Creating 3D volume from multiple 2D lines
![]()
![]()
A Pseudo-3D volume is a 3-dimensional seismic dataset created from 2D seismic lines, even though true 3D data was not acquired.
It is called “pseudo” because:
•It simulates a 3D cube
•But it is constructed from 2D profiles, not from dense 3D acquisition
•It is not a true amplitude-preserved 3D dataset
Think of it as stacking and interpolating multiple 2D lines into a 3D grid, giving interpreters a cube-like view where no actual 3D data exists.
Why Create a Pseudo-3D Volume?
You create a pseudo-3D volume when:
✔ You only have several 2D seismic lines (typical in exploration or old data)
✔ You want a 3D-like interpretation environment
✔ You want to visualize horizons and faults across lines
✔ You need to do:
•3D horizon mapping
•Structural modeling
•Fault framework building
•Depth conversion
•Early reservoir evaluation
•Visual QC of 2D alignment
A pseudo-3D cube is NOT used for:
•AVO analysis
•True amplitude studies
•3D inversion
•3D migration
Because it does not have true spatial fold or 3D acquisition geometry.
How a Pseudo-3D Volume Is Created?
1.Import multiple 2D lines into your (g-Platform) software
2.Convert each 2D line into an inline or crossline index
For example:
oLine 1 → Inline 100
oLine 2 → Inline 200
oLine 3 → Inline 300
3.Assign spatial coordinates
Each sample is placed at its true X,Y position.
4.Interpolate between lines (optional)
oLinear
oKriging
oGridding methods - This fills gaps between 2D lines.
5.Write a 3D cube file
Typically SEG-Y 3D or internal volume format.
Where Pseudo-3D Is Commonly Used?
•Early exploration blocks
•Old legacy basins
•Offshore basins with sparse 2D grids
•Areas where 3D acquisition is too expensive
•Government data packages (NDR, NPD etc.)
•Geological modeling of sparse datasets
•

![]()
![]()
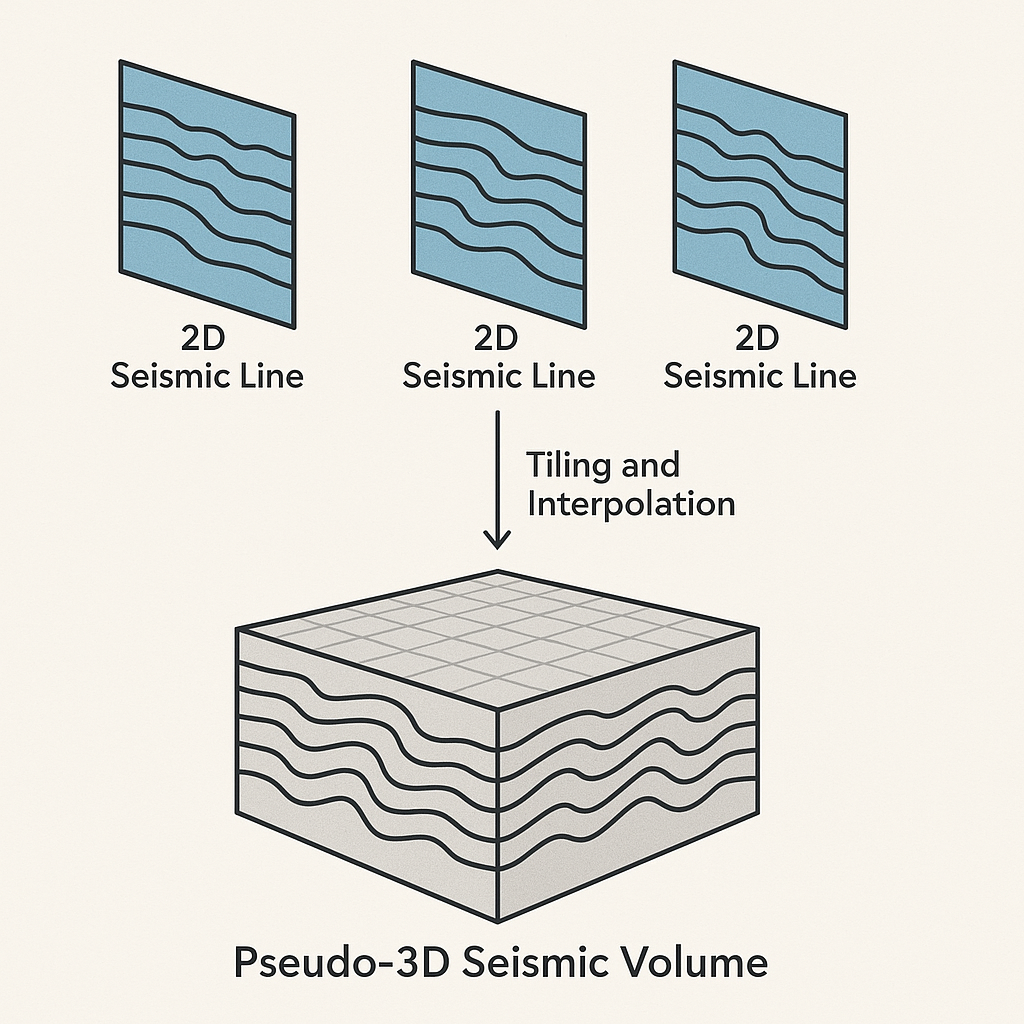
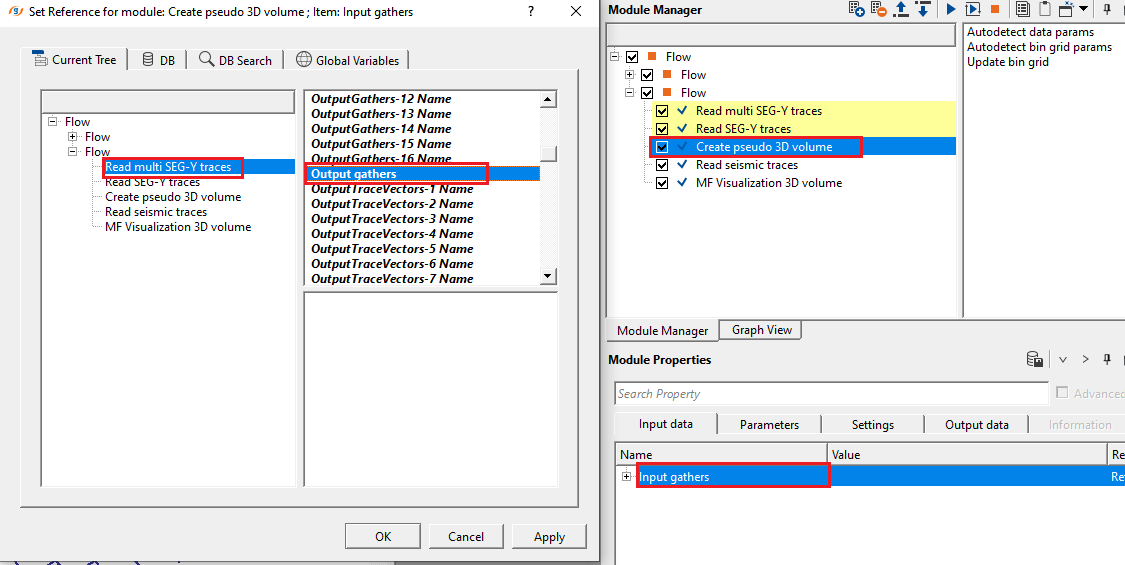
Input gathers - connect/reference to Output gather. For this, we read the input data as multiple 2D lines or combining all 2D lines into a single file. For the former option, we use Read multi SEG-Y traces module. For the later option, we first use concatenate seismic files module to combine all 2D lines into a single file then use Read seismic traces module and change Load data to RAM as YES from NO option.
