Converting magnetic tape recorded data format SEG-2 to SEG-Y format.
![]()
![]()
What Is SEG-B?
SEG-B is an early digital seismic data format developed by the Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) in the 1960s–70s for magnetic tape recording of seismic traces.It was one of the first standardized formats used for exchanging seismic data between acquisition and processing systems — the predecessor to the modern SEG-Y format (introduced in 1975).
Basic Characteristics of SEG-B
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
Medium |
Magnetic tape (9-track reel) |
Structure |
Sequential blocks (records) containing binary data |
Header Type |
Binary (no standardized ASCII textual header) |
Data Type |
Usually integer samples (12-, 16-, or 24-bit) |
Byte Order |
Big-endian (IBM mainframe convention) |
Record Type |
Each record = 1 seismic trace (header + samples) |
Time Stamp |
Includes shot number, trace number, and time info in header |
Velocity / geometry |
Usually stored separately in navigation or field files |
File Structure (Simplified)
Each SEG-B record consisted of:
1.Record Header – Binary identification info (trace number, sample rate, etc.)
2.Trace Samples – Seismic amplitude values in integer form.
3.End-of-record marker (tape block boundary).
There was no standardized reel header — only per-trace records.This made it hard to merge or interpret without acquisition documentation.
Why SEG-B Became Obsolete
•Lack of human-readable metadata (no textual header).
•Fixed magnetic tape block structure — not compatible with modern disk-based systems.
•Non-standard header definitions between contractors.
•Limited portability and flexibility.
Hence, in 1975, the SEG-Y format was introduced — adding:
•A 3200-byte ASCII textual header,
•A 400-byte binary reel header,
•Fully defined trace headers (240 bytes),
•Support for multiple data types and storage media.
Converting SEG-B → SEG-Y
To migrate legacy SEG-B tapes/files into a modern, readable SEG-Y format without losing any header or trace information.
General Workflow
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
1. Read SEG-B data |
Specialized software reads binary tape blocks, detects record boundaries, and extracts trace samples + headers. |
2. Decode headers |
Parse trace header bytes (shot number, channel, record length, sample rate). |
3. Build new SEG-Y headers |
Create SEG-Y standard headers (textual + binary + 240-byte trace headers) based on SEG-B info. |
4. Reformat sample data |
Convert from 12/16/24-bit integers to standard SEG-Y format (often IEEE floating-point). |
5. Write output SEG-Y file |
Using modern structure — 3200-byte textual header, 400-byte binary header, 240-byte per-trace header, followed by trace samples. |
6. QC verification |
Verify number of traces, sample rate, amplitudes, and timing integrity. |
Why Conversion Is Necessary
•To recover and preserve legacy data recorded in SEG-B format.
•To make data compatible with modern seismic software.
•To standardize metadata (headers, geometry, sample interval).
•To QC and process historical surveys for reprocessing or reimaging.
Key Challenges in Conversion
Issue |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Non-standard SEG-B variations |
Header definitions differ between contractors — need metadata to decode. |
Bit depth variations |
12-bit, 16-bit, or 24-bit integers require specific unpacking. |
Endianness mismatch |
Old IBM big-endian vs modern little-endian systems. |
Missing textual headers |
Must be created manually during conversion. |
Tape read errors |
Physical degradation of old magnetic tapes. |
![]()
![]()
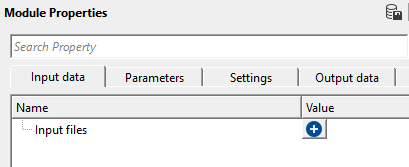
Input files - provide the input SEG-B files
![]()
![]()
Output file - in this section, the user should provide the output file name location and the corresponding trace header formats, type etc.
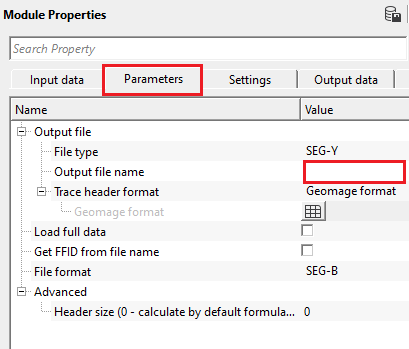
File type { SEG-Y } - choose the output file type from the drop down menu. By default, SEG-Y.
Output file name - provide the output file name.
Trace header format { Geomage format, SegFormat, Seg-Y, rev.1, 2002, Geomage Office Post, Coordinates Only, Constant Elevation, VSP format, teapot_dome_3d, segy_v2, Kingdom format, attaphol, d-001, Test_gom } - choose the SEG-Y trace header format from the drop down menu. By default, Geomage format which is SEG standard rev.1, 2002 format.
Geomage format - this is Geomage internal format which is equivalent to SEG-Y standard rev.1, 2002 format.
