3D View is a window that allows users to operate and visualize any geophysical and geological data, such as seismic volumes, well data, polygons, grids, horizons, maps and faults, in a 3D perspective.
To create seismic section view go to the Views bar on the Ribbon bar and:
to create view in time domain open Time tab and select 3D view:
to create view in depth domain open Depth tab and choose between views: 2D line (for 2D data), 3D inline/crossline (for 3D data) or arbitrary line (for both 2D and 3D):
g-Space provides a clear distinction between time and depth domains, organizing Horizons, Faults, and Maps into dedicated folders for each.
For 3D visualization, g-Space offers a feature that allows time-domain data to be displayed within the 3D depth view using the current velocity model. This is especially useful during interpretation, as it enables reviewing results in time without requiring full data conversion to the depth domain.
In order to allow 3D view objects drawing, the user should adjust the Performance section found under Module properties panel.
The main objective of these parameters is to optimize the performance of g-Space by unchecking them when the 3D view is not required. When more features are needed in the 3D view, the corresponding checkboxes should be selected.
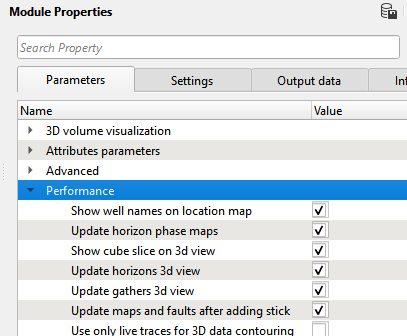
Show well names on location map Displays all well names on the location map when checked.
Update horizon phase maps Automatically refreshes horizon phase maps based on changes in horizon data.
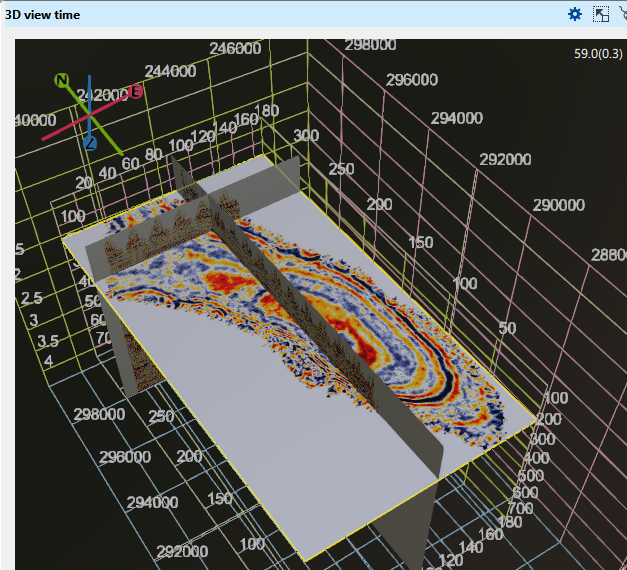
Show cube slice on 3d view Enables viewing a time/depth slice of the 3D volume when checked.
Update horizons 3d view Updates the 3D horizon view whenever changes are made to existing horizons (e.g., picking, adding new horizons).
Update gathers 3d view Updates the 3D gathers view when 2D lines are added or removed.
Update maps and faults after adding stick Automatically recreates the grid map of horizons and updates fault sticks when new fault sticks are added.
Use only live traces for 3D data contouring By default unchecked. When checked, only live traces are used for creating contour maps.
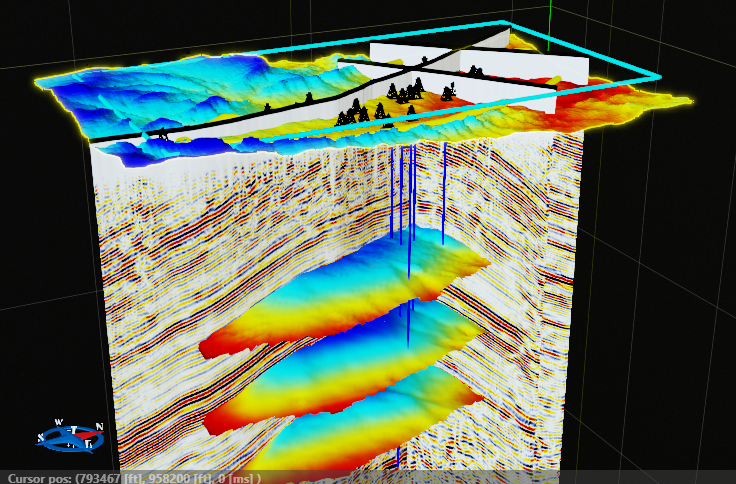
Displaying 3D volume
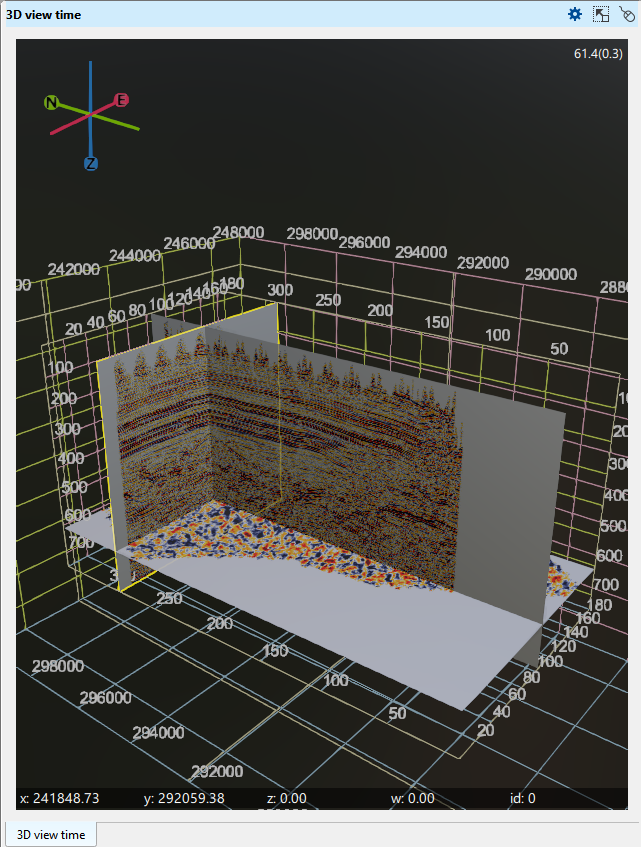
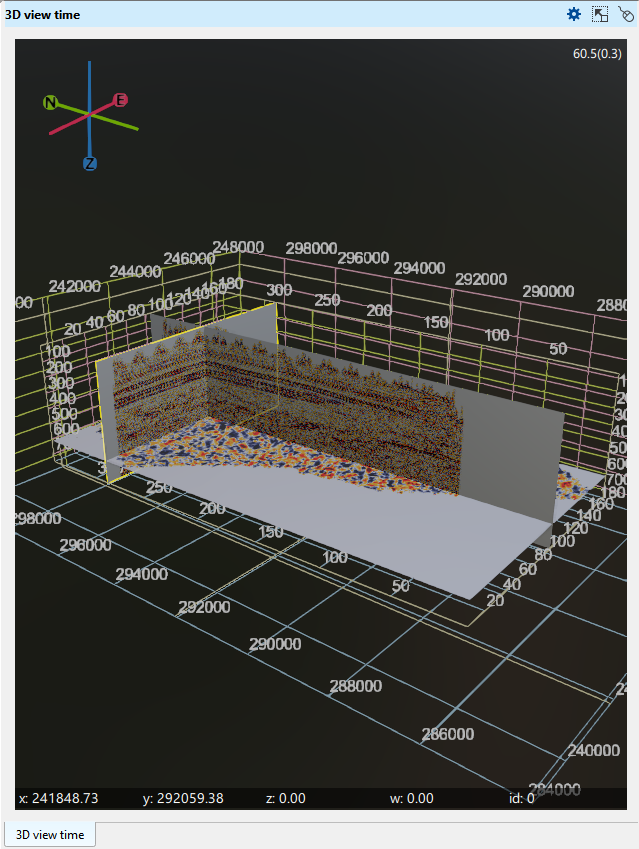
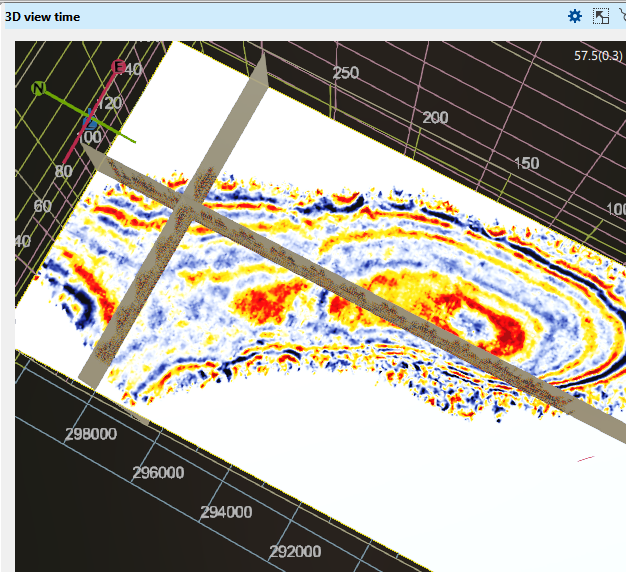
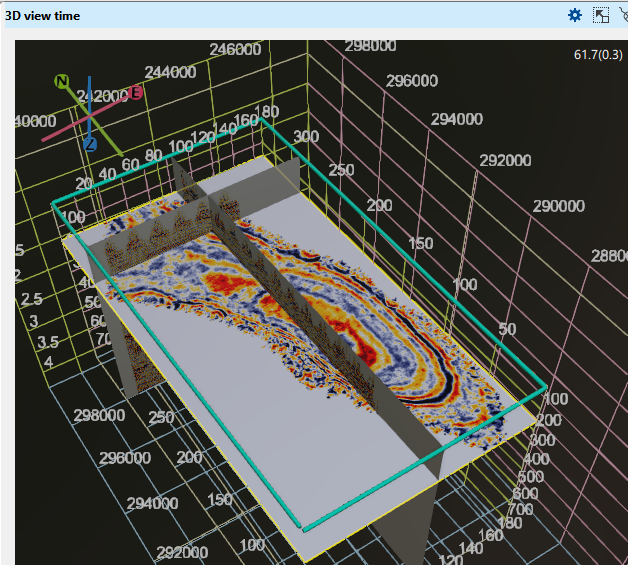
On the picture a few 2D lines, 3D volume, an arbitrary line, time slice, a topography map and wells are displayed on Time 3D view.
