Removing the seismic wavelet effects by using Wiener Deconvolution
![]()
![]()
Seismic wavelet undergoes many changes when it first started from the seismic energy source to recorded at the receivers. The wavelet shape changes due to attenuation, dispersion and geological changes like lithology etc. The objective of any deconvolution method is to improve the resolution of the seismic wavelet.
Seismic trace/wavelet is nothing but convolution of source wavelet with reflectivity. This also includes some noise component. As the source wavelet propagates through the sub-surface, it loses the energy and the higher frequencies (travel faster) get attenuated fast compared to the lower frequencies. To restore the reflectivity, we need to design a Wiener filter which minimizes the difference between the estimated reflectivity and original reflectivity.
Where:
•S(t) - seismic trace at time t
•W(t) - seismic wavelet at time t
•R(t) - seismic reflectivity at time t
•N(t) - noise at time t
•* - convolution
Wiener filter was named after Norbert Wiener. Wiener filter tries to minimize the difference between the original seismic signal reflectivity to estimated seismic signal reflectivity. This is called as Mean Square Error or MSE.
Estimated seismic reflectivity is achieved by convolving the seismic trace S(t) with Wiener filter F(t)
When the data is transformed from time domain to frequency domain, convolution becomes multiplication. So the Wiener filter F(f) becomes
Where :
•W(f) - seismic wavelet at frequency f
•S(f) - seismic trace at frequency f
•N(f) - noise at frequency f
•D(f) - density of reflectivity at frequency f
How does Wiener Deconvolution works?
1. Estimate the seismic wavelet S(t) from the input seismic data.
2. Do auto-correlation of seismic wavelet W(t) & seismic trace S(t).
3. Design the Wiener filter W(t) using Wiener - Hopf equation.
4. Convolve the seismic trace S(t) with Wiener filter F(t) to get the estimated reflectivity
Input seismic traces may be zero or minimum phase. According to parameters “Time window” and “Trace window” - traces selected (TT window), which converted into frequency domain (F-X). Then the procedure computes average frequency spectrum for defined TT window and deconvolution operator is computed by the below formula.
Deconvolution operator applying for selected time interval and applying band pass filter to each time interval (for high and low frequency artifacts attenuation). Then all filtered time intervals merged with taper zone. Taper zone equals ¼ of time window interval.
![]()
![]()
Input DataItem
Input gather - connect/reference to the output gather. In case it is inside the Seismic loop module, it will automatically connect/reference to the previous modules output gather.
![]()
![]()
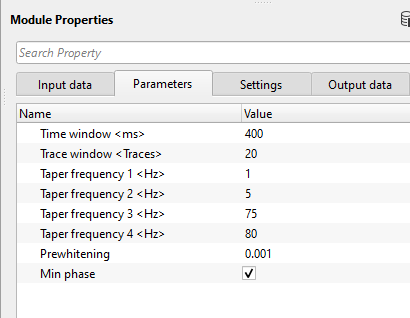
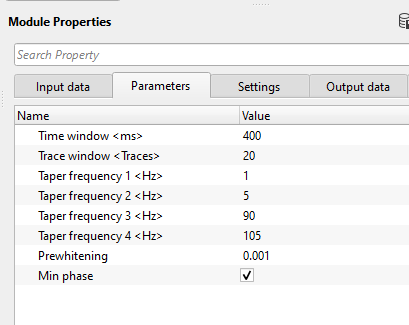
Time window - Time window for Wiener filter calculation. This is also considered as Deconvolution Operator.
Trace window - Trace window for Wiener filter calculation. Specify the number of traces participating in the Wiener filter calculation.
Taper frequency 1 - Frequency taper is applied to each time window/interval to attenuate/filter any artifacts after the application of deconvolution filter. Specify the lower frequency filter taper. Below this value, all frequencies are nullified or considered as zero.
Taper frequency 2 - specify the filter to be considered. All frequencies above this value are passed.
Taper frequency 3 - specify the higher frequency to be considered. All frequencies inside this value are passed.
Taper frequency 4 - specify the higher frequency value. All frequencies beyond this will be nullified.
Prewhitening - specify the % while noise added to the data to stabilize the spectrum.
Min phase - By default, TRUE (Checked). Deconvolution expects the input data in minimum phase (the reason being is that the seismic source generates the energy and the seismic wavelet gets it's maximum energy/peak at the beginning and it gradually decreases. So, it is easier for the deconvolution operator to work on the minimum phase wavelet).
![]()
![]()
Auto-connection - By default, TRUE(Checked).It will automatically connects to the next module. To avoid auto-connect, the user should uncheck this option.