Load full data - it will load all the data in the file. By default, FALSE (Unchecked).
Get FFID from file name - extracts the FFID information from the input file name. By default, FALSE (Unchecked).
File format { SEG-B, GSegBSn339 } - select the SEG-B input file format. By default, GSegBSn339
File format - SEG-B - this is the standard SEG-B file format with an extension of .segb
Advanced - this section deals with any additional advanced parameters.
Header size (0 - calculate by default formula) - By default, 0. Specify the header size if the user have this information otherwise it will automatically calculated.
![]()
![]()
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
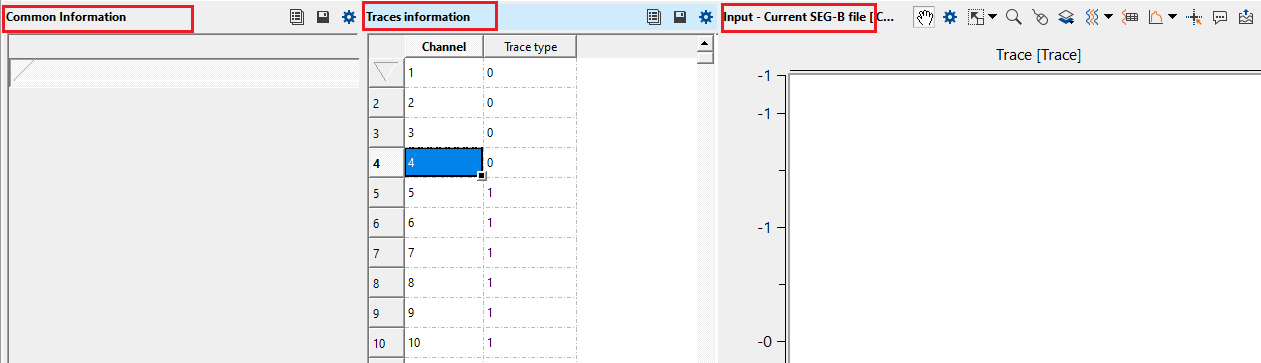
Current SEG-B file - this is an output vista item of current SEG-B file among the Vista items generated by the module.
Current SEG-B trace - one of the vista items and displays the selected/current SEG-B trace
Common Information - displays the information of the file, FFID, no of samples, sample size etc
Traces information - displays the trace information like the FFID and the corresponding trace.
There is no information available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
In this example workflow, we are adding a single SEG-B file. To add any input files, click on ![]() icon. It will open a new window. Click on
icon. It will open a new window. Click on ![]() icon again. It will allows the user to browse and provide the input SEG-B file(s).
icon again. It will allows the user to browse and provide the input SEG-B file(s).
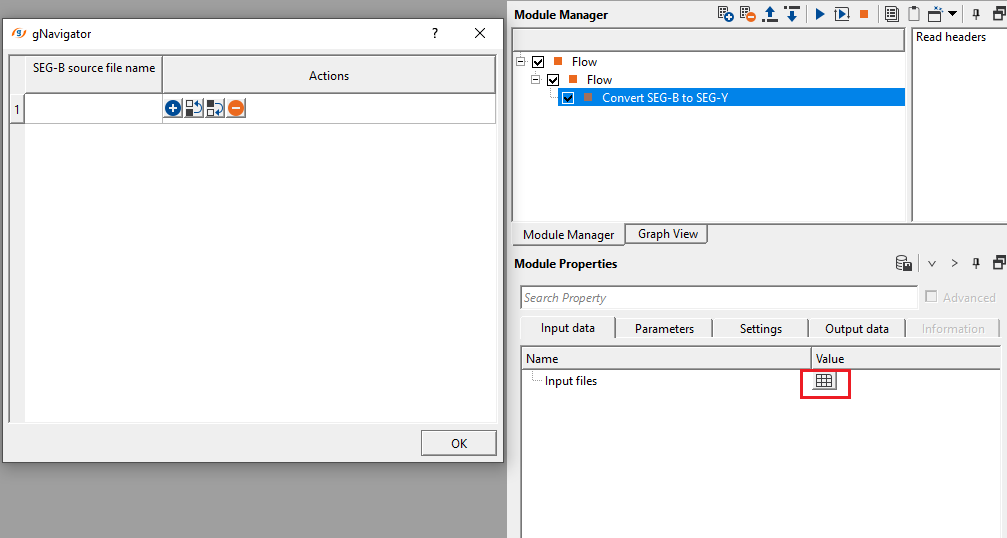
Click on Read headers action item and add Vista items by right clicking on the Convert SEG-B to SEG-Y module and add Vista Groups-> All Group-> In new window.
![]()
![]()
Read headers - this action items allows the user to read the input trace headers. This will generate all the trace headers information that can be displayed as Vista items.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
![]()