Finding the similarities between two seismic wavelets
![]()
![]()
In seismic data processing, correlation refers to a mathematical measure that helps to understand the relationship between two seismic signals over time. The idea is to find similarities in the seismic data, which can be useful for signal enhancement, noise reduction etc.
There are two types of correlations we can discuss about.
1. Cross-Correlation
Cross-correlation can be used to compare the recorded seismic trace with a known reference signal, such as the theoretical source wavelet. By measuring how well the signals matches/correlate over time, we can identify the time shift i.e. lag that best aligns the signals.
Mathematically, if we define the cross-correlation as two functions, where f(t) and g(t) are two functions separated by a time lag Delta T or Tau. If the cross-correlation function is high it means that both the functions f(t) & g(t) are similar with a time lag.
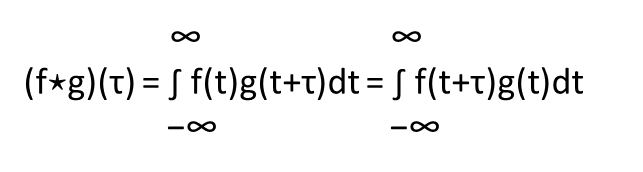
Cross-correlation helps in
•signal enhancement like signal to noise ratio improvement
•time shift estimations
![]()
2. Auto-Correlation
Auto-correlation is the process of correlating a signal with the signal itself. In seismic data, this technique can be used to identify repeating patterns or periodicity in the data. The auto-correlation function may show a peak at certain intervals, indicating recurring patterns in the seismic activity.
Auto-correlation has its maximum when time lag is zero. It Measures the similarity of a signal to itself over different time lags (useful for identifying periodicity in the data).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Input data
Input gather 1 - Provide the input gather that needs to be considered for correlation
Input gather 2 - Provide the second input gather that needs to be considered for correlation
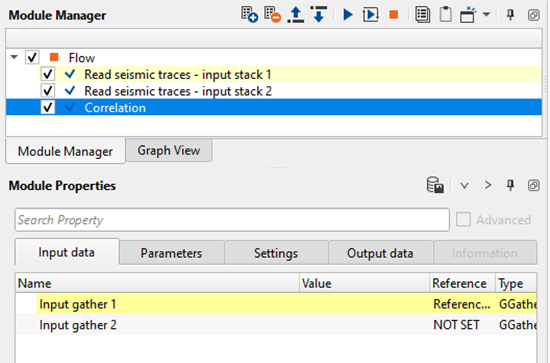
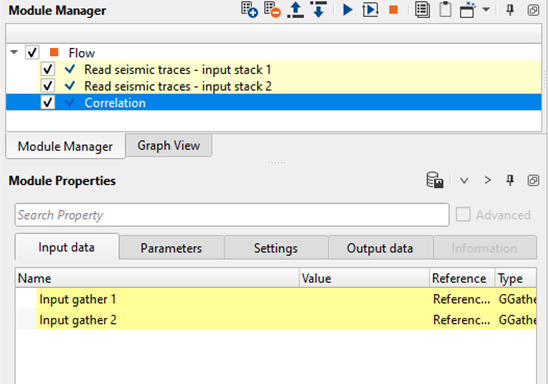
When we use the auto-correlation, we connect/reference to only one input gather. In the above example, we've referenced the input gather 1 to "Read seismic traces - input stack 1". Similarly, if we want to perform the cross-correlation, we'll reference both the input gather 1 and 2.
![]()
![]()
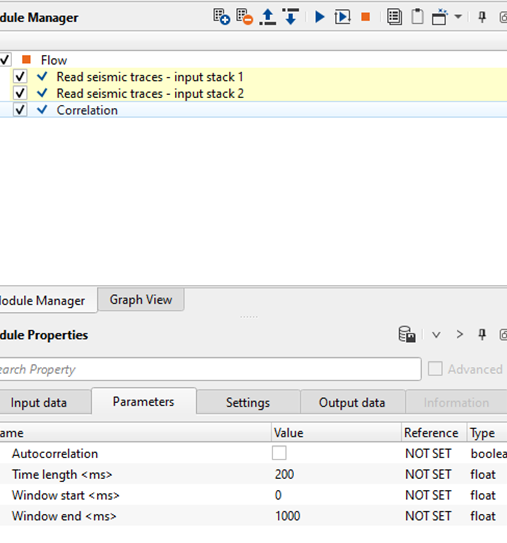
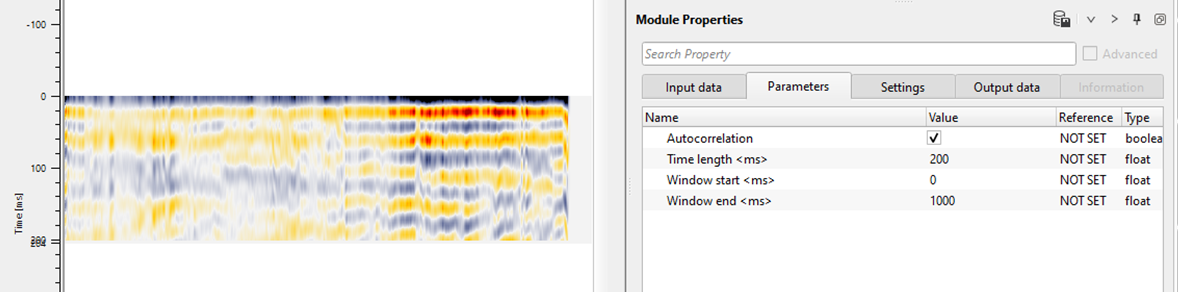
Autocorrelation - By default, Unchecked. If checked this option, it will do the auto-correlation of the same input. When this option is checked, 2nd input gather isn't required.
Time length - Define the time length that will be used for the correlation. This time length parameter displays the correlation output.
Window start - Define the starting time window for the correlation
Window end - Define the ending time window to perform the correlation
![]()
![]()
Skip - By default, No (Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output gather - This module outputs the cross-correlated/auto-correlated gather as an output gather.
![]()
![]()
In this example, we are reading stack sections. Input gather 1 is a denoise stack and Input gather 2 is also a denoise stack with different processing parameters. We would like to see the results of the cross-correlation and auto-correlation of these stacks sections.
After executing the correlation with the above parameters, we generate the Vista items. We'll get the input 1 & input 2 stack displays and Correlation window display. The default display of the correlation is in wiggle mode. The user can change the wiggle mode to density mode by changing it from the View/show properties of the Correlation window.
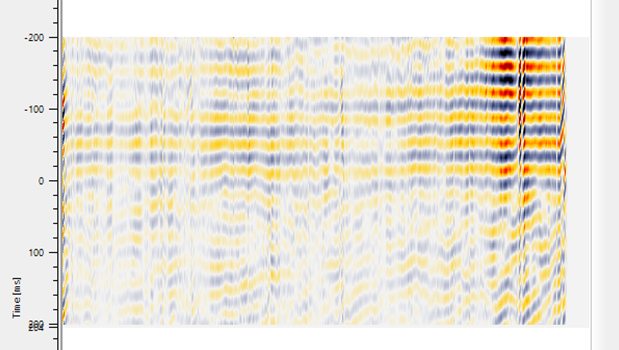
For the same stack section, if we want to perform the auto-correlation with the same parameters, we need to turn on/check the Auto-correlation option in the parameters. As mentioned earlier, for auto-correlation, we don't require the 2nd input gather.
Auto-correlation helps in finding out the signal response at the different time lags. It is helpful in designing the deconvolution parameters for any water bottom ringing etc.
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module. So the user can ignore this part.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *