AI Faults Wizard is a tool for automatic fault detection in 3D seismic data using neural networks. The wizard performs a complete processing cycle: from fault detection to generation of geometric objects ready for interpretation and analysis.
Purpose
The tool is designed for:
•Automating fault detection in seismic data
•Accelerating structural features interpretation
•Improving quality and detail of fault mapping
•Reducing subjectivity in manual interpretation
Features
•Automatic fault detection using trained neural networks
•Calculation of planarity (reflector continuity) and faultness (fault centerline) attributes
•Determination of fault orientation in space
•Generation of fault geometry (fault sticks) with automatic clustering into faults
•Preset parameters for quick start
Workflow
The wizard includes three sequential steps (tabs):
1.AI Fault Attribute — fault detection using neural network
2.Attribute Processing — calculation of planarity and fault characteristics (faultness and orientation)
3.Sticks & Faults — fault geometry construction
Requirements
•3D seismic cube in SEGY format loaded into the project
•Seismic data available in Data Manager
•Sufficient RAM for cube processing
Launching the Wizard
Launch methods:
•Through Wizards panel (if activated)
•Through Ribbon menu → Faults → AI Faults Wizard
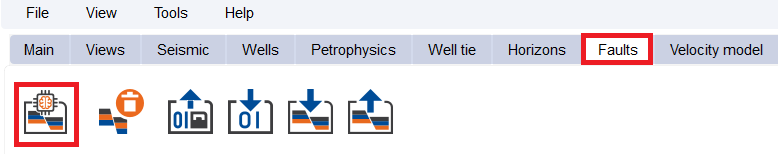
The wizard opens as a dialog window with three tabs (AI Fault Attribute, Attribute Processing, Sticks & Faults). Each tab contains parameters for the corresponding processing stage.
Results:
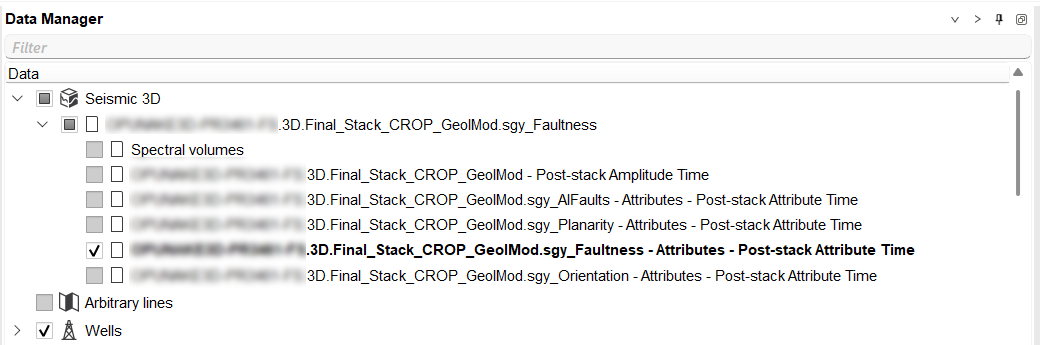
•All calculated attributes are automatically saved in Data Manager in the Seismic Data / Attributes section
•Each attribute is assigned a suffix for identification: _AIFaults, _Planarity, _Faultness, _Orientation
•Visual indicators (green checkmark) show successful stage completion
•Results from one step automatically become available for selection in the next step
Step-by-Step Guide
AI Fault Attribute Tab: Fault Detection
Application of a trained neural network for automatic fault detection in seismic data. The neural network analyzes fracture patterns and creates a probability map of fault presence.
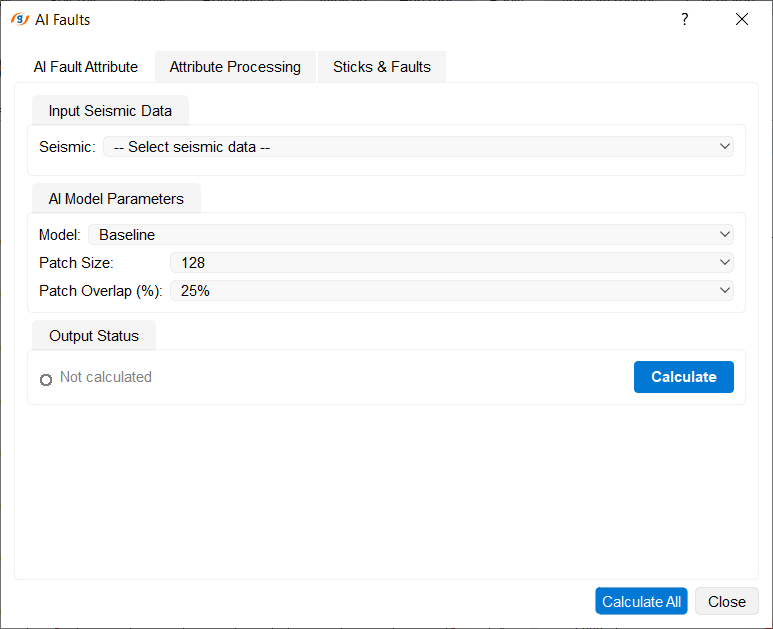
Procedure:
1. Select seismic cube
•In the Input Seismic Data group, select a 3D seismic cube from the Seismic: dropdown list
•Only 3D data is supported (2D is not supported)
2. Configure parameters
In the AI Model Parameters group:
Model: — neural network model selection
•Baseline — base model (default)
Patch Size: — neural network processing window size:
•32/64 — fast processing, but worse at capturing large structures (for preview)
•128 — optimal balance of speed and quality, good for medium and large structures (default, recommended)
•192/256 — maximum detail, best for large structures, but slow processing (for final analysis)
Patch Overlap (%): — overlap of adjacent processing windows:
•0% — maximum speed, possible artifacts at window boundaries
•10% — fast with minimal boundary smoothing
•25% — optimal balance (default, recommended)
•50% — maximum quality, minimum artifacts, slow processing
3. Run calculation
•In the Output Status group, press the Calculate button
•Processing may take from several minutes to several hours depending on cube size and parameters
•Result is automatically saved in Data Manager with suffix _AIFaults
•After completion, a green checkmark and the calculated attribute name appear in the Output Status group
Result:
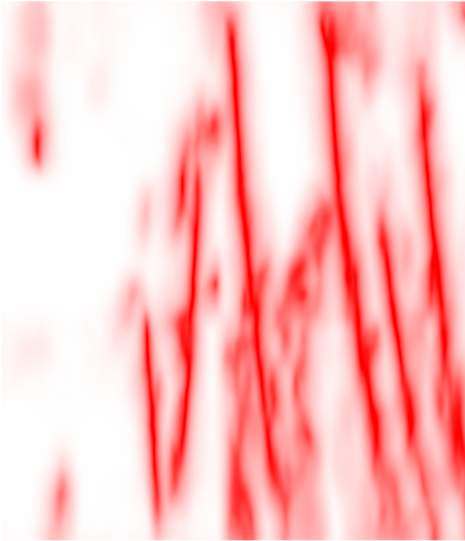
AI Faults attribute (SEGY format) — probability map of fault presence, where high values correspond to areas with high fault probability.
Attribute Processing Tab: Attribute Processing
Calculation of planarity and fault characteristics attributes. The tab contains two processing stages.
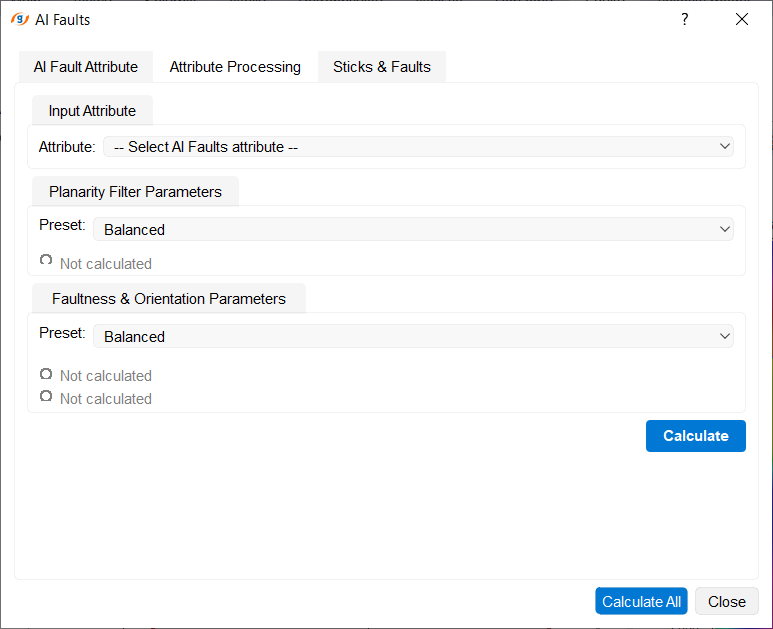
Stage 1a: Planarity
Calculation of planarity — a measure of seismic reflection continuity. Planarity helps identify areas with disrupted continuity (faults) and improves quality of subsequent analysis.
