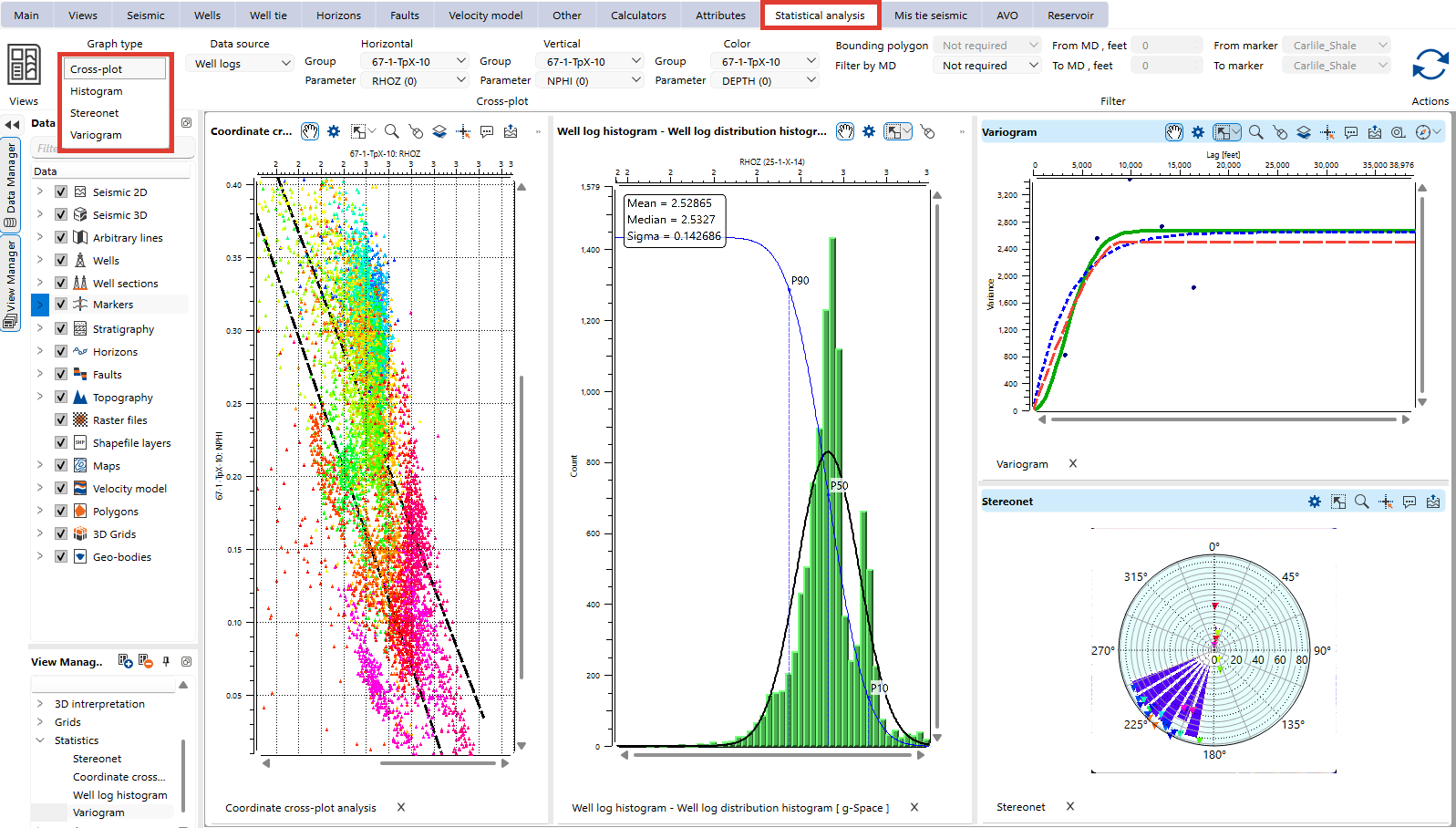
Statistical analysis view in g-Space is a powerful tool for analyzing and visualizing relationships between different attributes.

It provides three graph types:
1.Cross-plot
2.Histogram
3.Variogram
4.Stereonet View
5.Pine graph
Each graph type serves a unique purpose in analyzing subsurface data and identifying trends, patterns, or distributions.
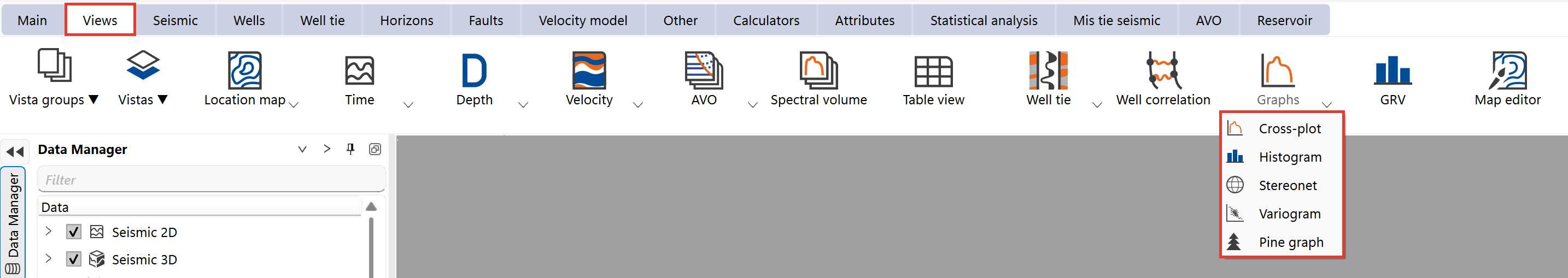
To access these Views:
1.Navigate to the Views Bar in the Ribbon.
2.Select the Graphs option.
3.Open the desired graph type: Cross-plot, Histogram, Variogram, Stereonet or Pine graph View.
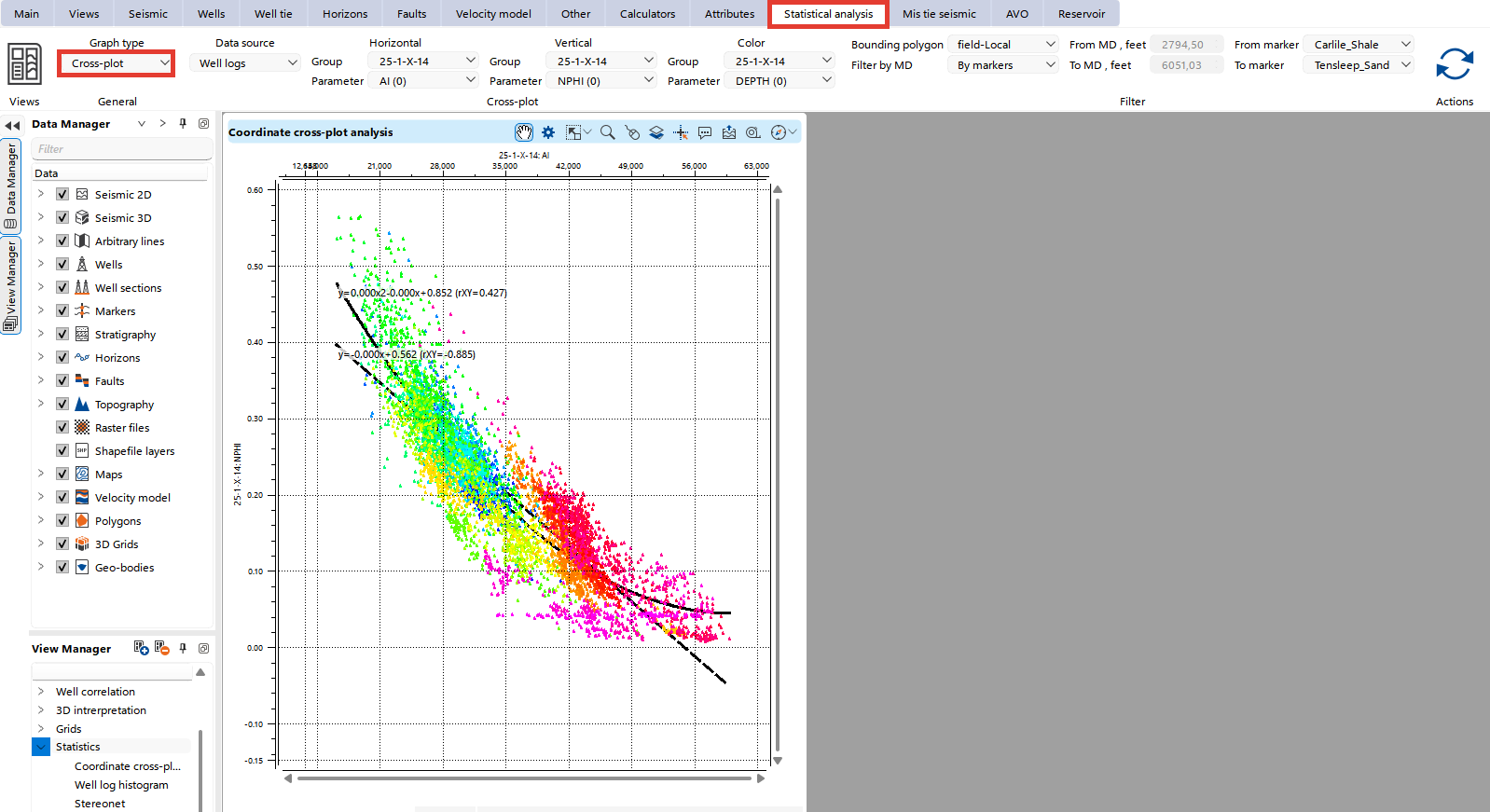
In the Statistical Analysis Bar users can configure their plots.
Cross-Plot view is used to visualize the relationship between two selected attributes (X and Y axes). This is particularly useful for identifying correlations or patterns between the two variables.
Data Source: Choose the type of data to analyze (e.g., Well Logs or XY Data).
Horizontal Axis: Select the Group and corresponding Parameter for the X-axis.
Vertical Axis: Select the Group and corresponding Parameter for the Y-axis.
Color: Optionally assign a parameter for point coloring to enhance visualization.
Bounding Polygon: Limit points displayed on the cross-plot using a predefined polygon.
Filter by MD/Markers: For well data, filter points within specific measured depth (MD) ranges or between selected markers.
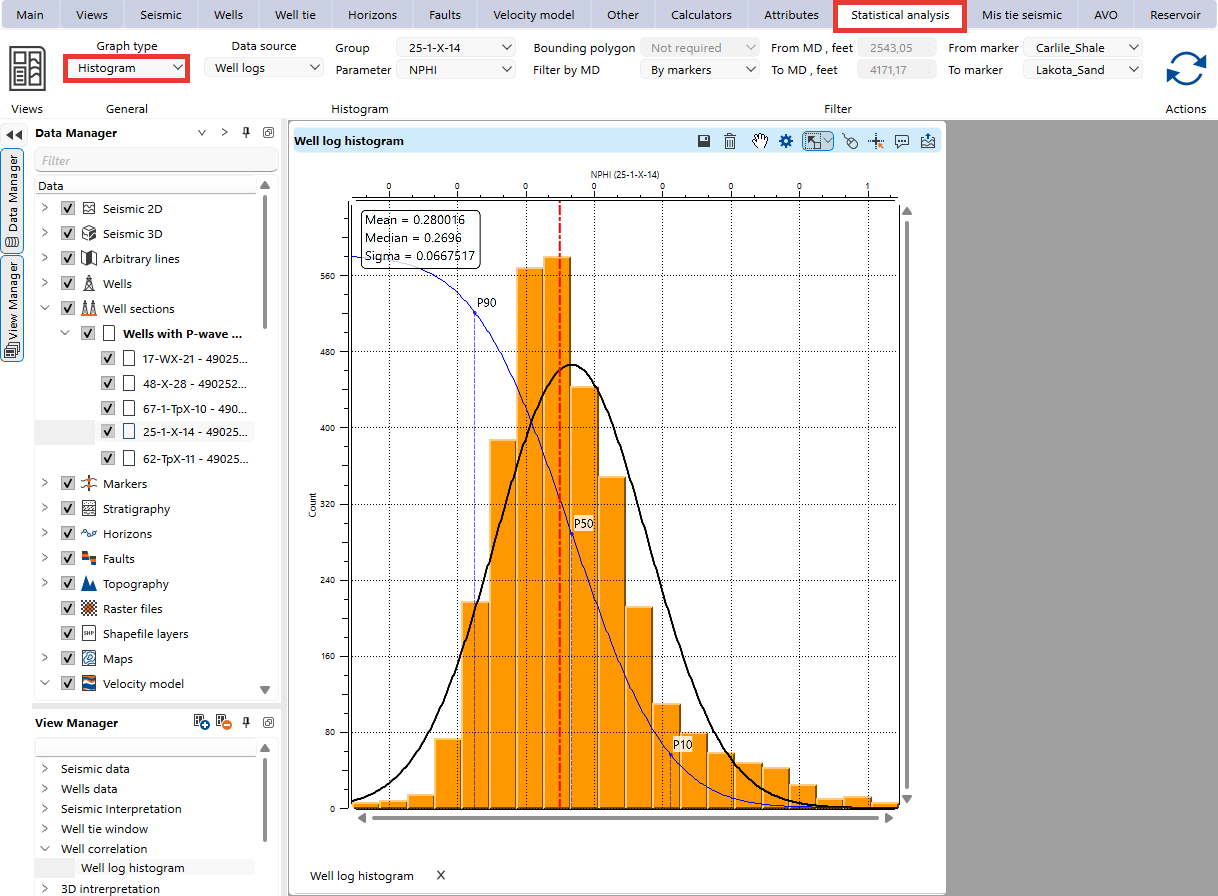
Histogram view provides a graphical representation of the distribution of an attribute, giving users insights into the frequency and range of data values.
Data Source: Choose the type of data to analyze (e.g., Well Logs or XY Data).
Group: Select the well log group to be analyzed.
Parameter: Choose the parameter to visualize.
Bounding Polygon: Limit points displayed on the cross-plot using a predefined polygon.
Filter by MD/Markers: For well data, filter points within specific measured depth (MD) ranges or between selected markers.
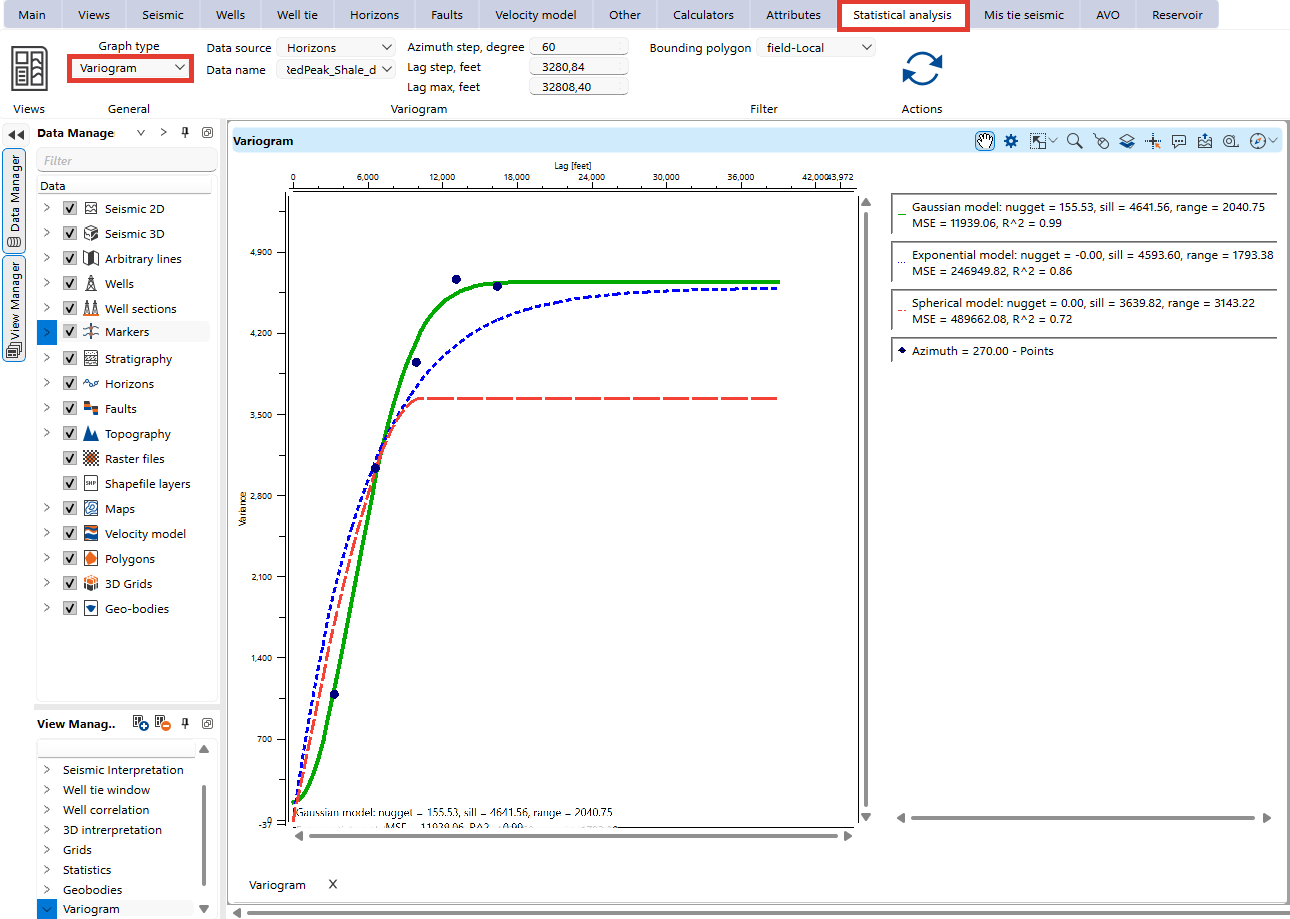