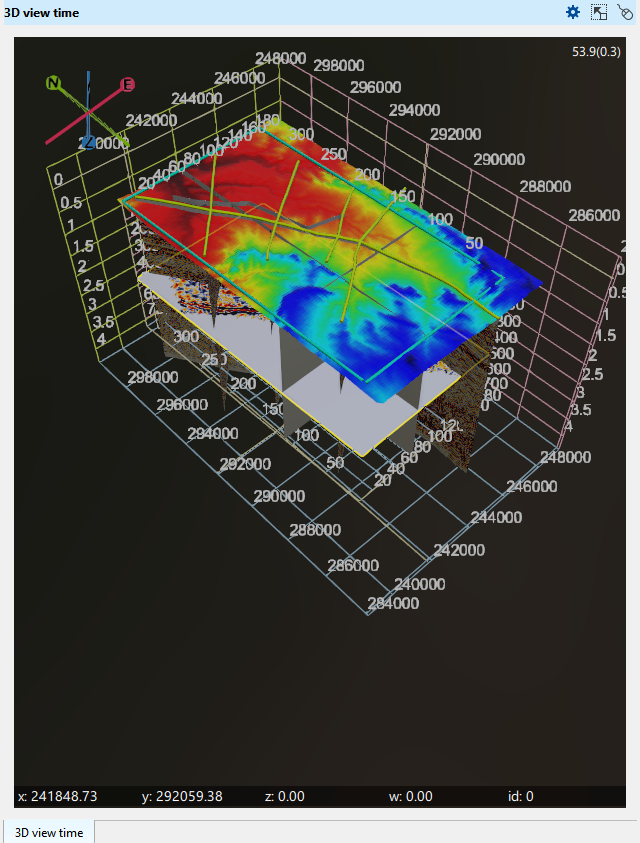
At the bottom of the display, the X, Y, and Z axes are shown, displaying the mouse position and its corresponding values. In the top right corner, the FPS (frames per second) value is displayed.
Vertical scale
In 3D view, two vertical scales exist. One is inside the volume and other is outside the volume. These two vertical scales shows us two different set of values.
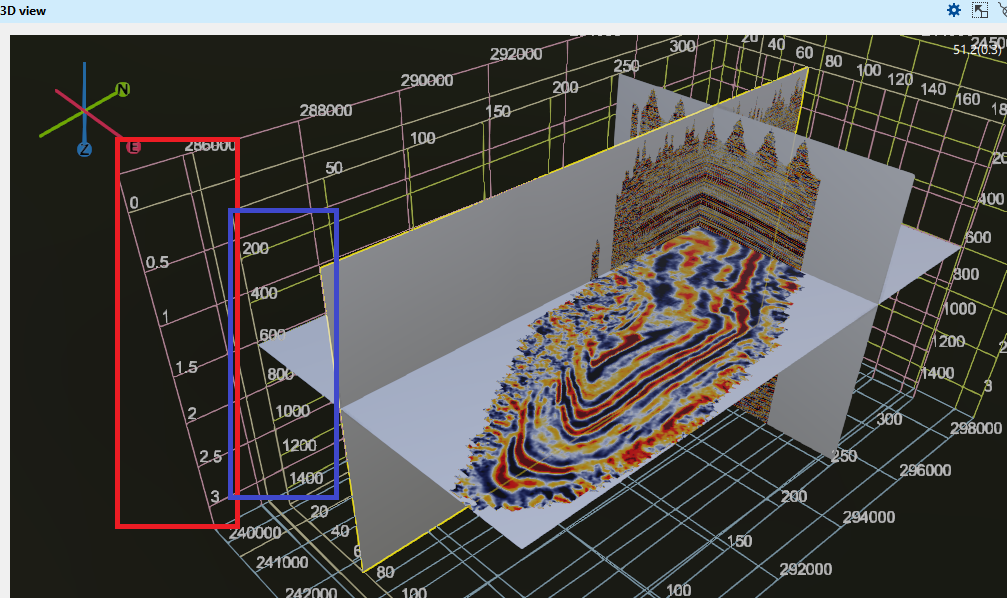
The vertical scale of the inside grid (marked as blue rectangle) is showing the volume in samples. Like if we have 3000ms of record length and we have 4ms of sample interval, it will display like 200, 400 etc.
