Improving seismic resolution by Gabor Deconvolution
![]()
![]()
Gabor deconvolution is used when the seismic wavelet is not stable. In case of the Wiener deconvolution, it works on the stable or stationary (where frequency won't changes with the time in the Fourier transformation) wavelets and it may not work well with the attenuation. In contrast, Gabor deconvolution works with the non-stationary wavelets with the consideration of the attenuation. It is a time-frequency domain method that uses the Gabor transformation to analyze the data in both time and frequency domains.
Gabor transform decomposes the seismic signal into frequency constituents and its variations over the time. It is performed by applying the Gaussian window to the seismic signal and computing the Fourier transformation of the windowed signal. Generally, we use the Gaussian half window to analyze the seismic signal locally in time.
Gabor transformation of a seismic signal can be written as
Where
•s(t) - Input seismic signal at time t
•g(t-t') - Gaussian window centered at time t'
•f - frequency
•t' - time shift
How does Gabor transformation works?
1.Select the desired Gaussian window (half window) for better time and frequency resolution
2.Apply the Gaussian window by multiplying the signal s(t) with the Gaussian window g(t-t') centered at time t'.
3.Computed the Fourier transformation of the windowed signal. This gives frequency content at time t'.
4.Shift the window along the time axis to get the time-frequency representation. Repeat this for all time shifts.
In Gabor deconvolution, seismic trace is represented by time - frequency domain. Deconvolution is performed by multiplying the Gabor transformation of seismic signal by Gabor transformation of seismic wavelet.
Where:
• - Gabor transform of the seismic signal
• - Gabor transform of the seismic wavelet
• - Estimated reflectivity in time-frequency domain
Final reflectivity series is obtained by applying inverse Gabor transform to
How does Gabor Deconvolution works?
1.Compute the Gabor transform of the seismic signal
2.Estimate the seismic wavelet first and compute the Gabor transform of the wavelet
3.Divide the Gabor transform of seismic signal by Gabor transform of wavelet. This gives the estimated reflectivity.
4.Apply the inverse Gabor transform to the estimated reflectivity to get the final reflectivity series.
![]()
![]()
Input DataItem
Input gather - connect/reference to the output gather. In case it is inside the Seismic loop module, it will automatically connect/reference to the previous modules output gather.
![]()
![]()
Gauss half window - It is a one sided window that is used for localizing time-frequency analysis. In the Gabor transformation, Gaussian half window is used to analyze a signal locally in time.
Step window - specify the time window to perform the Gabor transformation within the user specified step size. This will determines how much the window should be shifted along the time axis to perform the Gabor transformation.
Minimum frequency - specify the minimum/lowest frequency used in the Gabor transformation.
Maximum frequency - specify the maximum/highest frequency used in the Gabor transformation.
Smooth spectrum frequency - specify the frequency value to smooth the spectrum of the amplitude of the seismic trace.
Prewhitening - specify the % white noise added to the data to stabilize the deconvolution process.
Min phase - By default, TRUE (Checked). Deconvolution expects the input data in minimum phase (the reason being is that the seismic source generates the energy and the seismic wavelet gets it's maximum energy/peak at the beginning and it gradually decreases. So, it is easier for the deconvolution operator to work on the minimum phase wavelet).
![]()
![]()
Auto-connection - By default, TRUE(Checked).It will automatically connects to the next module. To avoid auto-connect, the user should uncheck this option.
Bad data values option { Fix, Notify, Continue } - This is applicable whenever there is a bad value or NaN (Not a Number) in the data. By default, Notify. While testing, it is good to opt as Notify option. Once we understand the root cause of it, the user can either choose the option Fix or Continue. In this way, the job won't stop/fail during the production.
Notify - It will notify the issue if there are any bad values or NaN. This is halt the workflow execution.
Fix - It will fix the bad values and continue executing the workflow.
Continue - This option will continue the execution of the workflow however if there are any bad values or NaN, it won't fix it.
Calculate difference - This option creates the difference display gather between input and output gathers. By default Unchecked. To create a difference, check the option.
Number of threads - One less than total no of nodes/threads to execute a job in multi-thread mode. Limit number of threads on main machine.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output DataItem
Output gather - generates Gabon deconvolution filter applied deconvolution output gather.
Gather of difference - generates the difference display gather between input and output gathers.
