gather
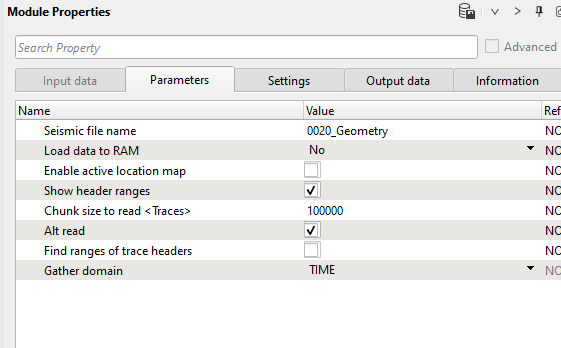
1) Read seismic traces loads seismic trace from the previous step, input file name is 0020_Geometry. Execute the module by double click on it or press on run button ![]() from the upper menu.
from the upper menu.
Define module parameters:
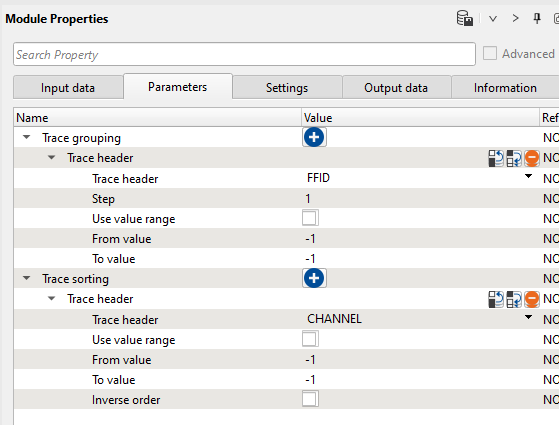
2) Sort traces Here we need to sort seismic traces for Seismic loop. Add Sort traces module and set FFID header for Trace Grouping and CHANNEL as Trace Sorting as it is shown below
3) Seismic loop Connect trace headers vector (Input sorted headers) from the Sort traces module output and seismic (Input SEG-Y data handle) from Read seismic traces. Depending on the sorting order, it will display the corresponding values in the Parameters tab. In this case, we have sorted in FFID vs Channel so it will display the First FFID value and the total no of sequences. It automatically detects these values and user don't have to input anything here.
4) Tau-P deghost Connect the input trace headers to Seismic loop. In the first pass of deghosting, we sort the data into FFID Vs Channel to attenuate the source ghost effect. In the 2nd pass, we sort the data into Receiver_SP Vs Channel and try to attenuate the receiver ghost effect. Make sure that the water velocity, source and receiver water depths plays an important role in deghosting.
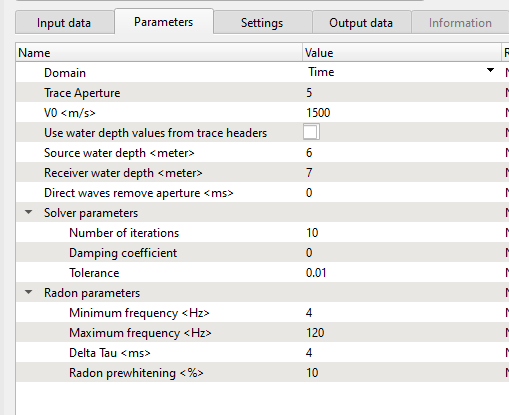
Domain - Choose the domain to perform the deghosting operation. We have time and frequency. By default, Time domain.
Trace Aperture - Provide the number of traces to perform the Tau-P operation. If user provides 5 as trace aperture then there will be 2 traces on either side of it and the center trace will act as pilot trace.
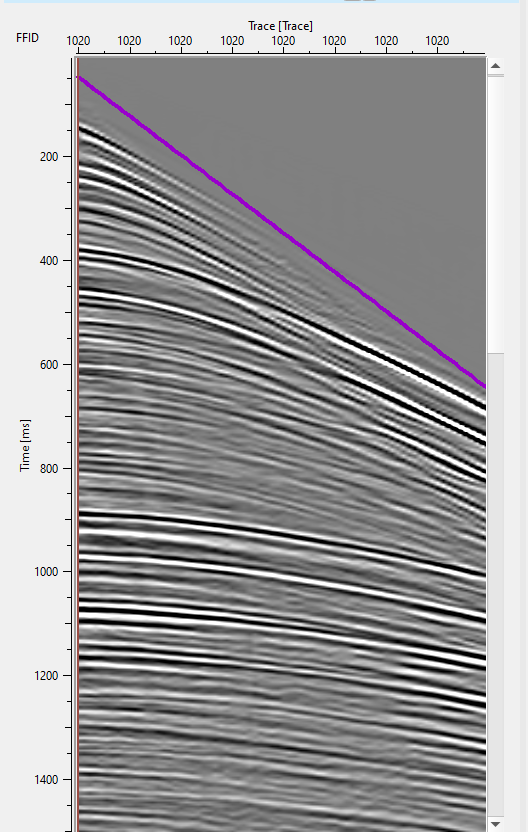
V0 - Provide the accurate water velocity. This water velocity is used to mute the direct arrivals since the direct arrivals doesn't have any ghost reflections. With the combination of V0 and Direct waves remove aperture (ms), it will mute the data.
Use water depth values from trace headers - If checked, it will read the elevations information from the trace headers.
Source water depth - In case the source water depth is not present in the trace headers, provide the source water depth value.
Receiver water depth - Similar to the source water depth, provide the receiver(s) water depth if this information is not available in the trace headers.
Direct waves remove aperture - To mute the direct wave arrivals. With the provided V0 (water velocity) and aperture value, it calculates the offset information and accordingly mute the direct arrivals. This parameter is optional and the user can ignore it if the direct arrivals are already well taken prior to deghost.
Solver parameters - These parameters are to solve the deghosting parameter in Tau-P domain.
Number of iterations - Define the number of iterations to perform in Tau-P domain
Damping coefficient - This parameter related to out put data regularization. By default it is Zero (0) which means no regularization of the output data. This coefficient depends on the input amplitudes.
Tolerance - Define the tolerance value. This value acts as stoppage point when the difference between the input and expected output spectrum reaches this value.
Radon parameters
Minimum frequency - Provide the minimum frequency used for radon transformation
Maximum frequency - Provide the maximum frequency used for radon transformation
Delta Tau - Radon trace delta time defined at the farthest offset
Radon prewhitening - Specify the Prewhitening noise percentage applied to the data to stabilize the result