The Variogram View in g-Space is a powerful tool for analyzing the spatial continuity and correlation of subsurface attributes. It helps users evaluate the variability of geological properties over different distances and directions.
Data Source: Choose the type of data to analyze (e.g., Well Logs, Well Attributes, Grid Maps, Horizons, Markers, Topography).
Data name: Choose the specific parameter to visualize spatial correlation.
Azimuth step, degree: Defines the angular interval for directional variogram calculations. A smaller step provides more detailed anisotropy analysis, while a larger step smooths directional variations.
Lag step: Determines the spatial separation between data points used in the variogram calculation. A smaller lag step provides finer resolution, while a larger lag step captures broader trends.
Lag max: Specifies the maximum distance to be analyzed. It defines how far the variogram extends before reaching the sill (where spatial correlation becomes negligible).
Value extraction: Determines how values are sampled for variogram computation. Here are the Value Extraction options for the Variogram View in g-Space:
1.Average – Computes the mean value of the selected attribute within the defined lag step.
2.RMS (Root Mean Square) – Calculates the square root of the average of the squared values, emphasizing higher values in the dataset.
3.Minimum – Extracts the lowest value within the defined lag step.
4.Maximum – Extracts the highest value within the defined lag step.
5.Dominant – Selects the most frequently occurring value within the lag step.
6.Median – Determines the middle value of the dataset, reducing the influence of outliers.
Filter by Time/Horizons: Allows users to limit the variogram analysis to specific time intervals or geological horizons. This is useful for analyzing variations within a particular stratigraphic unit or time frame.
Bounding Polygon: Limit points used in the variogram calculation by defining a spatial boundary.
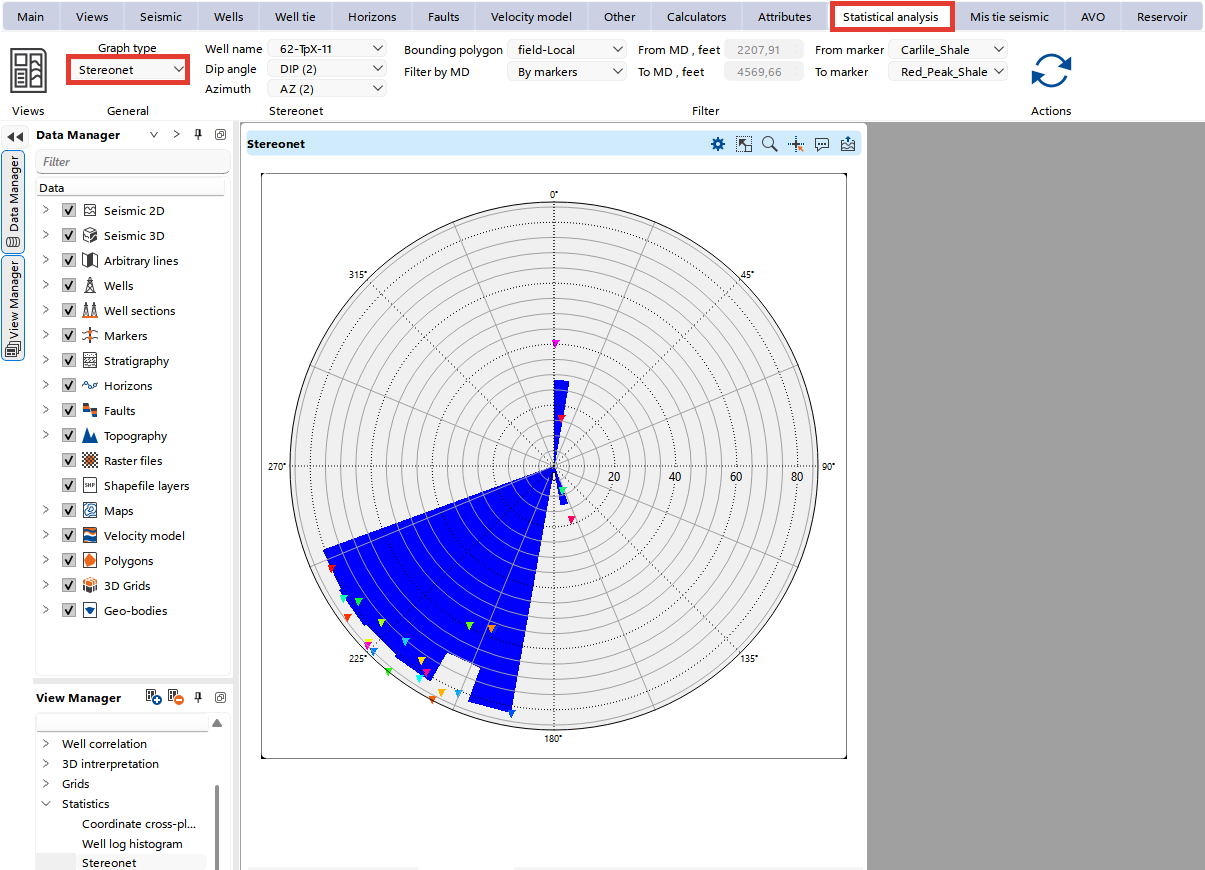
The Stereonet view is used to visualize the orientation of structural data, such as dip and azimuth, on a stereographic projection.
Well Name: Select the well to be analyzed.
Dip Angle: Choose the well log parameter for dip.
Azimuth: Select the well log parameter for azimuth.
Bounding Polygon: Limit points displayed on the cross-plot using a predefined polygon.
Filter by MD/Markers: For well data, filter points within specific measured depth (MD) ranges or between selected markers.
 click Update to see updated results after changing settings.
click Update to see updated results after changing settings.
For more information about the cross-plotting please refer to Statistical analysis