Procedure:
1. Select attribute
•In the Input Attribute group, the AI Faults attribute from the AI Fault Attribute tab is automatically selected
•You can manually select a different attribute if needed
2. Configure parameters
In the Planarity Filter Parameters group:
Preset: (recommended to start with):
•Sharp — for clear, well-defined faults (minimal smoothing)
•Balanced — universal option for most cases (default)
•Smooth — for noisy data or weakly expressed faults
•Custom — manual adjustment of all parameters
When Custom is selected, the following parameters become available:
•Downsample: Data simplification for faster calculation (1 = full resolution, 2 = every second trace/sample)
•Edge blur (Sigma): Smoothing radius when detecting fault edges
•Fault continuity (Rho): Structural continuity analysis radius around a point
3. Run calculation
•Press the Calculate button (at the bottom of the tab)
•Result is automatically saved with suffix _Planarity
•After completion, a green checkmark and calculated attribute name appear in the Planarity Filter Parameters group
Stage 1b: Fault Attributes
Calculation of fault centerline (Faultness) and fault orientation (Orientation) attributes.
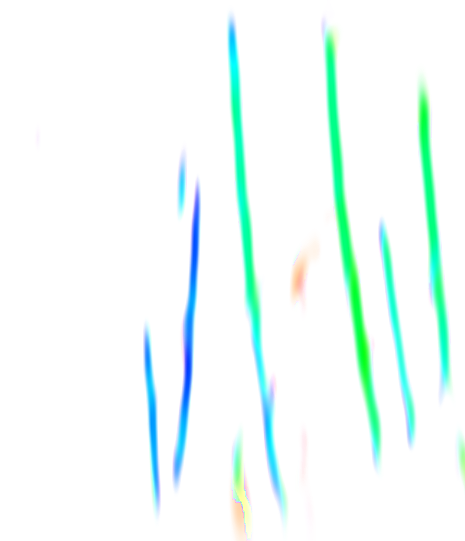
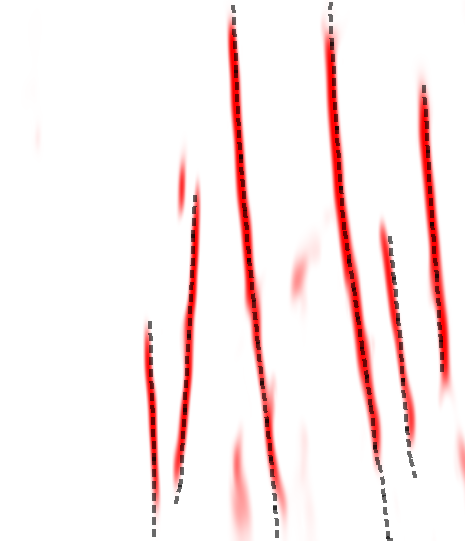
Faultness — attribute that highlights the fault centerline (ridge), showing the fault axis where the value is maximum. Instead of a wide fault zone, faultness creates a thin centerline, which is used for automatic stick construction. This allows precise determination of fault position and geometry construction along its axis.
Orientation — attribute of fault strike azimuth in the horizontal plane (fault direction in map view), necessary for correct geometry construction and grouping of sticks into individual faults.
Input data:
•Planarity result from Stage 1a is used automatically
Configure parameters:
In the Faultness && Orientation Parameters group:
Preset:
•Sharp — clear faults, minimal smoothing
•Balanced — universal option (default)
•Smooth — smoothed results for noisy data
•Custom — manual adjustment of all parameters
Run calculation:
•Press the Calculate button (at the bottom of the tab)
•Two attributes are generated simultaneously: Faultness (fault centerline for stick construction) and Orientation (fault strike azimuth in horizontal plane)
Results:
•Planarity attribute (SEGY) — planarity map
•Faultness attribute (SEGY) — fault centerline (ridge)
•Orientation attribute (SEGY) — fault strike azimuth in map view

Sticks & Faults Tab: Fault Stick Generation
Construction of three-dimensional fault geometry (fault sticks) based on fault centerline (Faultness) and orientation (Orientation) attributes. Faultness highlights the fault axis (ridge), allowing automatic stick construction along the centerline.
Process consists of two stages:
1.Stick tracing — construction of vertical lines along fault central axes. Each stick extends while the fault remains pronounced (high Faultness) and the fault strike azimuth does not change more than the tolerance (Orientation Tolerance).
2.Grouping into faults — for each stick in each time slice, the algorithm searches for neighbors in two directions along the fault strike (along the high Faultness line). Sticks are combined into one fault only if they are mutual neighbors: if stick A sees stick B on the left, then stick B must see stick A on the right. This prevents erroneous merging at fault branches.
