Random noise attenuation (Prestack / Poststack)
![]()
![]()
Cadzow De-Noise Filter is based on rank reduction of matrix on frequency slices to attenuate the random noise. This can be done in pre and/or post stack data. Even though the parameters are similar to RNA (Random Noise Attenuation) module, the working principle is slight different as far as the Eigen values are concerned. In this case, these Eigen vectors are applied on multiple dimensions (3 or more) unlike the two dimensions in RNA. The other advantage of Cadzow De-Noise Filter is that it can work on flat or dipping events. It preserves the dips of steeply dipping events while attenuating the random noise.
![]()
![]()
No actions
![]()
![]()
Prestack or post stack seismic data, any sorting.
![]()
![]()
Horizontal sliding window <Traces>
Number of traces for creating spatial sliding window.
Time interval in milliseconds for creating spatial sliding window. Usually starts from 50 ms, there may be artifacts on the output image in case of too small window
Start frequency for processing.
End frequency for processing.
Number of eigenvalues, actually it is representation of the matrix of samples for each frequency section - high value, harsh denoise effect. In other words, it is number of dips in the superposition. Pay attention on geological structures (dips), the main task is to find a balance between denoise and structure preserving (or signal event in case of prestack data).
,
ʎ - eigen value, v - eigen vector
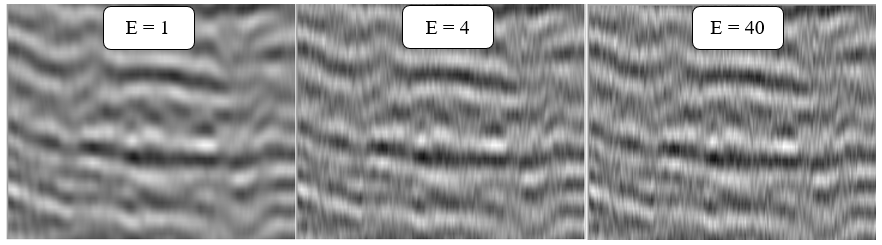
Fig.1 seismic image with different eigen values - 1, 4 ,40.
![]()
![]()
Skip - switch-off this module (do not use in the workflow).
Auto-connection - module is connected with previous (and next) modules in the workflow by default.
Bad data values option
There are 3 options for corrupted (NaN) samples in trace:
Fix - fix corrupted samples.
Notify - notify and stop calculations.
Continue - continue calculations without fixing.
Number of threads - perform calculation in the multi-thread mode.
![]()
![]()
Output gather - input seismic data minus random noise.
![]()
![]()
In this example we use a stack section as an input data and main goal is to attenuate random+linear noise.
Usually geophysics create these type of workflows on the poststack stage in order to remove remains of noise events after PSTM/PSDM procedures.
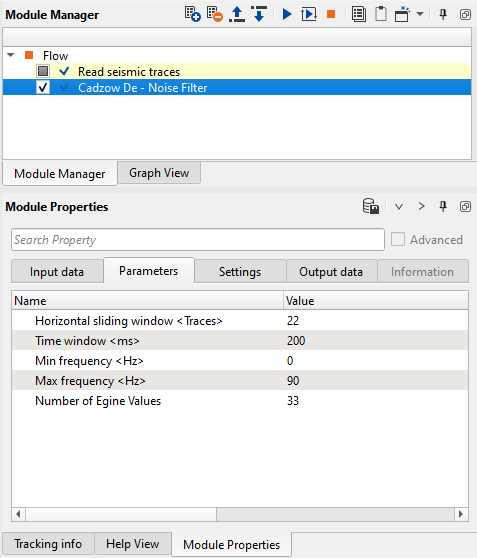
Fig.2 Workflow and module's parameters.