The vertical scale of the outside gird (marked as red rectangle) is showing the volume in seconds. If the record length is 3000ms then we can see it as 1s, 1.5s etc.
View appearance parameters and object visualization parameters can be set on the View properties panel as for other views.
Anyway a few settings related to 3D view only described below.
View tab:
Well scale This property changes the thickness (size) of the displayed wells in the 3D view. By default it is 100. When the user changes it into 500 the thickness(size) increase.
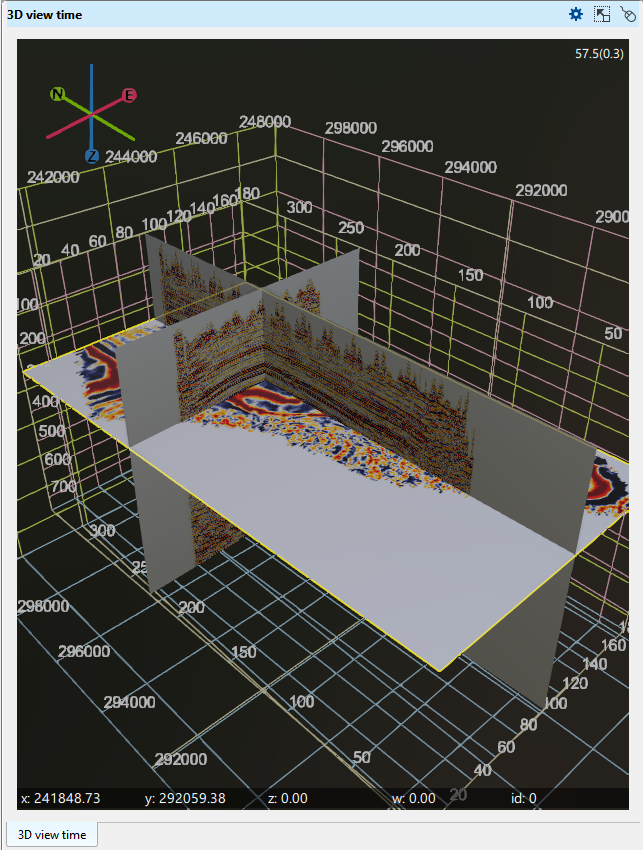
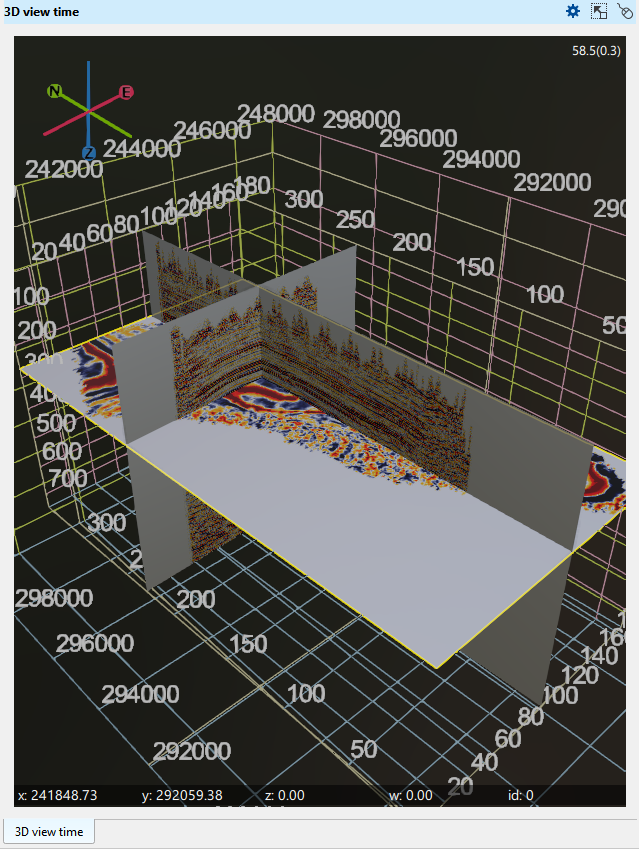
Label size - The user can change the size of the X, Y, Inline, Crossline, Time/Depth slice labels. By default it is 1. Here we are changing it from 1 to 1.5. We can see the changes in the below image.