Procedure:
1. Select attributes
•In the Input Attributes group, select the fault centerline attribute (Faultness) and orientation attribute (Orientation) from the Fault Attributes stage
•Both attributes are selected automatically if the Attribute Processing tab is completed
2. Configure parameters
In the Sticks Parameters group:
•Downsample Factor: Resolution reduction coefficient for faster processing
•Stick Spacing Factor: Distance between sticks as a multiplier of fault thickness (1.0 = spacing equals thickness)
•Point Spacing (ms): Distance between points along the stick (0 = no reduction, keep all points)
•Min Stick Length (ms): Minimum stick length for inclusion in results
•Orientation Tolerance (deg): Allowable change in fault strike azimuth when extending the stick
In the Fault Clustering Parameters group:
•Enable fault clustering: Enable/disable automatic grouping of sticks into faults
•Min Sticks Per Fault: Minimum number of sticks to form a fault
•Meshing Mode: Surface (continuous surface reconstruction) or Sticks (display as individual stick lines)
3. Run calculation
•Press the Calculate button (at the bottom of the tab)
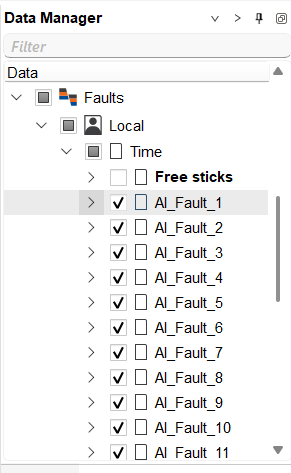
•Results are automatically added to Data Manager (Faults / Time or Depth)
Result:
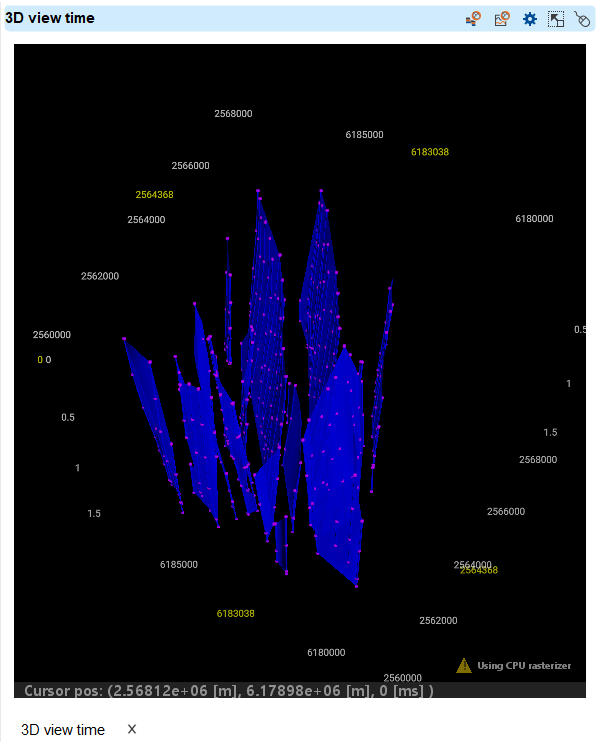
Fault Sticks — three-dimensional fault geometry represented by a set of vertical lines (sticks), grouped into individual faults. Available for:
•Visualization in 3D View, Map View, Seismic Sections
•Conversion to Surface Mode (fault surfaces)
•Export to other applications
•Further editing and interpretation
Calculate All
The Calculate All function performs all three steps sequentially in automatic mode — from fault detection to geometry generation. This is the most convenient method for complete processing.
Procedure:
1.Go to the AI Fault Attribute tab and select the seismic cube
2.Review and configure parameters on all three tabs (or leave defaults for quick start)
3.Press the Calculate All button (at the bottom of the wizard window, next to the Close button)
4.The wizard will automatically execute all stages in correct sequence
Advantages:
•Time saving: No need to manually switch between tabs
•Reliability: Automatic transfer of results between stages
•Convenience: Ideal for first run with default parameters
Visualization of Results
Viewing Attributes:
After executing AI Fault Attribute and Attribute Processing, attributes are available in Data Manager → Seismic Data / Attributes. Attributes can be visualized in 2D/3D Seismic Views.
Viewing Fault Sticks:
Sticks & Faults results are available in Data Manager → Faults / Time (or Depth). Visualization options: 3D View, Map View, Seismic Sections. Mode switching: Free Sticks or Surface Mode. Display settings in View Properties (color, thickness, transparency).
Recommendations
General Approach:
•Start with Preset=Balanced for first run
•Use Calculate All for automatic execution of all steps
•Follow iterative approach: quick assessment → result analysis → detailed processing
•Use polygons to limit processing area for parameter testing
Performance Optimization:
•Reduce Patch Size (64) and Overlap (10%) for quick assessment
•Use Downsample=2 or 4 on large cubes
•Increase Stick Spacing Factor to 2.0-3.0 for preview calculations
Quality Improvement:
•Check seismic data quality (structural smoothing can improve results)
•For clear faults: use Preset=Sharp with minimal smoothing
•For noisy data: use Preset=Smooth with increased regularization
•For curved faults: increase Orientation Tolerance to follow fault bends in horizontal plane
See Also