![]()
![]()
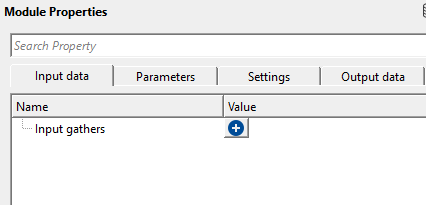
Grid definition - bin grid information is used for creating a 3D grid to accommodate all 2D lines within the 3D bin grid. For the same reason, the user must provide the bin grid information. This can be achieved automatically by clicking "Auto detect bin grid params" option from the action items. Similarly, "Auto detect data params" option for data parameters.
Inline bin spacing - specify the distance between two adjacent inlines or inline bin distance
Crossline bin spacing - specify the distance between two adjacent crosslines
Grid starting point X coord - this is the starting point of the bin grid. Specify the x-coordinate value
Grid starting point - Y coord - specify the y-coordinate value of the starting bin grid.
Inline azimuth - the direction/angle in which the inline axis is oriented on the map.
First inline number - provide the 1st inline number
First crossline number - provide the starting crossline number
InLine distance - distance across the inline direction of the grid or the distance covered by the inline direction
Crossline distance - distance across the crossline direction of the grid.
Angle between inline and crossline - both inline and crosslines are perpendicular to each other so ideally it should be 90 degrees
Data length - specify the output record length
DT - specify sample interval. By default, 2 ms.
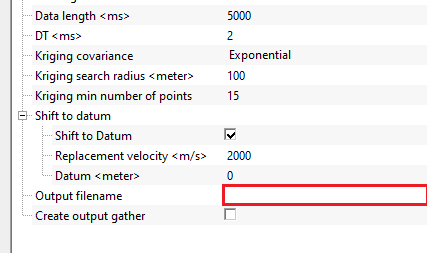
Kriging covariance { Spherical, Gaussian, Exponential } - this is used for interpolation. Krigging uses a covariance model (variogram) to describe how similar two points are depending on the distance between these two points. They are 3 types of covariances
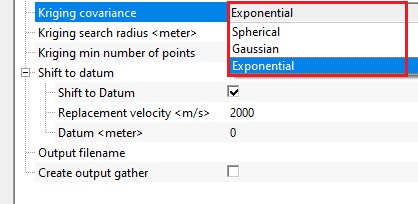
Spherical - this model assumes spatial continuity increases smoothly then becomes constant. Increases from 0 to full correlation and flattens at a distance called range.