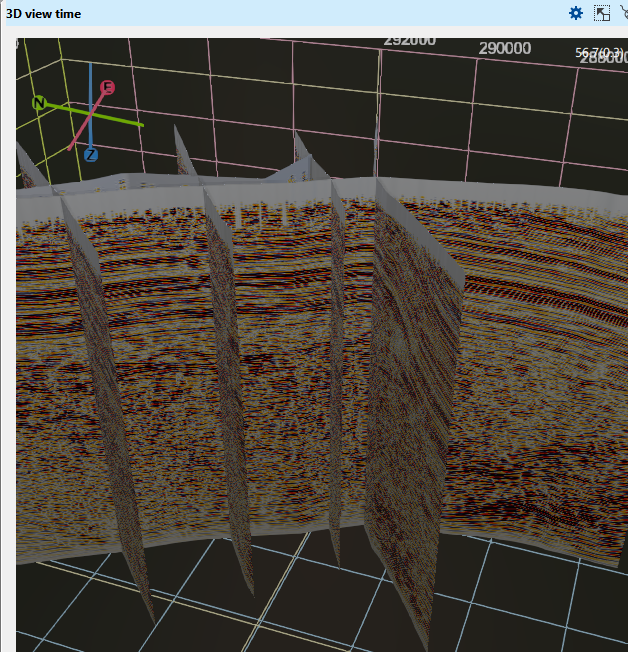
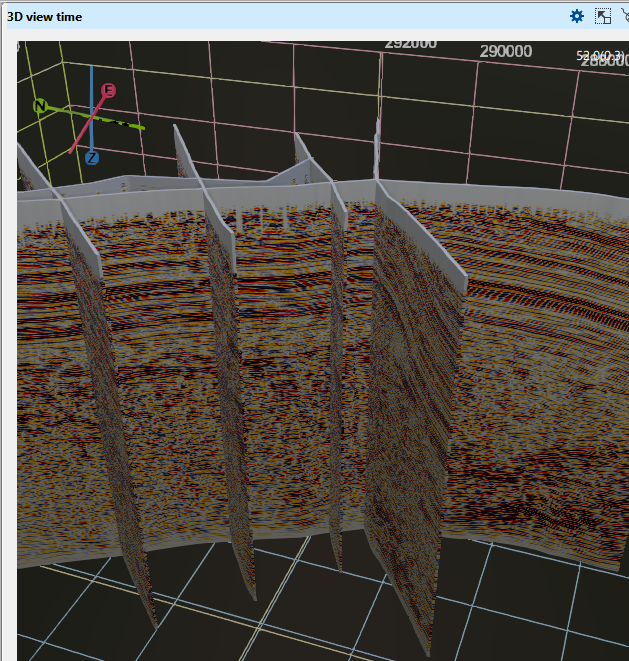
Premitive thickness This parameter increases the display thickness of the 2D, 3D(Inline/crossline/time slice) and arbitrary line. In this instance, we have 1 as by default and changed that into 50 and we can able to see the thickness of the 2D lines as shown below.
Points size It is a scalar for all 3D points like well markers, well rigs etc.
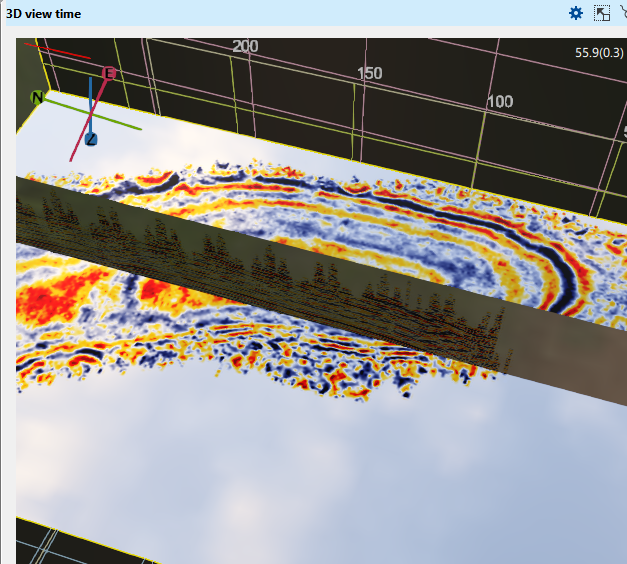
Metalness This parameter is similar to brightness/contrast. By default it is 1. If the user changes this to a lower value say 0.2, the contrast will increases as shown below.
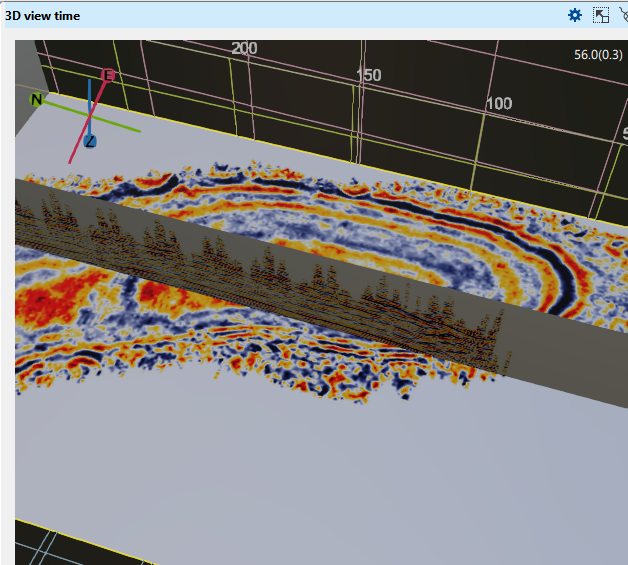
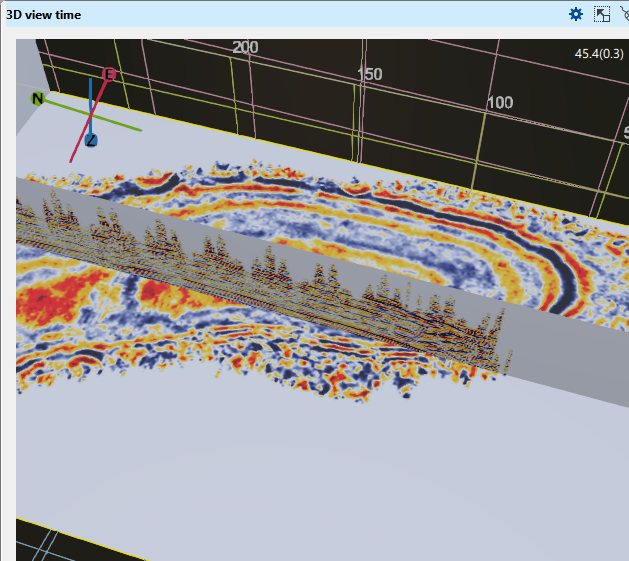
Roughness This parameter is also similar to Metalness. The default value is 0.75. It can acts like brightness/contrast as shown below. We changed the default value from 0.75 to 0.1 and this is how it looks like.

TTD Time To Depth adjusts the volume’s size by either expanding or compressing it. The default TTD value is set to 2000. In the display, the left side shows the volume with a TTD of 2000, while the right side shows the same volume with a TTD of 1000. In the latter case, the vertical scale appears reduced (zoomed out/in), effectively altering the vertical axis’s scalar value.
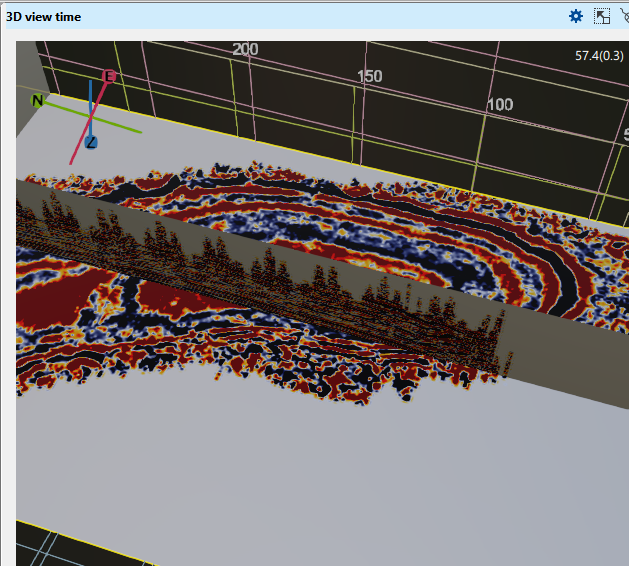
Attribute multiplier This parameter is like adding gain to the selected display. By default it is 1. When we change it from 1 to 5, it looks like the below shown image.

Perspective It is related to 3D projection. By default it is checked, if it is unchecked the object (in that case like a well marker) the one closer to the focus point is bigger than the one far way from the focus point.
AO AO stands for Ambient Occulusion.
Surface value from Z If the horizons are having attributes (frequency, envelope etc) and the the surface value from Z is turned off, it will take the colorization from the actual attribute value. If the surface value from Z is checked, the colorization will take it from the Z value (time/depth)
IBL enabled IBL stands for Image Based Lighting (IBL). By default, it is checked(TRUE). It is also related to the display parameters. When this is disabled, the display looks very less in brightness.
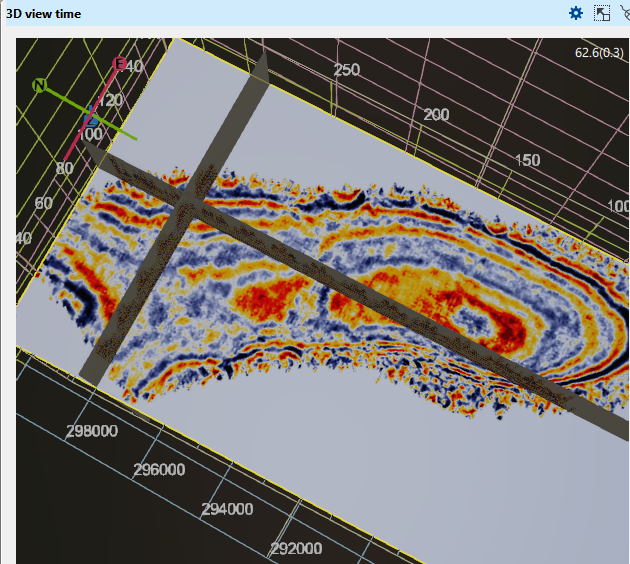
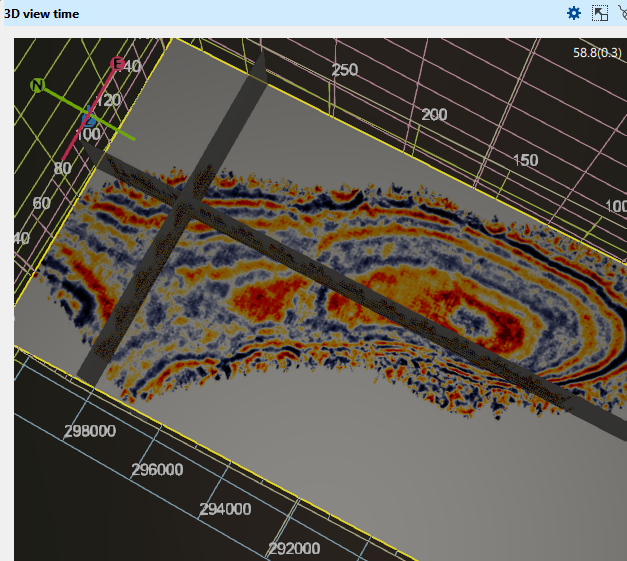
IBL multiplier This parameter is directly associated with the IBL enabled parameter. By default it is 1. If we change it into say 10, it exponentially increases the brightness.