There is no information available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
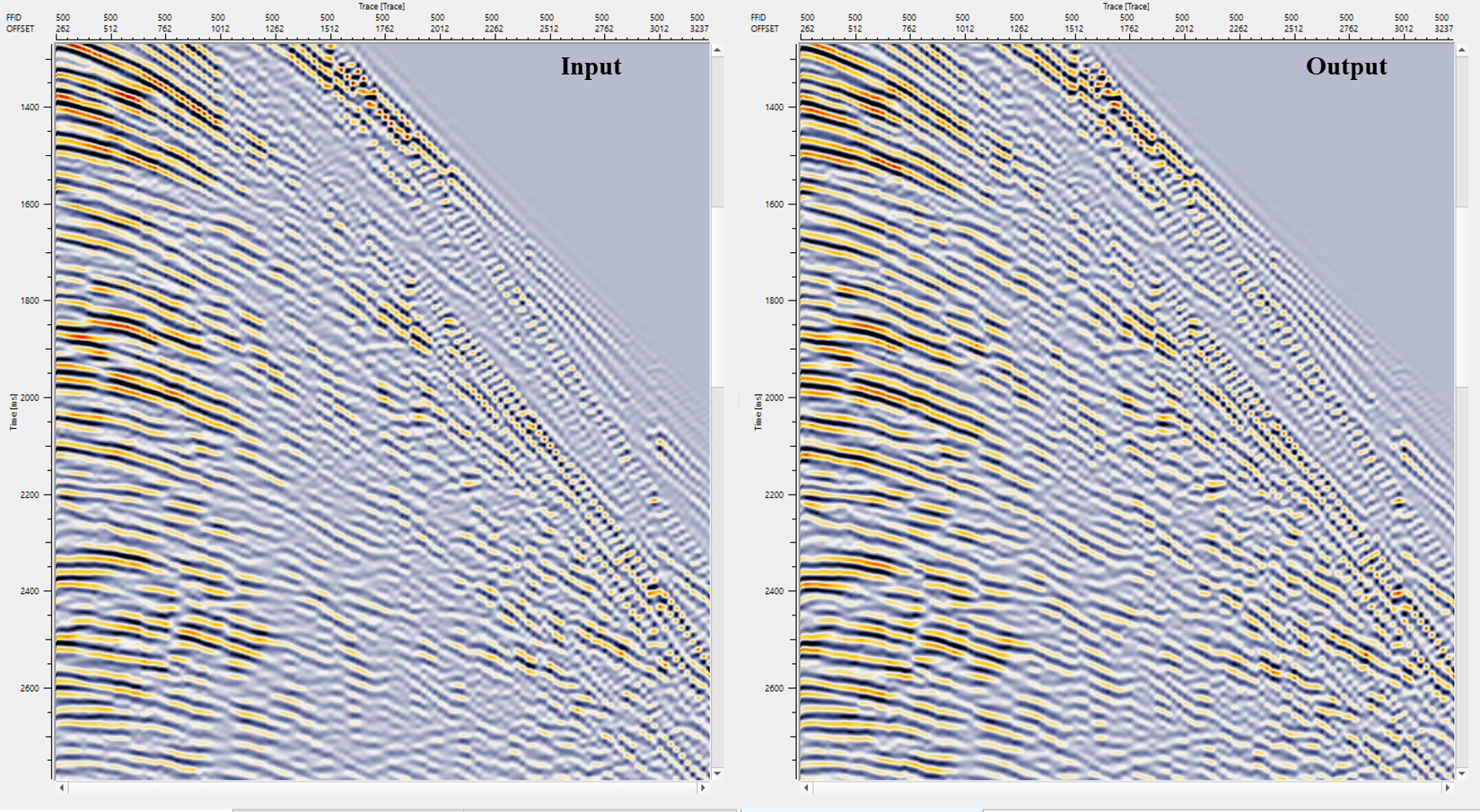
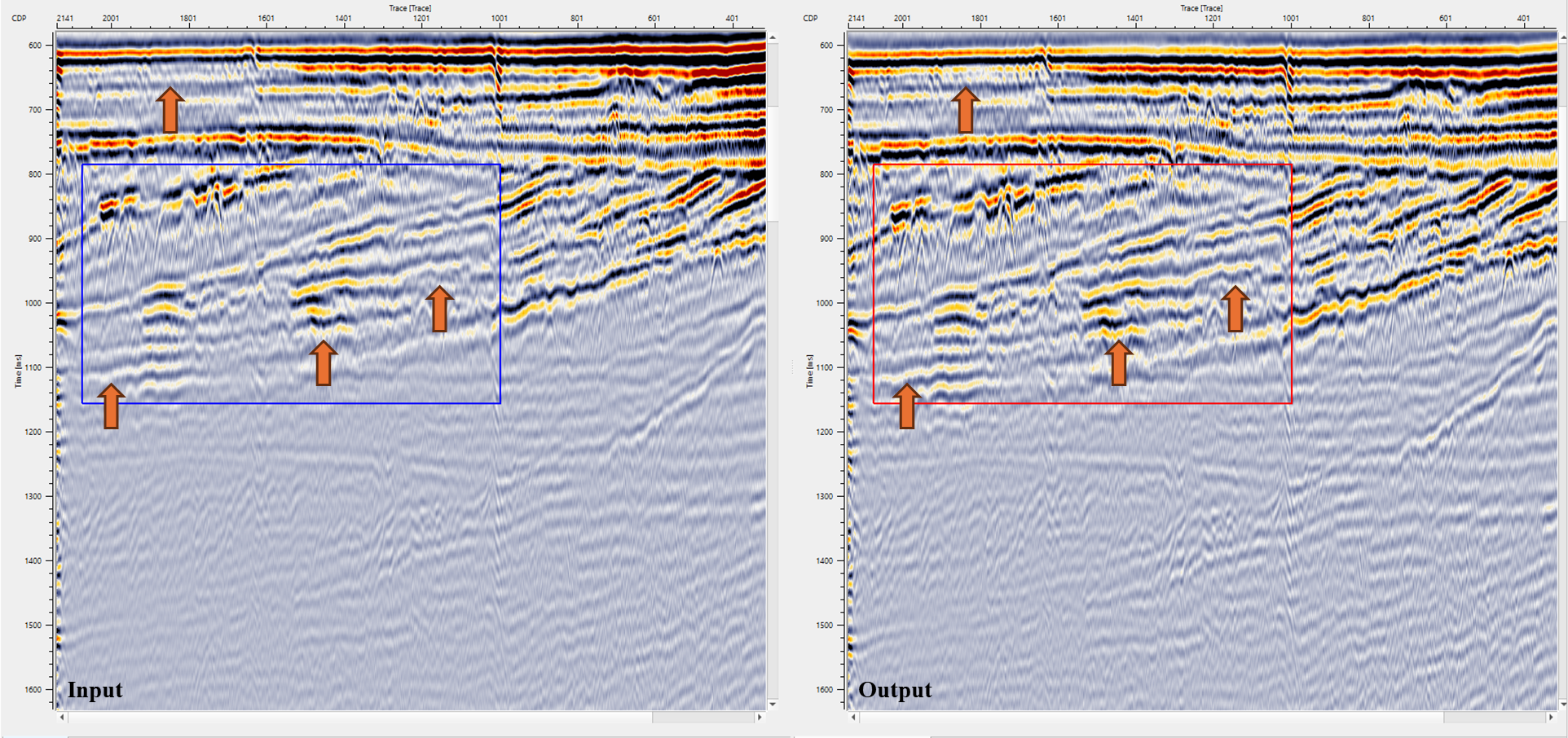
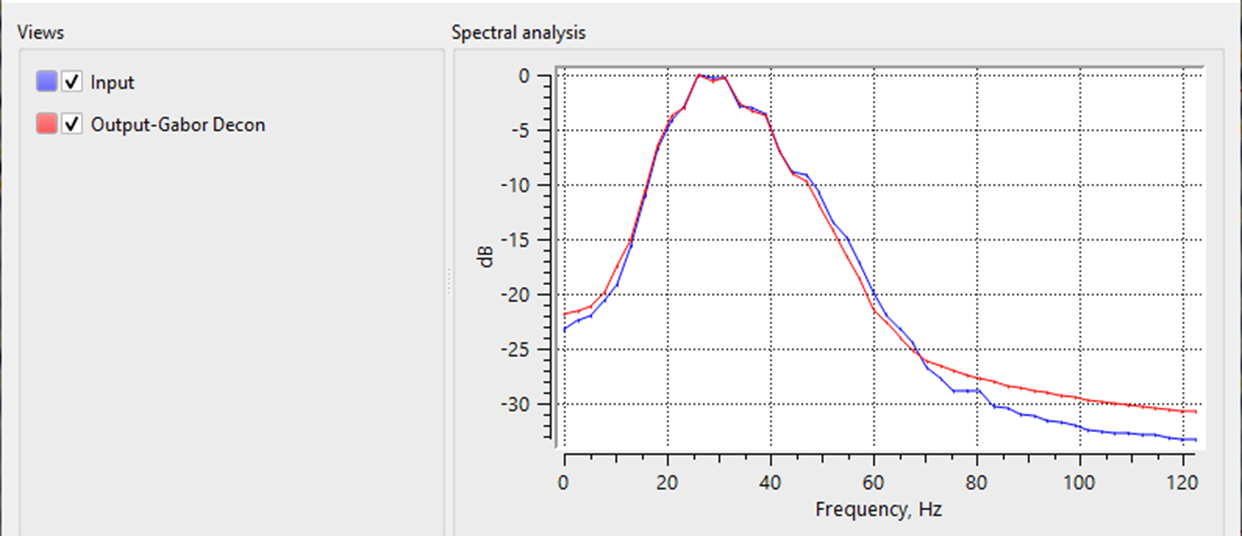
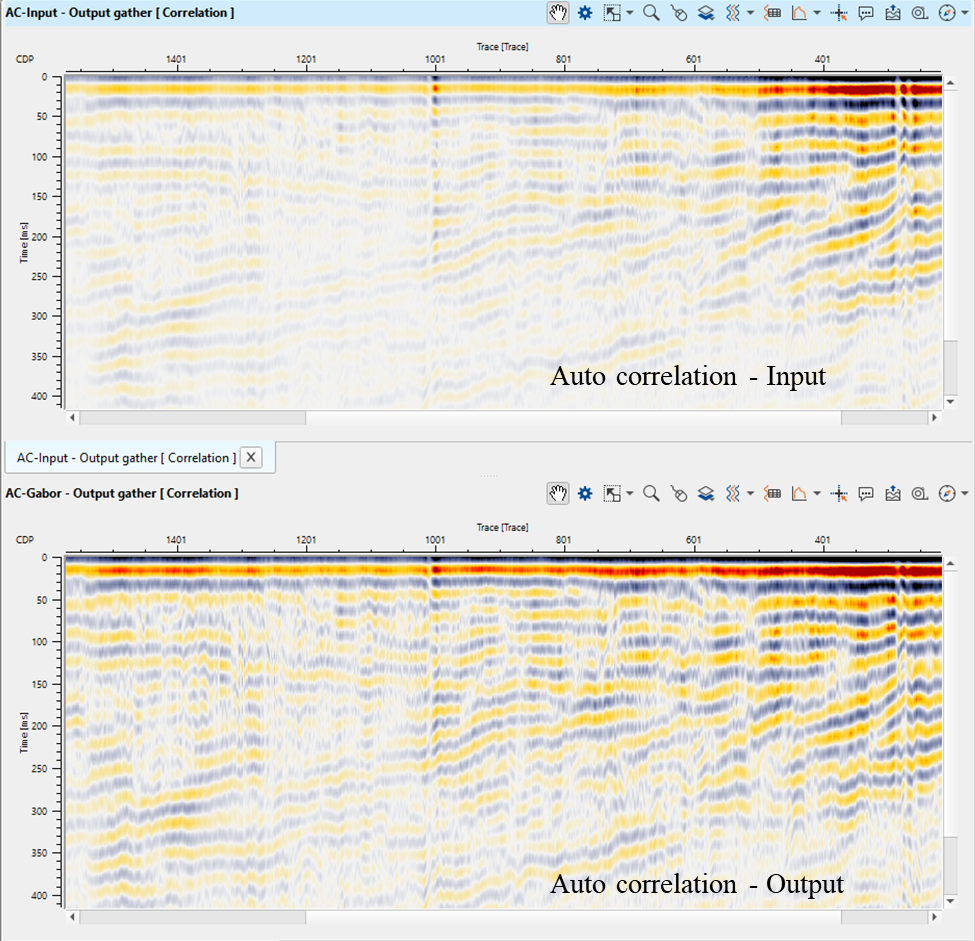
In this example workflow, we are using Gabor Deconvolution to improve the resolution of the seismic traces.
During the parameter testing, look into the Prewhitening % values. Unlike the Decon Wiener where the % while noise added to the seismic trace in Decon Gabor is on the higher side.
![]()
![]()
There are no action items available for this module so the user can ignore it.
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
![]()