Gaussian - Very smooth curve. Correlation drops slowly near the origin but decreases strongly
Exponential - represents noiser data and correlation drops rapidly at short distances however never reaches zero.
Kriging search radius - the maximum distance from the estimation point from which kriging can search for data points. For example, if the search radius is 1000m, it will consider points within 1000m for interpolation.
Kriging min number of points - the minimum number of points kriging used for interpolation to estimate the new value.
Shift to datum - it will shift the output volume to final datum
Shift to Datum - it will shift the data to final datum
Replacement velocity - specify the replacement velocity
Datum - specify the datum value.
Output filename - provide the final output pseudo 3D volume name.
Create output gather - this option allows the user to create output gather.
![]()
![]()
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output gather - generates output pseudo 3d volume
There is no information available to this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
In this example workflow, we are reading multiple 2D lines by using "Read multi SEG-Y traces" module. The output dataitem will be connected to Create pseudo 3D volume.
![]() Read multi SEG-Y traces must have load data to RAM as YES
Read multi SEG-Y traces must have load data to RAM as YES
For Parameters, we can automatically detect the Grid definition and Data length, DT from the action items menu.
Setup all the parameter and give an output file name against the Output file name parameter and execute the module.
Launch Vista items. It will generate, Inline, Crossline, Location map etc.
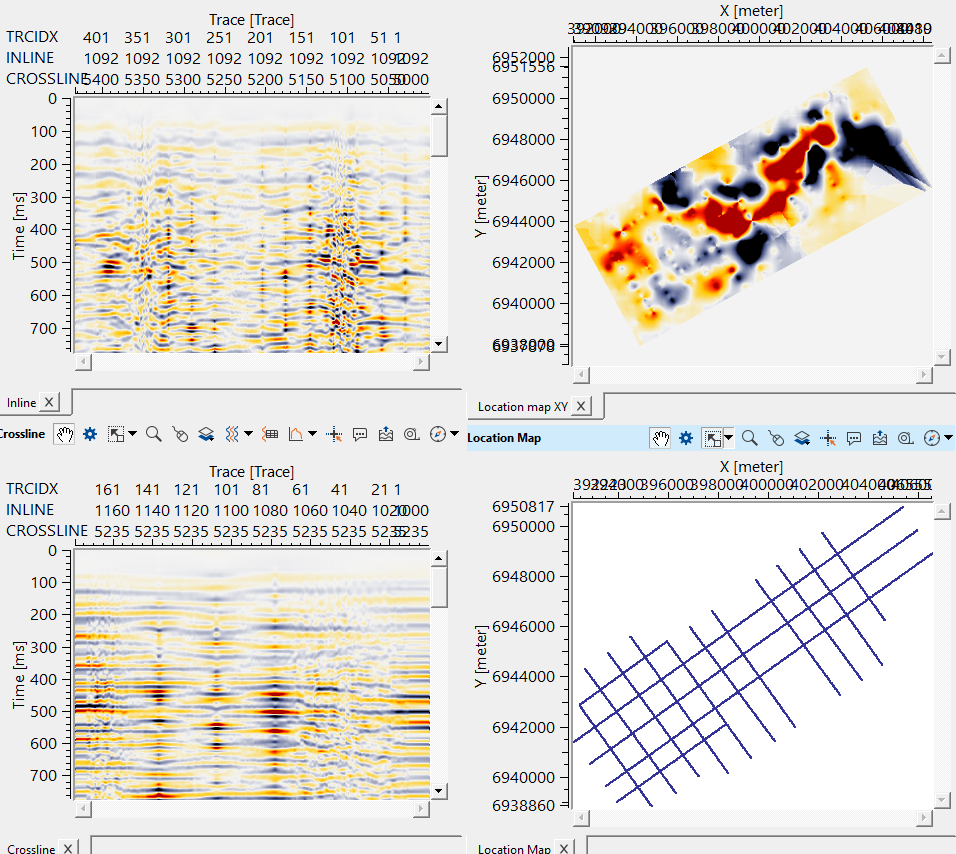
Test Kriging search radius and minimum number of points. These are the key parameters for the better interpolation.
![]()
![]()
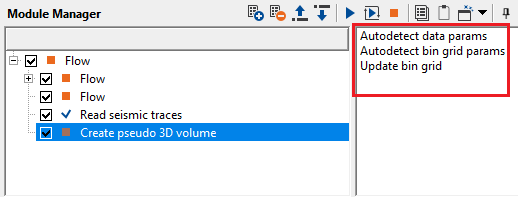
Autodetect data params - this option automatically detects the data parameters of the input files.
Autodetect bin grid params - this options detects the bin grid parameters from the input files.
Update bin grid - in case the user provides bin grid parameters, it will update the bin grid.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
![]()