Vista(s) tab:
AVO colored bins displaying the calculated AVO parameters and selected on AVO crossplot
Loaded gathers displaying all the loaded 2D lines in the 3D view time window
3D volume time displaying all the loaded 3D volumes
3D Cube attribute time displaying any available attributes like frequency, envelope, coherency
Surface seismic 2D geometry displaying the loaded 2D seismic lines geometry i.e. the line boundary
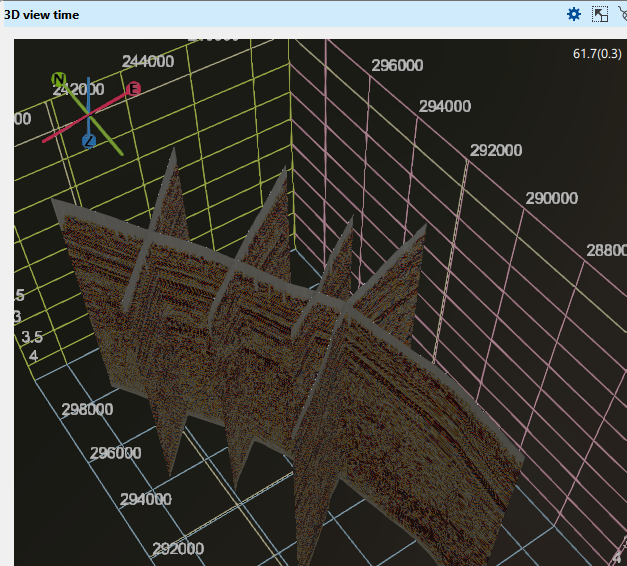
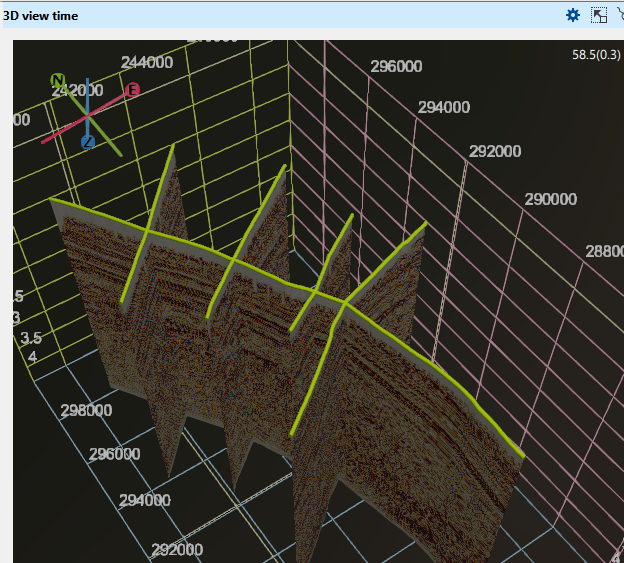
Surface seismic 3D geometry It will display the loaded 3D volume boundary like all the corner points.
Arbitrary line 3D Displays an arbitrary line
Horizon 3D Topo Displays the topographical horizon
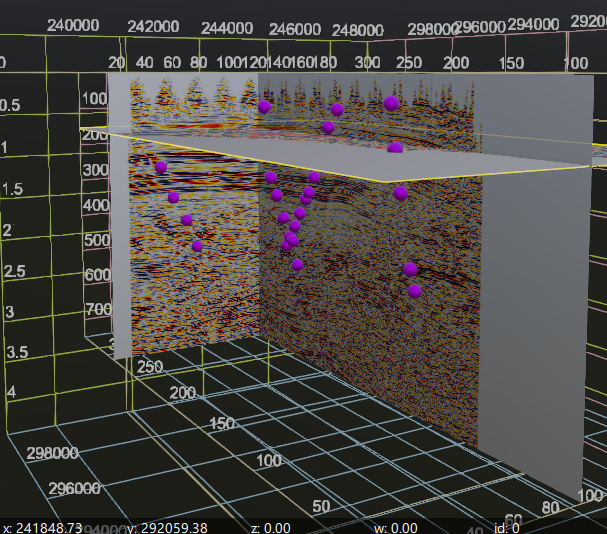
Fault picks This section displays the fault picks. By default, the Vista item properties are set to a size of 0.2. Users can adjust this value to view the fault picks in a larger size.
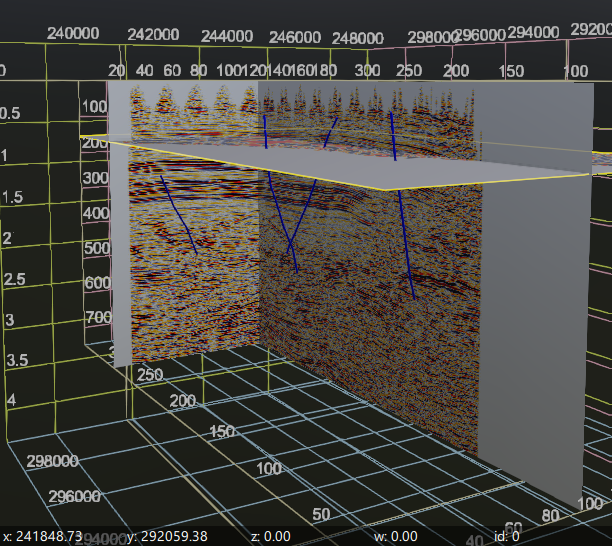
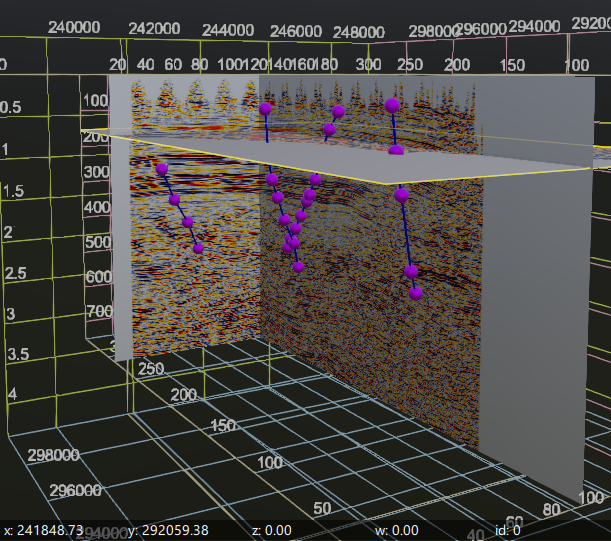
Fault sticks 3D This feature functions similarly to the Fault Picks Vista item but displays the fault points as a line or stick. It connects the fault points into a continuous line. When both Fault Picks and Fault Sticks are enabled, the display will show a combined view, as illustrated in the right image below.
Fault 3D Shows a surface that connects all the sticks associated with the same fault, displaying all the picked or loaded faults in 3D view.
Wells 3D All the loaded wells are displayed here. To manage the visibility of the wells, expand the Wells 3D Vista item to check or uncheck them.
Well rig 3D Displays the well rig.
Markers 3D Displays all the well markers.
Observing segment Whenever the user selects any bin on the location map, the corresponding position is displayed on the 3D view time window.
Polygon 3D Displays all the loaded polygons.
Polygon selection 3D Displays the current/selected or default polygon.
Handling the volume if the memory (RAM) is not enough
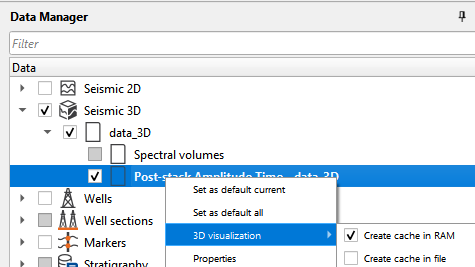
If the user is having enough memory for considerable volume size, they can use the option "Create cache in RAM". To do that, the user should go to Data Manager --> Seismic 3D --> Post-stack Amplitude Time - data_3D (whatever the name the user has given during the loading of the 3D volume) --> Right click --> 3D visualization --> Create cache in RAM. This will use the on board memory to display the 3D volume.
In case the user doesn't have enough memory then they can select the option "Create cache in file". This will take little longer time to create cache file when compared to RAM option (depending on the size of the volume, hard disk type (HDD/SSD)). Once the process is completed, now it will access the file from the hard disk and display the 3D volume. The visualization of the 3D volume speed is as good as accessing from the RAM.
Hot keys
To rotate the volume in any direction use MB3 (Right mouse button). User can also able to do the rotation by holding Ctrl+MB3 button.
To move the volume either up/down or left/right, use Shift+MB3(Right mouse button). This option won't rotate the volume. It will remain in it's original position during the movement of volume quite contrast to using Ctrl+MB3 where it rotates the volume
To move any inline/xline, just click/select on that inline/xline with MB1 and move wherever you want.
To move the time/depth slice, it's as same as the inline/xline. Simply hold MB1 and move up/down.
The user can use the mouse wheel (MB2 or middle mouse button) to zoom in/out the volume.