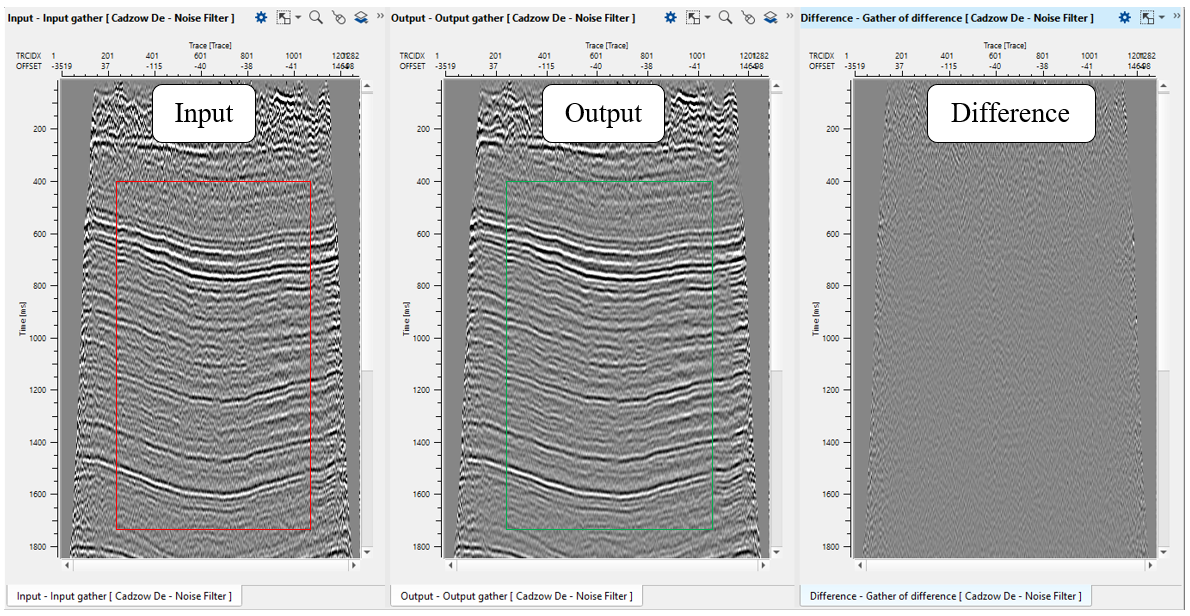
Fig.3 Stack section: before noise attenuation (left), after (middle) and difference (right).
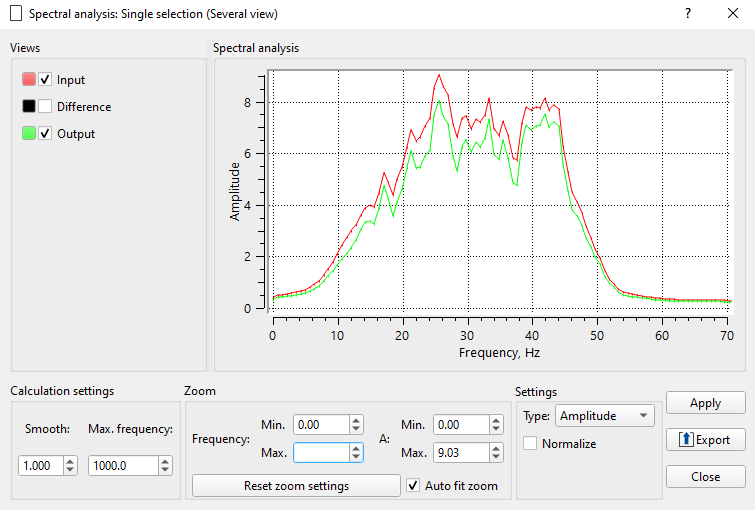
Fig.3 Amplitude frequency spectrum: before noise attenuation (red), after (green).
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Cadzow, J.A.: Signal enhancement—a composite property mapping algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. (1988)
Gillard, J.: Cadzow’s basic algorithm, alternating projections and singular spectrum analysis.
 If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com
If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com