Bad data values option { Fix, Notify, Continue } - This is applicable whenever there is a bad value or NaN (Not a Number) in the data. By default, Notify. While testing, it is good to opt as Notify option. Once we understand the root cause of it, the user can either choose the option Fix or Continue. In this way, the job won't stop/fail during the production.
Notify - It will notify the issue if there are any bad values or NaN. This is halt the workflow execution.
Fix - It will fix the bad values and continue executing the workflow.
Continue - This option will continue the execution of the workflow however if there are any bad values or NaN, it won't fix it.
Calculate difference - This option creates the difference display gather between input and output gathers. By default Unchecked. To create a difference, check the option.
Number of threads - One less than total no of nodes/threads to execute a job in multi-thread mode. Limit number of threads on main machine.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output DataItem
Output gather - generates Wiener filter applied deconvolution output gather.
Gather of difference - generates the difference display gather between input and output gathers.
There is no information available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
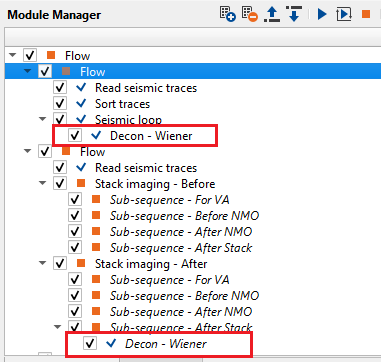
In this example workflow, the user can test different Decon Wiener filter parameters and QC the results.
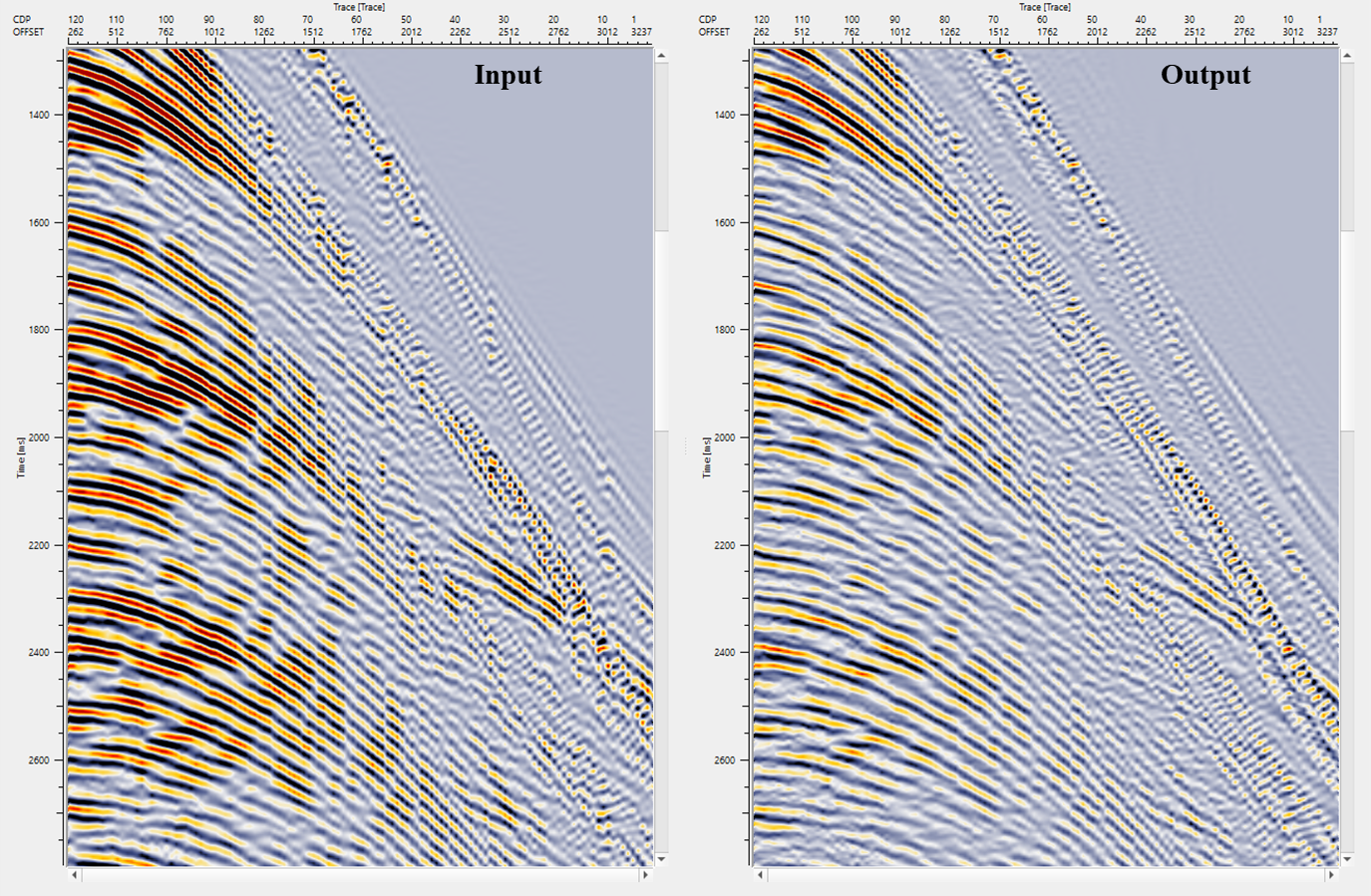
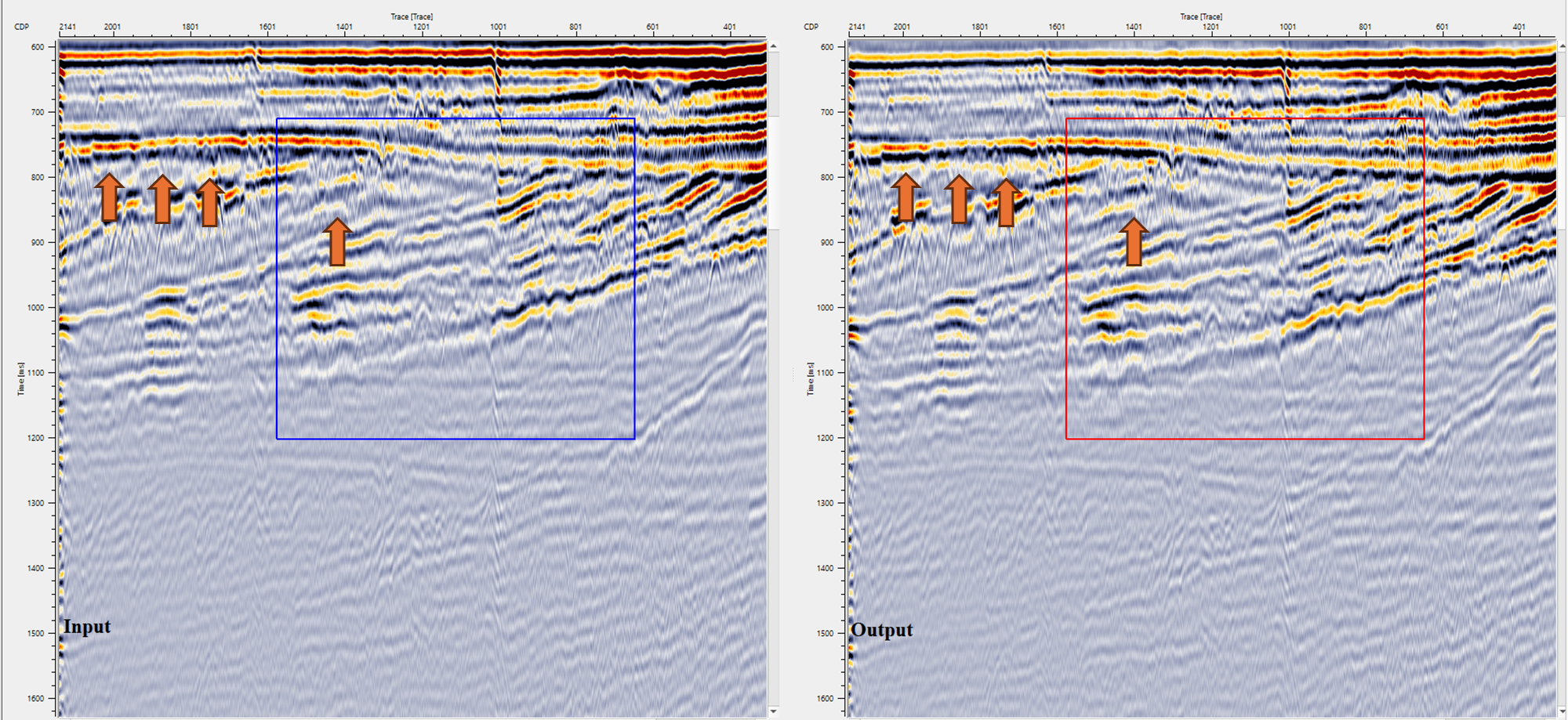
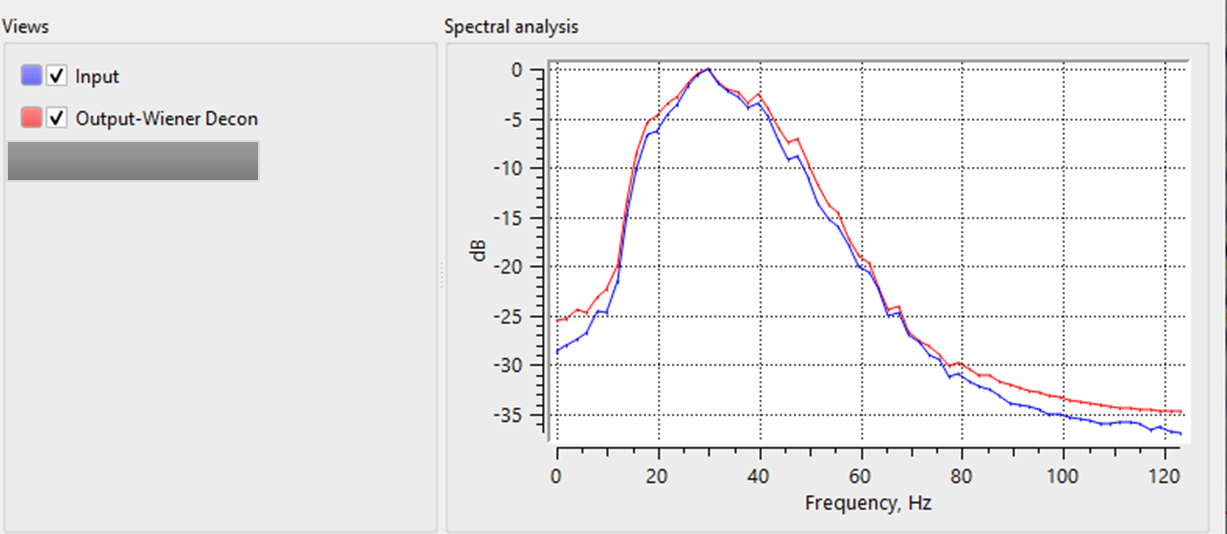
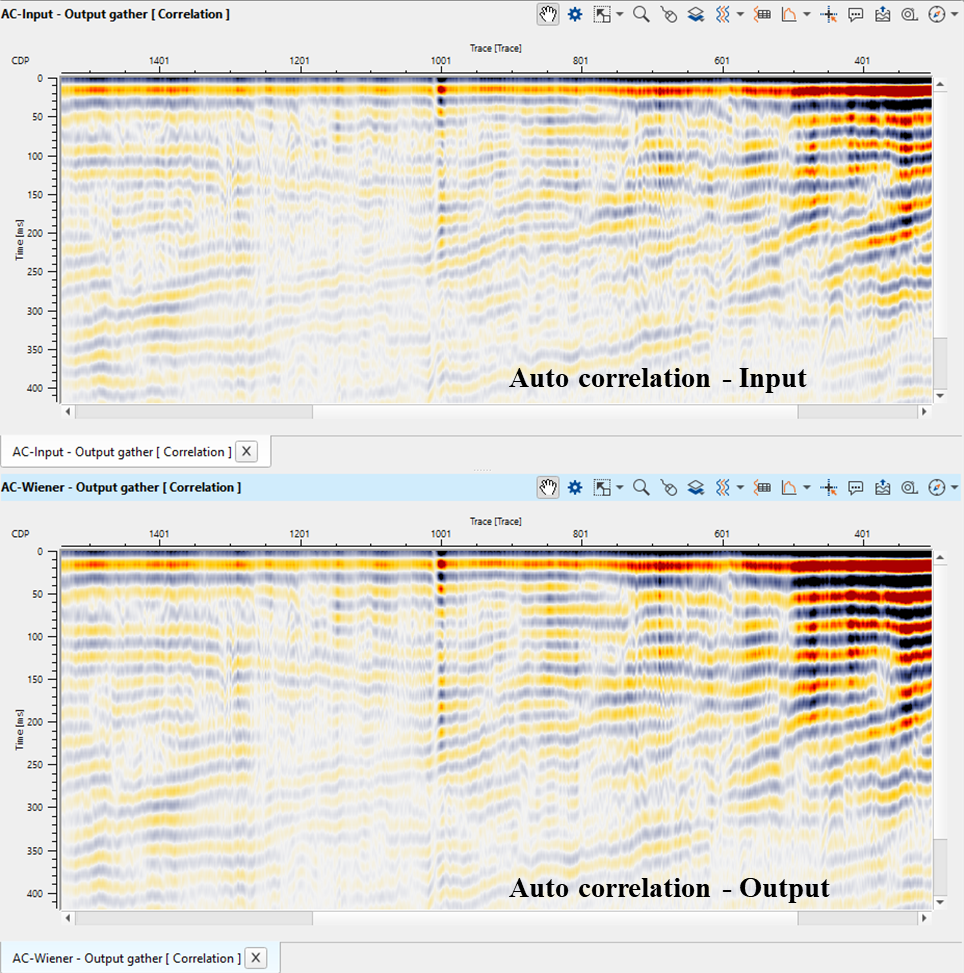
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *