This module is used to calculate velocity semblance and velocity picking.
![]()
![]()
Velocity analysis is a fundamental step in seismic data processing used to estimate the subsurface velocity structure. These estimated velocities allow proper Normal Moveout (NMO) correction, improved stacking, enhanced signal-to-noise ratio, and form the foundation for building velocity models used in migration and inversion.
The main objective of velocity analysis is to identify the velocity that best aligns reflection events across all offsets in a Common Midpoint (CMP) gather. When the correct velocity is applied, reflection events become flat, resulting in high coherence on semblance or other velocity scanning attributes.
Concept of Velocity Scanning
During velocity analysis, a range of trial velocities is applied to a CMP gather. For each trial velocity:
1.NMO correction is applied.
2.The data are checked for how well the reflection energy aligns.
3.A coherence measure (such as semblance) quantifies the alignment.
4.The results are displayed on a velocity spectrum or semblance panel.
High semblance values indicate that seismic events are well aligned for that velocity and time, meaning it is a good estimate of the subsurface velocity at that reflector depth.
Semblance as a Coherence Measure
Semblance is the most widely used indicator for velocity picking. It measures the similarity of waveforms across traces after NMO correction. When the correct velocity is used, aligned waveforms produce high semblance values. Semblance can be enhanced using smoothing, weighting, or similarity measures to reduce noise and increase stability.
Velocity Picking
Velocity picks are selected manually or automatically from the semblance panel. These picks are interpolated to build a velocity function that is then used for:
•NMO correction
•Stacking
•Migration
•Depth conversion
Accurate velocity analysis directly impacts the quality of stacked and migrated images.
![]()
![]()
Velocity picking -
Input gather - connect/reference the Output gather. It collects the trace headers information from the input gather.
Velocity picking item - connect/reference to the velocity picking item (internal velocity).
![]()
![]()
Start velocity - the lowest trial velocity used in the velocity scan. It sets the lower bound of the velocity range to be tested, ensuring shallow, low-velocity layers can be evaluated.
End velocity - the highest trial velocity for the scan. This ensures deeper or high-velocity layers (such as carbonates or basement) are included in the search.
Step velocity - specifies the increment between consecutive trial velocities. Smaller steps give finer resolution but increase computation time; larger steps reduce resolution but speed up processing.
Semblance smooth window - smoothing operator applied over time and/or offset to stabilize semblance values. It reduces noise, enhances coherent events, and produces cleaner semblance panels for easier picking.
Stretch Factor - controls the allowable level of NMO stretch, which occurs at far offsets or shallow times. Samples exceeding the stretch limit may be muted or downweighted to prevent distortion in semblance and stacked data.
Normalization window - defines a time window over which amplitudes are normalized for semblance calculation. This ensures that amplitude variations do not dominate the coherence measure, making semblance more reliable and stable.
Real time NMO applying - enables the software to apply NMO correction dynamically during scanning rather than relying on pre-corrected gathers. This ensures each trial velocity is evaluated accurately and independently.
Surface velocity V0 - starting near-surface reference velocity used in moveout calculations and as a baseline for shallow events. It can help stabilize the velocity spectrum by anchoring early-time velocity behavior.
Weighted semblance { None, Weighted, Similarity-weighted } -
•None: Standard semblance without weighting.
•Weighted: Amplitude-based weighting improves robustness in noisy gathers.
•Similarity-weighted: Enhances semblance by prioritizing waveform similarity rather than just energy alignment, useful in complex or noisy areas.
Weight power - defines how strongly the selected weighting scheme influences the semblance calculation. Higher power increases the effect of weights, sharpening peaks but possibly suppressing weaker events.
![]()
![]()
Number of threads - One less than total no of nodes/threads to execute a job in multi-thread mode. Limit number of threads on main machine.
Skip - By default, FALSE(Unchecked). This option helps to bypass the module from the workflow.
![]()
![]()
Output Vrms gather - output RMS velocity gather as an output gather.
Output NMO applied gather - outputs NMO corrected gather as an output gather.
There is no information available for this module.
![]()
![]()
In this example workflow, we are calculating the velocity semblance and picking the velocities of a 2D line.
We read an internal seismic data and sort the data into CDP - OFFSET combination. Inside the Velocity analysis module, we provide the corresponding parameters for velocity semblance calculation. Also, we can opt for Real time NMO application so that the user can look into the gather changes as the velocity picking progresses.
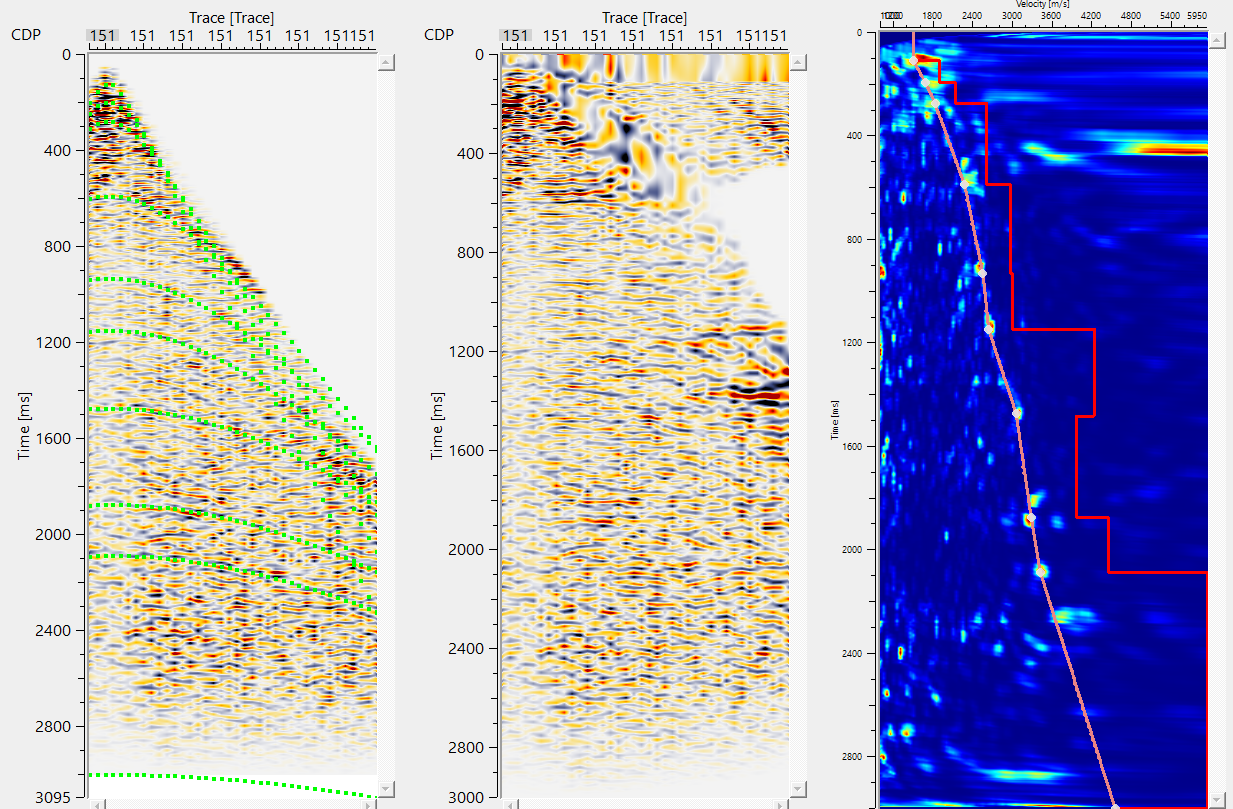
To pick velocities, make a simple click with LMB (MB1) on the Velocity analysis window. A white dot appear(yellow circle). Along with it a brown color line appears(pointed out with a yellow straight line noted as Curve in the View properties). Also, a red line appears which is known as interval velocity line(Purple straight line noted as Interval velocity in View properties).
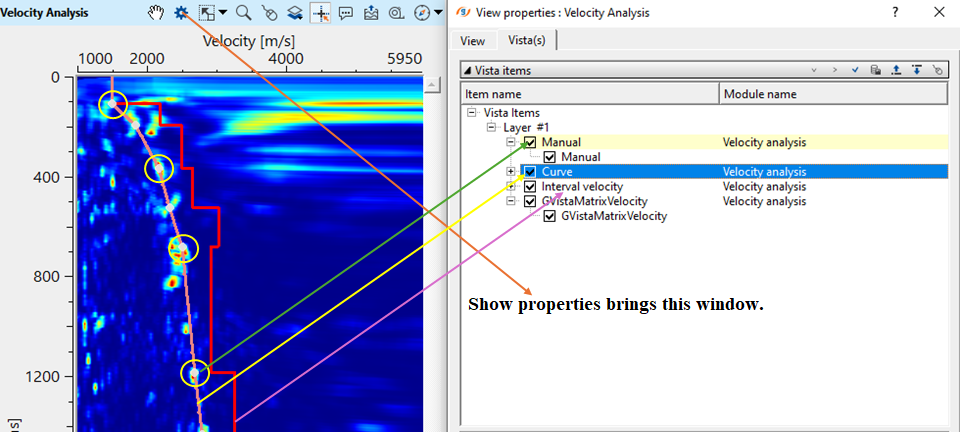
Likewise, we've Input gather with time arrival graphs & Output NMO Seismogram displays/Vista items of Velocity Analysis module.
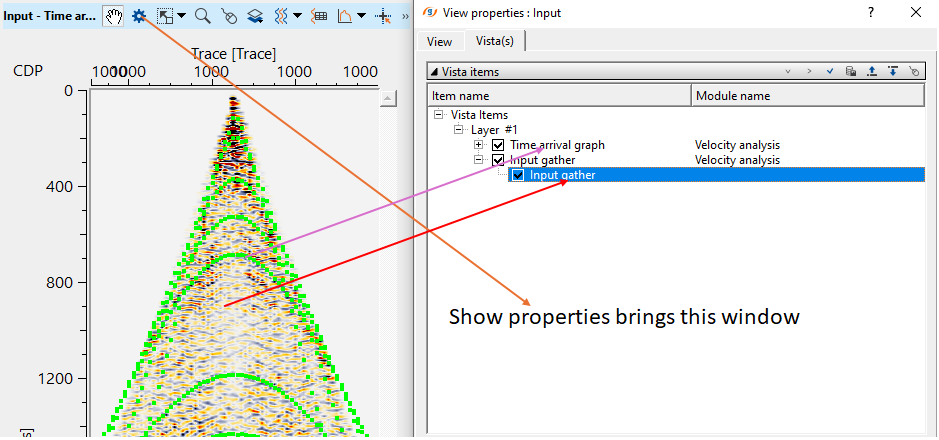
In the above image, we've Input gather (Before NMO, as marked by a red straight line). Over the input gather, we've dotted green curves appears. These are the automatically calculated time arrival graphs on the input gather(marked as a purple straight line).
Likewise, we'll have Output NMO gather as a vista item from Velocity Analysis module.
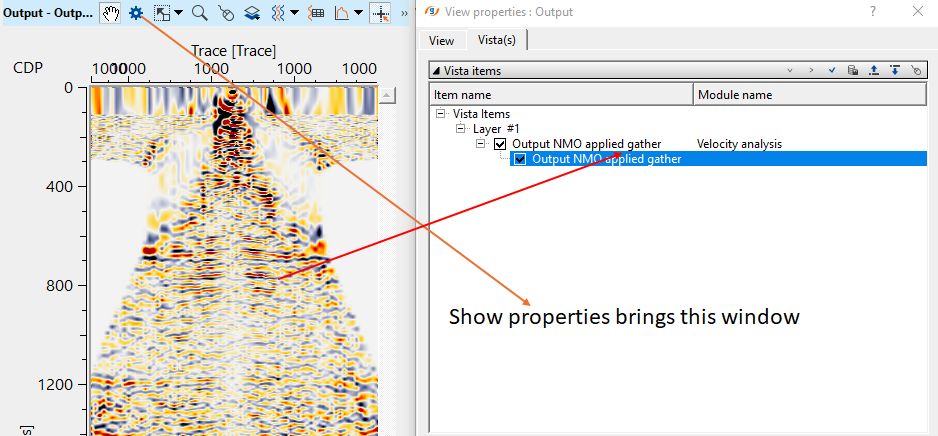
Output NMO Applied gather is marked as a red straight line. Also, we've Location map as a vista item. In the location map, whenever the user makes a velocity pick, it will display the picked velocity locations (a green dot circled in blue as shown in the below) appears.
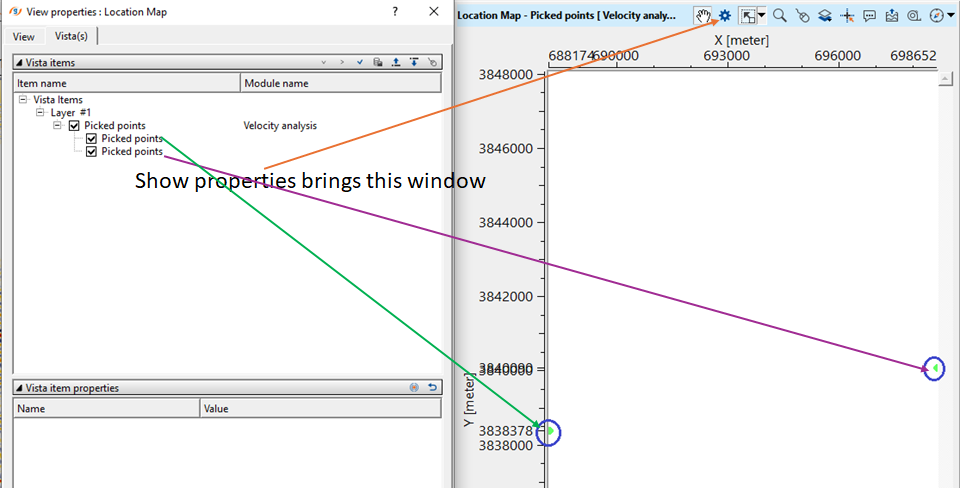
In this way, the user can pick the velocities by using Velocity Analysis module.
![]()
![]()
Clear all picking - this actions allows the user to clear all the velocity picks.
Load picking - this allows the user to load any velocity picks by providing a file.
Save picking - this allows the user to save the current velocity picks into an internal format file (.corr).
![]()
![]()
YouTube video lesson, click here to open [VIDEO IN PROCESS...]
![]()
![]()
Yilmaz. O., 1987, Seismic data processing: Society of Exploration Geophysicist
 * * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *
* * * If you have any questions, please send an e-mail to: support@geomage.com * * *